(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Researchers continue to expand the case for the Younger Dryas Impact hypothesis. The idea proposes that a fragmented comet smashed into the Earth’s atmosphere 12,800 years ago, causing a widespread climatic shift that, among other things, led to the abrupt reversal of the Earth’s warming trend and into an anomalous near-glacial period called the Younger Dryas.
Now, UC Santa Barbara emeritus professor James Kennett and colleagues report the presence of proxies associated with the cosmic airburst distributed over several separate sites in the eastern United States (New Jersey, Maryland and South Carolina), materials indicative of the force and temperature involved in such an event, including platinum, microspherules, meltglass and shock-fractured quartz. The study appears in ScienceOpen’s journal Airbursts and Cratering.
“What we’ve found is that the pressures and temperatures were not characteristic of major crater-forming impacts but were consistent with so-called ‘touchdown’ airbursts that don’t form much in the way of craters,” Kennett said.
The Earth is bombarded every day by tons of celestial debris, in the form of tiny dust particles. On the other end of the scale are the extremely rare and cataclysmic impacts like the Chicxulub event that 65 million years ago caused the extinction of dinosaurs and other species. Its 150-kilometer-wide (93 miles) impact crater can be found in the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico.
Somewhere in between are the impacts that don’t leave craters on the Earth’s surface but are nevertheless destructive. The shockwave from the 1908 Tunguska event knocked down 2,150 square kilometers (830 square miles) of forest, as the roughly 40-meter (130 ft) diameter asteroid collided with the atmosphere almost 10 kilometers (6 miles) above the Siberian taiga.
The comet thought to be responsible for the Younger Dryas cooling episode is estimated to have been 100 kilometers wide (62 miles) — much larger than the Tunguska object, and fragmented into thousands of pieces. The sediment layer associated with the airburst stretches across much of the northern hemisphere, but can also be found in locations south of the equator. This layer contains unusually high levels of rare materials associated with cosmic impacts, such as iridium and platinum, and materials formed under high pressures and temperatures, such as magnetic microspherules (cooled-down metallic droplets), meltglass and nanodiamonds.
Shocked quartz and amorphous silica
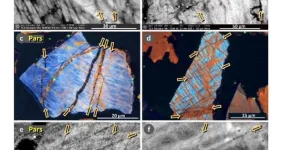
The researchers are particularly interested in the presence of shocked quartz, indicated by a pattern of lines, called lamellae, that shows stress great enough to deform the crystal structure of quartz, a very hard material. This “crème de la crème” of cosmic impact evidence is present in impact craters, however linking shocked quartz to cosmic airbursts has proven to be more of a challenge.
“In the extreme form, such as when an asteroid hammers into the Earth’s surface, all the fractures are very parallel,” Kennett explained. In the realm of cosmic airbursts, different variables are present in the realm of cosmic airbursts. “When you think about it, the pressures and temperatures that produce these fractures will vary depending on the density, entry angle, altitude of the impact and the impactor’s size.
“What we found — and this is what is characteristic of the impact layer, called the Younger Dryas Boundary — is that although we do occasionally see in the quartz grains examples of the ‘traditional’ shocked quartz with parallel fractures, we mostly see grains that are not parallel,” he said. These fractures are seen in an irregular, web-like pattern of intersecting, meandering lines and surface and subsurface fissures, in contrast to the parallel and planar deformations of impact-associated shocked quartz found at craters. These subparallel and subplanar deformations are due in large part to the relatively lower pressures caused by explosions that occur above the ground, the researchers assert, as opposed to impacts that make contact with the Earth.
What these sediments do share with the shocked quartz at crater sites is the presence of amorphous silica — melted glass — in these fractures. And that, the researchers say, is evidence of the combination of pressure and high temperatures (greater than 2000 degrees Celsius) that could have come from a low-altitude bolide airburst. Similarly fractured quartz grains and meltglass have been found in more present-day samples of above ground explosions, such as at the Trinity atomic bomb test site in New Mexico. The roughly 20-kiloton bomb was detonated atop a 30.5 meter (100 foot) tower.
These lower-pressure shocked quartz grains join a growing suite of impact proxies that together make a case for a fragmented comet that not only caused widespread burning, but also abrupt climatic change that resulted in the extinctions of 35 genera of megafauna in North America, such as the mammoths and giant ground sloths, and led to the collapse of a flourishing human culture called Clovis, according to the researchers.
“There’s a whole range of different shocked quartz, so we have to make a well-documented case that they are indeed significant for interpreting cosmic impact, even though they’re not reflecting a traditional major crater-forming event,” Kennett said. “These are from very-low-altitude ‘touchdown’ airbursts almost certainly associated with cometary impact.”
END
Shocked quartz reveals evidence of historical cosmic airburst
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chemotherapy disrupts gut microbiome in patients with breast cancer
2024-06-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Chemotherapy is known to cause behavioral side effects, including cognitive decline. Notably, the gut microbiome communicates with the brain to affect behavior, including cognition.
“For the first time ever, our Intelligut Study found that the gut microbiome has been implicated in cognitive side effects of chemotherapy in humans,” said senior author Leah Pyter, associate professor of psychiatry and neuroscience with The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine. ...
Microrobot-packed pill shows promise for treating inflammatory bowel disease in mice
2024-06-26
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a pill that releases microscopic robots, or microrobots, into the colon to treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The experimental treatment, given orally, has shown success in mice. It significantly reduced IBD symptoms and promoted the healing of damaged colon tissue without causing toxic side effects.
The study was published June 26 in Science Robotics.
IBD, an autoimmune disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of the gut, ...
Sharing false political information on social media may be associated with positive schizotypy
2024-06-26
Sharing false political information on social media by users may be associated with aspects of personality such as positive schizotypy, a set of traits including paranoia, suspicion and disrupted thinking patterns. It may also be linked to a motivation to increase awareness according to a study published June 26, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Tom Buchanan, University of Westminster, UK, and colleagues.
The spread of false political information on social media can tarnish trust in authentic news and even contribute to social unrest. Knowingly or not, a small portion of social media users actively share false material.
Buchanan and ...
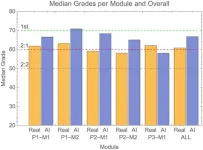
AI-generated exam submissions evade detection at reputable UK university
2024-06-26
In a test of the examinations system of the University of Reading in the UK, artificial intelligence (AI)-generated submissions went almost entirely undetected, and these fake answers tended to receive higher grades than those achieved by real students. Peter Scarfe of the University of Reading and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 26.
In recent years, AI tools such as ChatGPT have become more advanced and widespread, leading to concerns about students using them to cheat by submitting AI-generated work as their own. Such concerns are heightened ...
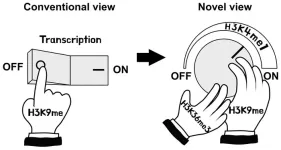
The on-and-off affair in DNA
2024-06-26
Researchers led by Kannosuke Yabe, Asuka Kamio, and Soichi Inagaki of the University of Tokyo have discovered that in thale cresses histone H3 lysine-9 (H3K9) methylation, conventionally thought to be a mark of turning off gene transcription, can also turn on gene expression via the interactions of two other proteins and histone marks. The molecular mechanisms demonstrate that rather than functioning as a simple “off switch,” H3K9 methylation is more like a “dimmer switch” that fine-tunes DNA transcription. The discovery suggests there might be similar mechanisms in other ...
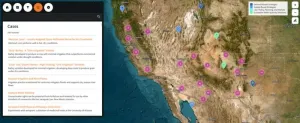
New interactive atlas of water scarcity solutions in the US Southwest shares a library of case studies to help adapt to drought
2024-06-26
New interactive atlas of water scarcity solutions in the U.S. Southwest shares a library of case studies to help adapt to drought.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000246
Article Title: The water adaptation techniques atlas: A new geospatial library of solutions to water scarcity in the U.S. Southwest
Author Countries: United States
Funding: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. END ...
AI generated exam answers go undetected in real-world blind test
2024-06-26
Experienced exam markers may struggle to spot answers generated by Artificial Intelligence (AI), researchers have found.
The study was conducted at the University of Reading, UK, where university leaders are working to identify potential risks and opportunities of AI for research, teaching, learning, and assessment, with updated advice already issued to staff and students as a result of their findings.
The researchers are calling for the global education sector to follow the example of Reading, and others who are also forming new ...
How do our memories last a lifetime? New study offers a biological explanation
2024-06-26
Whether it’s a first-time visit to a zoo or when we learned to ride a bicycle, we have memories from our childhoods kept well into adult years. But what explains how these memories last nearly an entire lifetime?
A new study in the journal Science Advances, conducted by a team of international researchers, has uncovered a biological explanation for long-term memories. It centers on the discovery of the role of a molecule, KIBRA, that serves as a “glue” to other molecules, thereby solidifying memory formation.
“Previous efforts to understand ...
Mechanical computer relies on kirigami cubes, not electronics
2024-06-26
North Carolina State University researchers have developed a kirigami-inspired mechanical computer that uses a complex structure of rigid, interconnected polymer cubes to store, retrieve and erase data without relying on electronic components. The system also includes a reversible feature that allows users to control when data editing is permitted and when data should be locked in place.
Mechanical computers are computers that operate using mechanical components rather than electronic ones. Historically, these mechanical components have been things like levers or gears. However, mechanical computers can also be made using structures that are multistable, meaning ...
Acting for a common goal with humanoid robots
2024-06-26
Genova (Italy), 26 June 2024 – Researchers at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT-Italian Institute of Technology) have demonstrated that under specific conditions, humans can treat robots as co-authors of the results of their actions. The condition that enables this phenomenon is that a robot behaves in a human-like, social manner. Engaging in gaze contact and participating in a common emotional experience, such as watching a movie, are the key. The study was published in Science Robotics and paves the way for understanding and designing the optimal circumstances for humans and robots to collaborate in the same environment.
The ...