(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED UNTIL JULY 1, 2024 AT 3:00 PM U.S. EASTERN TIME
According to a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, extensive land areas have been left sitting idle after tropical forests were cleared in Indonesia, a country renowned for its biodiverse rainforests and carbon-rich peatlands. Since 1990, the country has lost 25% of its old-growth forest, and while over one-quarter (7.8 million hectares) of Indonesia’s deforested lands have been converted to palm oil plantations since 2020, an even larger area (8.8 million hectares, roughly the size of Maine), remain vacant.
The study, which focused on Indonesian deforestation trends from 1991 to 2020, also found that over half of Indonesia’s deforested lands were left idle for at least one year after forest clearing, and that 44% remained idle for at least five years.
“Old-growth tropical forests are an extremely valuable resource, both locally and globally,” said Diana Parker, a postdoctoral associate in the University of Maryland’s Department of Geographical Sciences and the lead author of the paper. “The fact that such a large area of old-growth forest has been cleared then left empty is surprising.”
To understand why so much idle land was being created, researchers first had to determine how the forests were cleared. During the 2015 El Niño event, forest and land fires in Indonesia created a major public health crisis both in Indonesia and in neighboring countries. Some researchers have speculated that forest fires such as those that occurred in 2015 are largely responsible for the extensive areas of idle non-forest land. This study, however, found that fires resulting in tree cover loss accounted for less than half of all idle land clearing; 54% were cleared mechanically, either through manual clearing or using heavy machinery.
“Forest fires can be either intentional or accidental,” said Parker. “Mechanical clearing, however, is not only intentional but can be time consuming and costly. Once we realized that more than half of idle areas were not created by fires, it led to a new question: why would people expend so much effort to clear forests then leave the land empty?”
To answer this question, the researchers involved in the study, “Land in limbo: nearly one third of Indonesia’s cleared old-growth forests left idle,” used satellite imagery to examine the histories of deforested areas, both before and after clearing. They found that most forests are degraded, for example by selective logging, before they are cleared, suggesting that timber demand is not the main cause of idle-land creation. Case studies in regions with extensive idle land have also found that clearing increases, rather than decreases, land prices, further suggesting that timber is not the primary driver.
After forest clearing, the researchers found that some idle areas were eventually converted to productive uses. Of mechanically cleared idle areas, about one quarter were converted to a productive land use within five years of the deforestation event and half were being used productively in 2020. In these cases, palm oil plantations were by far the most common outcome.
“About 80% of mechanically cleared idle land that was converted to a productive use became a palm oil plantation,” said Parker. “This means that the true environmental impact of palm oil is likely much larger than the area planted immediately after forest loss, and is potentially larger than the total deforested area currently planted with oil palms.”
This lagged conversion dynamic appears to be unique to palm oil. The researchers found that two-thirds of all palm oil plantations established in deforested areas were planted after a lag of at least one year. Other major deforestation drivers, such as smallholder land use or tree plantations, were almost always established immediately after clearing.
“The satellite imagery can’t tell us exactly how idle land creation and the palm oil industry are linked, but the land use trends suggest a relationship,” said Parker. “In some cases, companies or individuals may intend to sell deforested land but are waiting for land prices to rise. Or they may plan to develop the land later, holding it as part of their land bank.”
“In other cases, young seedlings may have died before they could be detected in satellite imagery, or conflicts with communities or other concession holders could have delayed planting,” Parker explained.
Findings from the study include some hopeful news for the country’s remaining forests: From 2017-2020, Indonesia experienced the lowest deforestation rates observed during the entire study period.
“Indonesia is one of the few tropical forest countries that has been able to successfully slow deforestation,” said Matthew Hansen, a professor at the University of Maryland and paper co-author. “Given how much idle land is currently available, Indonesia could stop clearing forests altogether while still increasing palm oil production.”
Governments and private companies have increasingly adopted policies designed to eliminate deforestation from commodity supply chains. Under the EU Deforestation Policy (EUDR), set to be implemented later this year, certain commodities, including palm oil, cannot be imported into the EU if they were produced on land deforested after 2020.
“This research shows that Indonesia contains vast areas of land deforested before 2020 that are underutilized,” Hansen said. “Using these areas for commodity expansion could allow Indonesia to comply with the EUDR while protecting its remaining natural forests.”
END
UMD-led study finds one-third of Indonesia’s deforested land left idle
2024-07-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Cincinnati study: Overlooked brain organ plays key role in promoting brain repair after stroke
2024-07-01
University of Cincinnati researchers have pioneered an animal model that sheds light on the role an understudied organ in the brain has in repairing damage caused by stroke.
The research, published July 5 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, sought to learn more about how the adult brain generates new neurons to repair damaged tissue.
The research team focused on the choroid plexus, a small organ within brain ventricles that produces the brain’s cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF circulates throughout the brain, carrying signaling molecules and other factors thought to be important for maintaining brain function. However, prior to this study, little ...
Harvard researchers find that gratitude is a useful emotional tool in reducing desire to smoke
2024-07-01
Smoking continues to rank as the foremost preventable cause of premature death. In a paper published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS), Harvard researchers report findings that evoking feelings of gratitude in people who smoke helps reduce their urge to smoke, and increases their likelihood of enrollment in a smoking cessation program. They note that these findings could inform newer approaches to public health messaging campaigns that aim to reduce so-called “appetitive” risk behaviors like smoking, drinking, and drug use.
The research team built on the Appraisal Tendency Framework, a theoretical model of emotiona and decision making, ...
Researchers disclose the effect of social media use on the mental health of college students during the pandemic
2024-07-01
The COVID-19 pandemic had an unprecedented effect on college students’ mental health: symptoms like anxiety and major depression in young adults ages 18-25 increased significantly compared to before the pandemic.
A new study from researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill looks at a possible contributing factor to the worsening trends in mental health: social media.
We know that college students and adolescents are using social media more. Last May, the US Surgeon General issued an advisory on social media and youth mental ...
July Issues of APA Journals cover new research on pharmacogenomics, ADHD medication use, associations between mental health and cardiometabolic complications later in life, and more
2024-07-01
WASHINGTON, D.C., July 1, 2024 — The latest issues of four American Psychiatric Association journals, The American Journal of Psychiatry, Psychiatric Services, American Journal of Psychotherapy and Psychiatric Research and Clinical Practice are now available online.
The July issue of The American Journal of Psychiatry brings together research on affective disorders, pharmacogenomics, and psychiatric illness-related cardiometabolic problems. Highlights include:
• Genome-Wide Association Study of Treatment-Resistant Depression: Shared Biology With Metabolic Traits.
• Pharmacogenomic Clinical ...
Most climate-vulnerable countries with highest hunger rates significantly under-represented in agrifood research
2024-07-01
The most climate-vulnerable countries with the highest hunger rates are significantly under-represented in agrifood research – sparking a need for urgent action and increased investments to redress this imbalance, a major new study has found.
The ‘State of the Field for Research on Agrifood Systems’ report, published by The Juno Evidence Alliance – a partnership of CABI, Havos.Ai and the University of Notre Dame, USA – found that only one out of eight research papers is led by scientists from ...
UMD researchers develop new and improved camera inspired by the human eye
2024-07-01
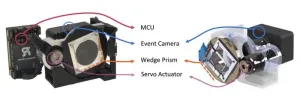
A team led by University of Maryland computer scientists invented a camera mechanism that improves how robots see and react to the world around them. Inspired by how the human eye works, their innovative camera system mimics the tiny involuntary movements used by the eye to maintain clear and stable vision over time. The team’s prototyping and testing of the camera—called the Artificial Microsaccade-Enhanced Event Camera (AMI-EV)—was detailed in a paper published in the journal Science Robotics in May 2024.
“Event cameras are a relatively new technology better at tracking ...
Self-assembling, highly conductive sensors could improve wearable devices
2024-07-01
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — To advance soft robotics, skin-integrated electronics and biomedical devices, researchers at Penn State have developed a 3D-printed material that is soft and stretchable — traits needed for matching the properties of tissues and organs — and that self-assembles. Their approach employs a process that eliminates many drawbacks of previous fabrication methods, such as less conductivity or device failure, the team said.
They published their results in Advanced Materials.
“People have been developing soft and stretchable conductors for almost a decade, but the conductivity ...
Lab values predict periprosthetic joint infection in patients with morbid obesity
2024-07-01
Waltham — July 1, 2024 — For patients with severe obesity undergoing knee or hip replacement, commonly obtained laboratory values – including markers of anemia and inflammation – are independent predictors of the risk of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Hemoglobin level, platelet count, and several markers of systemic inflammation may be relevant to the elevated ...
Study suggests states could cut healthcare costs by delivering patient tailored meals
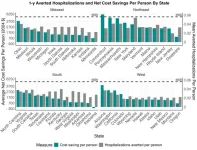
2024-07-01
Chicago (July 1, 2024) — According to new research looking at every U.S. state, programs that deliver medically tailored meals (MTMs) to people with diet-sensitive conditions such as diabetes and heart disease along with limitations in the ability to perform daily activities could lead to substantial savings in healthcare costs. Using computer models to estimate the benefits of such programs minus the expense of implementing them, researchers found significant variation between U.S. states but an overall net cost savings in almost every state.
“By ...
Novel spectroscopy technique sheds light on NOx reduction
2024-07-01
When power plants burn fossil fuels at high temperatures, nitrogen and oxygen molecules break apart and then recombine to form a class of compounds called nitrogen oxides, or NOx. These gasses are major pollutants and contribute to—among other things—acid rain and global warming.
One way to curb such emissions is with a catalytic converter, similar to what’s used in a vehicle.
“The catalytic converter injects ammonia into the plant’s emissions stream, and the hydrogen in the ammonia reacts with the oxygen in the NOx, and the products ...