(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, July 2, 2024 – An energy crisis hit Europe in 2021-2022, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, which sent electricity prices skyrocketing — even within countries that don’t rely on Russian gas. It begs the question: Was there more to it?
A team of researchers from the Institute for Energy and Climate Research at Forschungszentrum Jülich, the University of Cologne, and the Norwegian University of Life Sciences had already been working with electricity price data for years, exploring statistics and developing forecasting methods. Adopting a European perspective, they zeroed in on how prices in different countries relate and how countries were affected by the energy crisis.
In Chaos, from AIP Publishing, the team addresses the interdependencies of different markets.
“We use an empirical approach to these topics and complement modeling efforts by economists,” said Dirk Witthaut, a professor of network science for the Institute for Energy and Climate Research at Forschungszentrum Jülich and the University of Cologne.
This approach combines statistical physics and network science, which “provide very useful tools to study questions well beyond the traditional realm of physics,” said Witthaut. “The biggest step is to see the connections.”
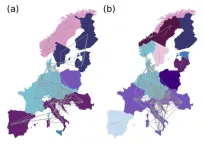
First, the researchers identify communities — groups of European countries whose markets are strongly correlated. Then, they identify the fundamental spatiotemporal patterns within the electricity price/time data from all countries. The exciting part for the researchers was how these structures and patterns changed during the energy crisis.
The team noticed Russian natural gas and skyrocketing electricity prices were frequently attributed to the soaring gas prices, while other factors were simultaneously at play with impacts that should not be underestimated.
“Remarkably, France and southern Norway saw the strongest increase in electricity prices — although they do not rely on Russian gas for electric power plants,” said Witthaut. “The high unavailability of nuclear power plants in France and the operation of new interconnectors from Norway to the continent surely played a role.”
The team found that when the energy crisis shook European electricity markets, the structures and patterns within the electricity price data changed in a variety of ways.
“Our results emphasize that a national perspective on electricity systems can be quite misleading,” he said. “Europe’s electric power system is highly integrated, which is overall highly beneficial for the customers.”
The researchers hope their work will strengthen the European perspective in the political debate about electricity markets and prices, because problems like this are best tackled via international cooperation. They expect immediate impacts within the field of electricity price forecasting.
“Most scientists only look at one national market, but the interactions with other countries must not be neglected,” said Witthaut. “We’ll get accurate forecasts only if we model all countries together.”
The next step for the team is to move beyond analyzing correlations to identifying cause and effects.
“There’s an intensive debate about how changes in our electricity mix affect prices and costs,” said Witthaut. “How does the rise of renewable power affect market prices? How important are nuclear power plants for the market? We can’t answer these questions by a simple correlation analysis. Instead, we need statistical tools that can quantify causal effects.”
###
The article “Patterns and correlations in European electricity pricing” is authored by Julius Trebbien, Anton Tausendfreund, Leonardo Rydin, and Dirk Witthaut. It will appear in Chaos on July 2, 2024 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0201734). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0201734.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Chaos is devoted to increasing the understanding of nonlinear phenomena in all areas of science and engineering and describing their manifestations in a manner comprehensible to researchers from a broad spectrum of disciplines. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/cha.
###
END
What was behind the 2021-2022 energy crisis within Europe?
Statistical physics and network science reveal factors behind skyrocketing electricity prices
2024-07-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Alterations in human gene TRPC5 cause obesity and postpartum depression
2024-07-02
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, the University of Cambridge and collaborating institutions have discovered that alterations in the human gene TRPC5 cause obesity and postpartum depression.
Taken together, their studies in cells, animal models and humans showed that TRPC5 acts on distinct neuronal populations in the hypothalamus, a brain region that regulates multiple innate behaviors including feeding, anxiety, socialization and maternal care. The findings, published in the journal Cell, ...
In-hospital delirium and disability and cognitive impairment after COVID-19 hospitalization
2024-07-02
About The Study: In this cohort study of 311 hospitalized older adults with COVID-19, in-hospital delirium was associated with increased functional disability and cognitive impairment over the 6 months following discharge. Older survivors of a COVID-19 hospitalization who experience in-hospital delirium should be assessed for disability and cognitive impairment during postdischarge follow-up.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Lauren E. Ferrante, M.D., M.H.S., email lauren.ferrante@yale.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.19640)
Editor’s ...
E-cigarette use and lung cancer screening uptake
2024-07-02
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, e-cigarette use was independently associated with lower use of lung cancer screening, particularly among individuals who had quit smoking combustible cigarettes. Emerging research suggests that e-cigarettes contain definite and probable carcinogens and cause similar cancer-associated gene deregulations as combustible tobacco.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Qian Wang, M.D., M.P.H., email qian.wang@uhhospitals.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
A study led by UPF describes how insulinomas, a rare type of pancreatic beta cell tumor, form
2024-07-02
An experimental study led by Pompeu Fabra University describes the mechanism whereby insulinomas, a rare type of neuroendocrine tumour that affects pancreatic beta cells. According to the study, insulinomas are the result of the accumulation of rare mutations that lead to a homogeneous change in the epigenetic profile of pancreatic beta cells. This profile change causes beta cells to express unusually high levels of oncogenes, growth and transcription factors, and genes related to insulin production.
Insulinomas are rare pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours that involve the excessive growth of beta cells, which are responsible for secreting insulin. Often, they are diagnosed ...
NIH researchers discover a new face-detecting brain circuit
2024-07-02
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have uncovered a brain circuit in primates that rapidly detects faces. The findings help not only explain how primates sense and recognize faces, but could also have implications for understanding conditions such as autism, where face detection and recognition are often impaired from early childhood. The newly discovered circuit first engages an evolutionarily ancient part of the brain called the superior colliculus, which can then trigger the eyes and head to turn for a better look. This better view enables different brain areas in the temporal cortex to engage ...
Potential new target for early treatment of Alzheimer's disease
2024-07-02
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A class of proteins that regulates cell repair and enhances cell growth-signaling systems could be a promising new target for the treatment of Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases, according to a new study led by researchers at Penn State. They found that disrupting necessary sugar modifications of these proteins promotes cell repair and reverses cellular abnormalities that occur in neurodegenerative diseases.
The study appeared today (July 2) in the journal iScience, and the researchers have a patent related to this work.
“Strategies ...
Subnormal serum liver enzyme levels
2024-07-02
Liver diseases are commonly diagnosed using serum enzyme assays, particularly for aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), and 5'-nucleotidase (5'-NT). While elevated levels of these enzymes are typically associated with liver and bile duct injuries, subnormal levels can also indicate various pathologies. This review consolidates current knowledge on diseases linked with subnormal liver enzyme levels, focusing on their pathogenesis, specificity, and treatment ...
Too much treadmill? This could help your shin splints
2024-07-02
Good news for all the treadmill runners who suffer from stubborn and painful shin splints: A little outdoor gait training may help, new research suggests.
A randomized controlled trial found that four weeks of gait training outdoors, in addition to home exercises often prescribed for shin splints, led to improved running biomechanics even when the runners were using a treadmill. These improvements included decreasing the time the runners’ feet were in contact with the ground or treadmill, a recently identified contributor to shin splints.
Based on the trial results, ...
Journal of Participatory Medicine announces new theme issue on Patient and Consumer Use of Artificial Intelligence for Health
2024-07-02
(Toronto, July 2, 2024) JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Patient and Consumer Use of Artificial Intelligence for Health” in its premier open access journal Journal of Participatory Medicine indexed in PubMed, SCOPUS, Sherpa Romeo, and DOAJ.
This theme issue will explore the use of AI for health (AIH) from the perspectives of patients and the public. The journal is seeking papers that examine (a) the experience and impact of patients and health consumers using AI applications, and (b) the involvement of patients, caregivers, and the public in the co-design and development of AIH.
For this theme issue, the journal ...
Unveiling the genetic secrets of Musa ornata and Musa velutina: insights into pericarp dehiscence and anthocyanin biosynthesis
2024-07-02
In a pioneering study, researchers have completed the chromosome-level genome assemblies for Musa ornata and Musa velutina, shedding light on the genetic underpinnings of pericarp dehiscence and anthocyanin biosynthesis in bananas. This genetic blueprint is poised to revolutionize the enhancement of bananas' ornamental appeal and nutritional quality, unlocking mysteries that were previously obscured by limited genomic data.
Musa ornata and Musa velutina, known for their ornamental appeal, face cultivation challenges ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] What was behind the 2021-2022 energy crisis within Europe?Statistical physics and network science reveal factors behind skyrocketing electricity prices