(Press-News.org) Owning cryptocurrency may be associated with certain personality and demographic characteristics as well as a reliance on alternative or fringe social media sources, according to a study published July 3, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Shane Littrell from the University of Toronto, Canada, along with colleagues from the University of Miami, USA.
Anonymous trading and unregulated markets hallmark cryptocurrency’s unique subculture. While some consider the digital currency to be financially unreliable, hundreds of millions of global investors think otherwise.
This study identified various political, psychological, and social characteristics differentiating crypto investors from those who abstain. Existing studies (which generally include smaller sample sizes) profile crypto owners as psychologically non-normative and politically non-mainstream.
To test this, Littrell and colleagues polled 2,001 American adults in 2022, about 30% of whom responded “Yes” to owning or having owned crypto. Participants reported demographic information and other responses revealing their political, psychological, and social traits. The researchers conducted several bivariate (two-variable) correlational analyses, which measured how strongly crypto ownership is associated with other variables individually, as well as a multivariate (multi-variable) regression analysis, which attempts to identify the variables that are most important for predicting cryptocurrency ownership.
The correlational analyses showed that crypto ownership is associated with belief in conspiracy theories, support of political extremism, identification with non-left-right political orientations (e.g., Christian nationalism), and the “Dark Tetrad” of personality traits (narcissism, Machiavellianism, psychopathy, and sadism).
The more holistic analysis revealed which self-reported qualities are most likely to predict crypto ownership, the most strongly associated factor being a reliance on fringe social media sources for news. Other strongly associated characteristics included maleness, argumentativeness, higher income, and feelings of victimhood.
Across all survey data, crypto owners reported diverse political orientations and identities with a mix of left and right leanings.
The researchers acknowledge that the correlations they identified are limited by their sample of participants and the fact that they self-reported their characteristics, and cannot be interpreted as causal. Because of the strong correlation between social media and crypto ownership, they encourage future research into the influence of specific media or rhetoric on crypto ownership.
The authors add: “Though our results certainly do not apply to every crypto user out there, on average, we found that crypto investment and ownership tends to appeal to people who are more argumentative, anti-authoritarian, and prefer to get their news from non-mainstream social media sites. There is still much work to be done in this area, but we hope our study helps lay the groundwork for future research aimed at understanding the psychological, political, and behavioral factors associated with this growing financial movement.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0305178
Citation: Littrell S, Klofstad C, Uscinski JE (2024) The political, psychological, and social correlates of cryptocurrency ownership. PLoS ONE 19(7): e0305178. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305178
Author Countries: Canada, USA
Funding: This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (#2123635). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Cryptocurrency investors are more likely to self-report “Dark Tetrad” personality traits alongside other characteristics
Crypto ownership was also associated with being male and high-income, consuming fringe media and reporting feelings of victimhood, in survey of 2,001 Americans
2024-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Smoking behavior is linked to personality traits
2024-07-03
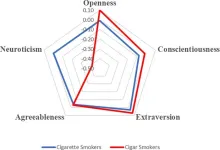
Cigarette smokers, cigar smokers, and non-smokers each have distinct personality profiles, according to a study published July 3, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Dritjon Gruda from Universidade Catolica Portuguesa, Portugal, and Jim McCleskey from Western Governors University, USA.
Tobacco use remains a formidable global public health challenge, responsible for more than 8 million deaths annually, including those attributed to second-hand smoke exposure. Emerging research underscores the critical role of psychological factors, including personality traits, in shaping ...
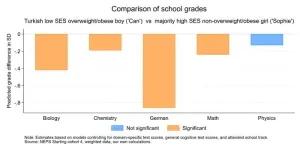
Minority status, social origin, gender, and weight can all count against a German kid’s grades
2024-07-03
A new study done in more than 14,000 ninth graders in Germany has revealed that students experience grading bias based on their gender, body size, ethnicity and parental socio-economic status. These negative biases stack on each other, meaning that students with multiple intersectional identities get significantly lower grades than their peers regardless of their true abilities. Richard Nennstiel and Sandra Gilgen of the University of Bern and University of Zurich in Switzerland present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 3, ...
Dengue linked to heightened short- and long-term risk of depression in Taiwan
2024-07-03
Analysis of the medical records of nearly 50,000 people who experienced dengue fever in Taiwan suggests that this disease is associated with elevated short- and long-term risk of depression. Hsin-I Shih and colleagues of National Cheng Kung University and National Health Research Institutes, Taiwan present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
People may develop dengue fever after being bitten by a mosquito carrying the dengue virus. Dengue fever can be mild, but it can also progress ...
Fighting COVID-19 with a cancer drug
2024-07-03
Twelve years ago, cancer researchers at University of California San Diego identified a molecule that helps cancer cells survive by shuttling damaging inflammatory cells into tumor tissue. In new research, they show that the same molecule does the same thing in lung tissue infected with COVID-19 — and that the molecule can be suppressed with a repurposed cancer drug. The work, published in Science Translational Medicine, represents a new approach to preventing irreversible organ damage in infectious diseases like COVID-19 and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
The two key players in this scenario are inflammatory cells called myeloid ...
From ‘hit to vial’: Discovery and optimization of a promising vaccine adjuvant
2024-07-03
Many vaccines are only partially effective, have waning efficacy, or do not work well in the very young or the very old. For more than a decade, Ofer Levy, MD, PhD, and David Dowling, PhD, in the Precision Vaccines Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, have tried improving vaccines by adding compounds known as adjuvants to boost vaccine recipients’ immune responses.
Now, under a large Adjuvant Discovery Program contract from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ...
Why do you keep your house so cold? Science says: Ask your parents
2024-07-03
Childhood home temperature and community connectedness can help predict how U.S. residents set their thermostats, offering new ways to encourage energy conservation and combat climate change, according to a study published July 3 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Dritjon Gruda from the National University of Ireland Maynooth and Paul Hanges from the University of Maryland.
Half of U.S. households’ annual electricity use goes to heating and cooling, but less than half of homeowners tweak their thermostats to save energy ...
Texas A&M center receives $7.6 million grant to promote research in environmental health
2024-07-03
The Texas A&M Center for Environmental Health (TiCER), a National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) Environmental Health Sciences Core Center, will be returning to the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) with a $7.6 million grant for the center’s new funding cycle.
Under the new leadership of Dr. Weston Porter, a VMBS professor in the Department of Veterinary Physiology and Pharmacology, the center will promote research in four areas of environmental health — climate ...
Deep machine-learning speeds assessment of fruit fly heart aging and disease, a model for human disease
2024-07-03
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Drosophila — commonly known as fruit flies — are a valuable model for human heart pathophysiology, including cardiac aging and cardiomyopathy. However, a choke point in evaluating fruit fly hearts is the need for human intervention to measure the heart at moments of its largest expansion or its greatest contraction, measurements that allow calculations of cardiac dynamics.
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham now show a way to significantly cut the time needed ...
U.S. Department of Energy issues request for proposals for contractor to manage and operate Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility
2024-07-03
Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the issuance of a Request for Proposals (RFPs) for the competitive selection of a management and operating contractor for the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF).
TJNAF is a DOE national laboratory and DOE-sponsored Federally Funded Research and Development Center that has a mission focused on delivering breakthrough science and technology in nuclear physics.
DOE expects to award the contract before the current agreement with Jefferson Science Associates, LLC expires on May 31, 2025, allowing for an anticipated three-month transition. DOE expects the selected ...
Survivorship standards help address the distinct needs of adult cancer survivors
2024-07-03
Key Takeaways
More people are surviving cancer than ever before and living longer. This growing population of adult cancer survivors requires distinct survivorship services focused on long-term well-being.
Survey study demonstrates the value of American College of Surgeons’ survivorship accreditation standards, though specialized services in fertility and sexual health are less accessible.
CHICAGO — With the number of adult cancer survivors in the United States expected to reach 23 million by 2032,* the long-term needs of this ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] Cryptocurrency investors are more likely to self-report “Dark Tetrad” personality traits alongside other characteristicsCrypto ownership was also associated with being male and high-income, consuming fringe media and reporting feelings of victimhood, in survey of 2,001 Americans