Clinical implications and procedural complications in patients with patent foramen ovale concomitant with atrial septal aneurysm
2024-07-03
(Press-News.org) https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/CVIA.2024.0038
Announcing a new article publication for Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications journal. Atrial septal aneurysm (ASA) is defined as excursion of the atrial septum exceeding 10 mm beyond the atrial septum into the right or left atrium, or a combined total excursion of 15 mm on the right and left sides during the cardiac cycle. According to previous studies, 20–40% of patent foramen ovale (PFO) cases are accompanied by ASAs. ASA is associated with the presence of PFO, left atrial dysfunction, cryptogenic stroke, migraine, and arterial embolism, thus making closure of PFO in patients with concomitant ASA necessary but challenging. The anatomy of ASAs associated with PFO has crucial effects on complications after the closure procedure; therefore, several factors must be considered. The authors of this article review the clinical implications of concomitant PFO and ASA; discuss the complications occurring after the closure procedure; and provide practical guidance for the closure of concomitant PFO and ASA.
CVIA is available on the ScienceOpen platform and at Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications. Submissions may be made using ScholarOne Manuscripts. There are no author submission or article processing fees. Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications is indexed in the EMBASE, EBSCO, ESCI, OCLC, Primo Central (Ex Libris), Sherpa Romeo, NISC (National Information Services Corporation), DOAJ, Index Copernicus, Research4Life and Ulrich’s web Databases. Follow CVIA on Twitter @CVIA_Journal; or Facebook.
Haowei Zeng, Beidi Lan and Xiaoqin Liu et al. Clinical Implications and Procedural Complications in Patients with Patent Foramen Ovale Concomitant with Atrial Septal Aneurysm. CVIA. 2024. Vol. 9(1). DOI: 10.15212/CVIA.2024.0038
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-03
Owning cryptocurrency may be associated with certain personality and demographic characteristics as well as a reliance on alternative or fringe social media sources, according to a study published July 3, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Shane Littrell from the University of Toronto, Canada, along with colleagues from the University of Miami, USA.
Anonymous trading and unregulated markets hallmark cryptocurrency’s unique subculture. While some consider the digital currency to be financially unreliable, hundreds of millions of global investors think otherwise.
This study identified various political, psychological, and social characteristics ...
2024-07-03
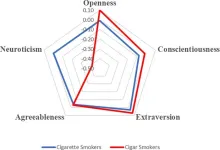
Cigarette smokers, cigar smokers, and non-smokers each have distinct personality profiles, according to a study published July 3, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Dritjon Gruda from Universidade Catolica Portuguesa, Portugal, and Jim McCleskey from Western Governors University, USA.
Tobacco use remains a formidable global public health challenge, responsible for more than 8 million deaths annually, including those attributed to second-hand smoke exposure. Emerging research underscores the critical role of psychological factors, including personality traits, in shaping ...
2024-07-03
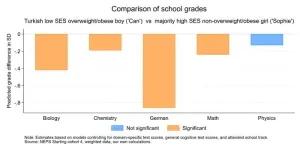
A new study done in more than 14,000 ninth graders in Germany has revealed that students experience grading bias based on their gender, body size, ethnicity and parental socio-economic status. These negative biases stack on each other, meaning that students with multiple intersectional identities get significantly lower grades than their peers regardless of their true abilities. Richard Nennstiel and Sandra Gilgen of the University of Bern and University of Zurich in Switzerland present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 3, ...
2024-07-03
Analysis of the medical records of nearly 50,000 people who experienced dengue fever in Taiwan suggests that this disease is associated with elevated short- and long-term risk of depression. Hsin-I Shih and colleagues of National Cheng Kung University and National Health Research Institutes, Taiwan present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
People may develop dengue fever after being bitten by a mosquito carrying the dengue virus. Dengue fever can be mild, but it can also progress ...
2024-07-03
Twelve years ago, cancer researchers at University of California San Diego identified a molecule that helps cancer cells survive by shuttling damaging inflammatory cells into tumor tissue. In new research, they show that the same molecule does the same thing in lung tissue infected with COVID-19 — and that the molecule can be suppressed with a repurposed cancer drug. The work, published in Science Translational Medicine, represents a new approach to preventing irreversible organ damage in infectious diseases like COVID-19 and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
The two key players in this scenario are inflammatory cells called myeloid ...
2024-07-03
Many vaccines are only partially effective, have waning efficacy, or do not work well in the very young or the very old. For more than a decade, Ofer Levy, MD, PhD, and David Dowling, PhD, in the Precision Vaccines Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, have tried improving vaccines by adding compounds known as adjuvants to boost vaccine recipients’ immune responses.
Now, under a large Adjuvant Discovery Program contract from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ...
2024-07-03
Childhood home temperature and community connectedness can help predict how U.S. residents set their thermostats, offering new ways to encourage energy conservation and combat climate change, according to a study published July 3 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Dritjon Gruda from the National University of Ireland Maynooth and Paul Hanges from the University of Maryland.
Half of U.S. households’ annual electricity use goes to heating and cooling, but less than half of homeowners tweak their thermostats to save energy ...
2024-07-03
The Texas A&M Center for Environmental Health (TiCER), a National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) Environmental Health Sciences Core Center, will be returning to the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) with a $7.6 million grant for the center’s new funding cycle.
Under the new leadership of Dr. Weston Porter, a VMBS professor in the Department of Veterinary Physiology and Pharmacology, the center will promote research in four areas of environmental health — climate ...
2024-07-03
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Drosophila — commonly known as fruit flies — are a valuable model for human heart pathophysiology, including cardiac aging and cardiomyopathy. However, a choke point in evaluating fruit fly hearts is the need for human intervention to measure the heart at moments of its largest expansion or its greatest contraction, measurements that allow calculations of cardiac dynamics.
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham now show a way to significantly cut the time needed ...
2024-07-03
Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the issuance of a Request for Proposals (RFPs) for the competitive selection of a management and operating contractor for the Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF).
TJNAF is a DOE national laboratory and DOE-sponsored Federally Funded Research and Development Center that has a mission focused on delivering breakthrough science and technology in nuclear physics.
DOE expects to award the contract before the current agreement with Jefferson Science Associates, LLC expires on May 31, 2025, allowing for an anticipated three-month transition. DOE expects the selected ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Clinical implications and procedural complications in patients with patent foramen ovale concomitant with atrial septal aneurysm