Case Western Reserve University receives $1.5M grant from Foundation Fighting Blindness to test possible new treatment for inherited retinal disease
2024-07-08
(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND—There’s only one U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved therapy for an inherited retinal disease, and dozens of retinitis pigmentosa (RP) genes for which no therapy is available.
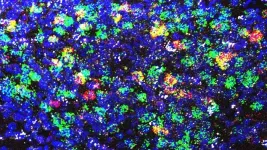
With a new three-year, $1.5 million grant from the Foundation Fighting Blindness, Shigemi Matsuyama, an associate professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, will test a possible breakthrough drug that can be taken by mouth—one that may address many RP disease manifestations, regardless of the underlying genetic mutation.
“We believe it can serve as the basis of an oral medicine to prevent blindness in RP patients, regardless of the underlying gene mutations,” Matsuyama said.
The disease…and promising science
RP causes blindness when cells in the retina that respond to light—called photoreceptors—die.
In a previous foundation-funded drug discovery program from 2017-20, Matsuyama and his research team developed a series of novel orally-active cell-death inhibitors—known as Cytoprotective Small Compounds (CPSCs)—which work by blocking the activation of Bax, a protein that contributes to cell death. Their lead compound prevented retinal cell death and vision loss in four mouse models of inherited retinal disease.
The proposed studies, which include toxicology evaluation and drug-formulation testing—for both oral drugs and eye drops—are aimed at advancing the technology to U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-regulated clinical trials.
“Our primary objective is bringing an CPSC-based therapeutic to RP patients who are suffering from the fear of blindness,” Matsuyama said.
Bax-induced cell death is also a major cause of various neurodegenerative conditions, including glaucoma, ischemia-reperfusion injury, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease.
“Therefore,” he said, “there is significant potential to expand the application of our Bax-inhibiting therapeutic for additional uses.”
“The Foundation Fighting Blindness is proud to support Dr. Shigemi Matsuyama's research,” said Chad Jackson, senior director of preclinical translational research at the foundation. “Through this award, we continue our commitment to advancing scientific discoveries that have the potential to realize tangible solutions for those affected by inherited retinal diseases.”
About the Foundation Fighting Blindness
The foundation is focused on treating and curing blindness caused by the spectrum of blinding retinal diseases including: RP, macular degeneration and Usher syndrome.
###
Case Western Reserve University is one of the country's leading private research institutions. Located in Cleveland, we offer a unique combination of forward-thinking educational opportunities in an inspiring cultural setting. Our leading-edge faculty engage in teaching and research in a collaborative, hands-on environment. Our nationally recognized programs include arts and sciences, dental medicine, engineering, law, management, medicine, nursing and social work. About 6,200 undergraduate and 6,100 graduate students comprise our student body. Visit case.edu to see how Case Western Reserve thinks beyond the possible.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-08
Cancer is insidious. Throughout tumor progression, the disease hijacks otherwise healthy biological processes—like the body’s immune response—to grow and spread. When tumors elevate levels of an immune system molecule called Interleukin-6 (IL-6), it can cause severe brain dysfunction. In about 50%-80% of cancer patients, this leads to a lethal wasting disease called cachexia. “It’s a very severe syndrome,” says Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Bo Li.
“Most people with cancer die of cachexia instead of cancer. And once the patient enters this stage, there’s ...
2024-07-08
Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is safe for treating patients with common types of atrial fibrillation (AF), according to the largest study of its kind on this new technology, led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The “MANIFEST-17K” international study is the first to show important safety outcomes in a large patient population, including no significant risk of esophageal damage, with PFA. PFA is the latest ablation modality approved by the Food and Drug Administration that can be used to restore a regular heartbeat. The findings, published July 8 in Nature Medicine, could lead to more frequent use of PFA instead of conventional therapies to manage AF patients.
“MANIEFST-17K ...
2024-07-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Why do employees sometimes accept working for an abusive boss?
A new study suggests that when a leader is seen as a high performer, employees are more likely to label abuse as just “tough love.”
Results showed that workers were less likely to show hostility to abusive bosses when the leader’s performance was high, and employees were even likely to think their career could be boosted by a successful – if abusive – boss.
The findings suggest that employees may be reluctant to call a successful boss abusive – ...
2024-07-08
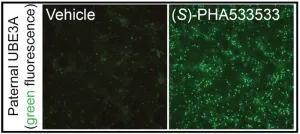
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Angelman syndrome is a rare genetic disorder caused by mutations in the maternally-inherited UBE3A gene and characterized by poor muscle control, limited speech, epilepsy, and intellectual disabilities. Though there isn't a cure for the condition, new research at the UNC School of Medicine is setting the stage for one.
Ben Philpot, PhD, the Kenan Distinguished Professor of Cell Biology and Physiology at the UNC School of Medicine and associate director of the UNC Neuroscience Center, and his lab have identified a small molecule that could be safe, non-invasively delivered, and capable of ...
2024-07-08
As climate change advances, the ocean’s overturning circulation is predicted to weaken substantially. With such a slowdown, scientists estimate the ocean will pull down less carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. However, a slower circulation should also dredge up less carbon from the deep ocean that would otherwise be released back into the atmosphere. On balance, the ocean should maintain its role in reducing carbon emissions from the atmosphere, if at a slower pace.
However, a new study by an MIT researcher finds that scientists may have to rethink the relationship between the ocean’s circulation and its ...
2024-07-08
The largest animals do not have proportionally bigger brains - with humans bucking this trend - a new study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution has revealed.
Researchers at the University of Reading and Durham University collected an enormous dataset of brain and body sizes from around 1,500 species to clarify centuries of controversy surrounding brain size evolution.
Bigger brains relative to body size are linked to intelligence, sociality, and behavioural complexity – with humans having evolved exceptionally large brains. The new research, published today (Monday, 8 July), reveals the largest animals do not have proportionally bigger brains, ...
2024-07-08
A multidisciplinary research team has developed a discovery platform to probe the function of genes involved in metabolism — the sum of all life-sustaining chemical reactions.
The investigators used the new platform, called GeneMAP (Gene-Metabolite Association Prediction), to identify a gene necessary for mitochondrial choline transport. The resource and derived findings were published July 8 in the journal Nature Genetics.
“We sought to gain insight into a fundamental question: ‘How does genetic variation determine our “chemical individuality” — the inherited differences that make us biochemically unique?” said Eric Gamazon, ...
2024-07-08
California must implement early retirement for existing heavy-duty vehicles as well as introducing zero-emissions vehicles (ZEVs) to protect Black, Latino and vulnerable communities and hit net zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions targets by 2045. This is the outcome of a new study published in Environmental Research: Infrastructure and Sustainability by researchers from Stanford University and Arizona State University.
Stringent policies for mandating both ZEVs and early vehicle retirement could reduce cumulative emissions by two-thirds (64%) and reduce half of pollution-related mortality, particularly among disadvantaged communities.
California is the world’s 5th largest ...
2024-07-08
This study presents a significant advancement in fuel cell technology. Researchers from Tokyo Tech identified hexagonal perovskite-related Ba5R2Al2SnO13 oxides (R = rare earth metal) as materials with exceptionally high proton conductivity and thermal stability. Their unique crystal structure and large number of oxygen vacancies enable full hydration and high proton diffusion, making these materials ideal candidates as electrolytes for next-generation protonic ceramic fuel cells that can operate at intermediate temperatures without degradation.
Fuel cells offer a promising solution for clean energy by combining hydrogen and oxygen to generate electricity, ...
2024-07-08
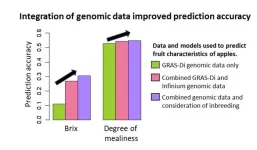
Over the past few decades, the world has witnessed tremendous progress in the tools used for genomic analysis. While it’s usually more common to associate these tools with the fields of biology and medicine, they have proven to be very valuable in agriculture as well. Using numerous DNA markers obtained from next-generation sequencing technologies, breeders can make genomic predictions and select promising individuals based on based on their predicted trait values.
Various systems and methodologies aimed at improving the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Case Western Reserve University receives $1.5M grant from Foundation Fighting Blindness to test possible new treatment for inherited retinal disease