(Press-News.org) Amsterdam UMC's Alzheimer Centre has developed a prediction model that can predict cognitive decline in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. The next step is developing an app that uses this prediction model, which would represent an important step towards personalised forecasts for patients. The study is published today in the journal Neurology.
After people have been diagnosed with Alzheimer's, their first question is often: "What can I expect now?". This question is difficult for doctors to answer. To aid them, Pieter van der Veere, physician-researcher at Alzheimer Centre Amsterdam, has developed a model that can predict cognitive decline, Although the predictions do not provide absolute certainty, the model does give an indication of the course of the disease over a period of 5 years. For practical use, a prototype of an app is available for scientific research. The next step is to develop a more user-friendly app with input from patients, family members, and professionals.
Focused on the individual
The prediction model is based on data from nearly 1000 patients with Alzheimer's disease. It uses general information such as age, gender, and cognitive test scores, as well as data from MRI scans and biomarkers, gathered from cerebrospinal fluid. "As a result, it gives a prediction that is really tailored to each individual person," says Van der Veere. Nevertheless, the model shows how difficult it is to make a precise prediction for each individual patient, because there are always uncertainties. These are always discussed with the patient. "Previous research shows that people still want information about their prognosis, even if this information is uncertain. An app with our prediction model can therefore meet an important need."
Personal prognosis as a future perspective
The prediction model is an important first step towards personal forecasting. "In the future, this will become even more important if we can treat Alzheimer's disease," says Wiesje van der Flier, Research Director at Alzheimer Centre Amsterdam. "Doctors can use the prediction model to explain what the possible effect of a treatment can be. For example, if patients start to live healthier lives or use medication." This can be a starting point for conversations between doctor, patient and family about the pros and cons of treatments, so that they can come to an appropriate decision together."
END
It is possible to predict cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease
Amsterdam UMC led research develops a prediction model for how Alzheimer's disease will develop
2024-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can we predict how fast cognitive decline will occur with early Alzheimer’s?
2024-07-10
MINNEAPOLIS – A new study looks at predicting how quickly people with early Alzheimer’s disease will experience cognitive decline. The study is published in the July 10, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. It also looked at how the new drugs recently approved for the disease may reduce decline.
“The rate of cognitive decline varies greatly from person to person, and people are very interested in what to expect from the disease in themselves or their loved ones, so better prediction models are urgently needed,” said study author Pieter J. van der Veere, M.D., of Amsterdam ...
New Consumer Food insights from Purdue explores consumer attitudes toward U.S. farm bill
2024-07-10
The general public has limited knowledge of the U.S. farm bill that politicians are debating on Capitol Hill, according to the June 2024 Consumer Food Insights (CFI) Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability (CFDAS) assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies, and trust in information sources. Purdue experts conducted and evaluated the survey, which included 1,200 consumers across the U.S
“Around one-third ...
Lion with nine lives breaks record with longest swim in predator-infested waters
2024-07-10
A record-breaking swim by two lion brothers across a predator-infested African river has been documented in a study co-led by Griffith University and Northern Arizona University.
Dr Alexander Braczkowski, from Griffith’s Centre for Planetary Health and Food Security, led a team that filmed a two-male lion coalition crossing the Kazinga Channel in Uganda at night, using high-definition heat detection cameras on drones. The work was done under the supervision of the Uganda Wildlife Authority.
One half of the lion brother duo was a 10-year-old ...
Pumpkin disease not evolving, could make a difference for management
2024-07-10
URBANA, Ill. -- The pathogen that causes bacterial spot is very good at what it does. Forming small lesions on the rinds of pumpkins, melons, cucumbers, and other cucurbits, it mars the fruits’ appearance and ushers in secondary pathogens that lead to rot and severe yield loss. The bacterium, Xanthomonas cucurbitae, is so successful that it has had no reason to evolve through time or space. That’s according to new University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign research characterizing ...
Aging exacerbates oxidative stress and liver fibrosis in an animal model of Down Syndrome
2024-07-10
“[...] our results put the basis for the use of antioxidants supplementation in Down Syndrome patients to prevent liver-associated pathologies.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 12, entitled, “Aging exacerbates oxidative stress and liver fibrosis in an animal model of Down Syndrome.”
Down Syndrome (DS) is a common genetic disorder characterized by an extra copy of chromosome 21, leading to dysregulation of various metabolic pathways. Oxidative stress in DS is associated ...
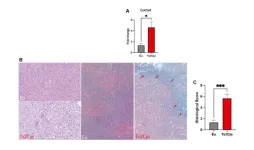
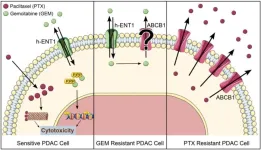
Targeting ABC transporters in PDAC – past, present, or future?
2024-07-10
“[...] it is crucial for the future application of ABC transporter inhibitors [...] to develop a stratification protocol [...] to identify those PDAC patients who are most likely to benefit from chemosensitization induced by these inhibitors.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 10, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 20, 2024, entitled, “Targeting ABC transporters in PDAC – past, present, or future?”
In this new editorial, Cecilia Bergonzini, Elisa Giovannetti and Erik ...
Machine learning models could enable earlier identification of at-risk children, aiding social workers and potentially improving outcomes, per Danish study of more than 100,000 children
2024-07-10
Machine learning models could enable earlier identification of at-risk children, aiding social workers and potentially improving outcomes, per Danish study of more than 100,000 children
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0305974
Article Title: Predictive risk modeling for child maltreatment detection and enhanced decision-making: Evidence from Danish administrative data
Author Countries: Denmark, France
Funding: Funding for this project was ...
Holiday season already? Anticipation might make time seem to fly
2024-07-10
Christmas or Ramadan might seem to come around more quickly each year, for people who pay more attention to time, are more forgetful of plans, and love a good holiday. A research team led by Ruth Ogden of Liverpool John Moores University, UK, and Saad Sabet Alatrany of Imam Ja'afar Al-Sadiq University, Iraq, published these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 10, 2024. They suggest this could mean that someone’s experience of time is shaped not only by what they’ve done, but what is left to do.
“Christmas seems to come quicker each year,” is a staple of small talk. But the ...
Perceived warmth, competence predict callback decisions in meta-analysis of hiring experiments
2024-07-10
Perceived warmth and competence predict the influence of race, gender and age on callback decisions, suggesting social perceptions might underlie such hiring bias. The meta-analysis of North American correspondence studies is published July 10, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Carina Hausladen from the California Institute of Technology and ETH Zürich, Marcos Gallo from the California Institute of Technology, and colleagues.
In the labor market, applicants from marginalized groups continue to face disparate treatment. To ...
Microproteins found in tumors could lead to cancer vaccines
2024-07-10
A study led by the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, with Cima University of Navarra and Pompeu Fabra University, has identified a group of small molecules exclusive to liver tumors that could be key to developing cancer vaccines. These are microproteins, very small proteins expressed only by tumor cells. This can result in the activation of immune cells against the tumor. The study is published in Science Advances.
By integrating data from tumors and healthy tissue from over one hundred liver cancer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
[Press-News.org] It is possible to predict cognitive decline in Alzheimer's diseaseAmsterdam UMC led research develops a prediction model for how Alzheimer's disease will develop