(Press-News.org) Machine learning models could enable earlier identification of at-risk children, aiding social workers and potentially improving outcomes, per Danish study of more than 100,000 children
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0305974
Article Title: Predictive risk modeling for child maltreatment detection and enhanced decision-making: Evidence from Danish administrative data
Author Countries: Denmark, France
Funding: Funding for this project was provided by TrygFonden (TrygFondens Centre for Child Research) (https://childresearch.au.dk/en/). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Machine learning models could enable earlier identification of at-risk children, aiding social workers and potentially improving outcomes, per Danish study of more than 100,000 children
2024-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Holiday season already? Anticipation might make time seem to fly
2024-07-10
Christmas or Ramadan might seem to come around more quickly each year, for people who pay more attention to time, are more forgetful of plans, and love a good holiday. A research team led by Ruth Ogden of Liverpool John Moores University, UK, and Saad Sabet Alatrany of Imam Ja'afar Al-Sadiq University, Iraq, published these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 10, 2024. They suggest this could mean that someone’s experience of time is shaped not only by what they’ve done, but what is left to do.
“Christmas seems to come quicker each year,” is a staple of small talk. But the ...
Perceived warmth, competence predict callback decisions in meta-analysis of hiring experiments
2024-07-10
Perceived warmth and competence predict the influence of race, gender and age on callback decisions, suggesting social perceptions might underlie such hiring bias. The meta-analysis of North American correspondence studies is published July 10, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Carina Hausladen from the California Institute of Technology and ETH Zürich, Marcos Gallo from the California Institute of Technology, and colleagues.
In the labor market, applicants from marginalized groups continue to face disparate treatment. To ...
Microproteins found in tumors could lead to cancer vaccines
2024-07-10
A study led by the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, with Cima University of Navarra and Pompeu Fabra University, has identified a group of small molecules exclusive to liver tumors that could be key to developing cancer vaccines. These are microproteins, very small proteins expressed only by tumor cells. This can result in the activation of immune cells against the tumor. The study is published in Science Advances.
By integrating data from tumors and healthy tissue from over one hundred liver cancer ...
Mount Sinai and City of Hope scientists first to demonstrate a combination treatment can increase human insulin-producing cells in vivo
2024-07-10
NEW YORK and LOS ANGELES — In preclinical studies, a team of researchers from Mount Sinai Health System in New York City and City of Hope in Los Angeles report new findings on a therapeutic combination that regenerated human insulin-producing beta cells, providing a possible new treatment for diabetes. The findings were published today in Science Translational Medicine.
This work, led by Andrew F. Stewart, MD, Irene and Dr. Arthur M. Fishberg Professor of Medicine and Director of the Mount Sinai Diabetes, Obesity ...
City of Hope and Mount Sinai scientists first to demonstrate a combination treatment can increase human insulin-producing cells in vivo
2024-07-10
LOS ANGELES and NEW YORK — In preclinical studies, a team of researchers from City of Hope® in Los Angeles and Mount Sinai Health System in New York reports new findings on a therapeutic combination that regenerated human insulin-producing beta cells, providing a possible new treatment for diabetes. The findings were published today in Science Translational Medicine.
This work, led by Andrew F. Stewart, M.D., Irene and Dr. Arthur M. Fishberg Professor of Medicine and Director of the Mount Sinai Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism Institute, began at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in 2015. The studies were a team effort. Adolfo ...
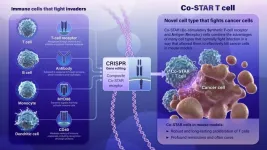
New Co-STAR receptor shows promise treating cancers in laboratory study
2024-07-10
Using genetic engineering techniques, investigators at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and its Ludwig Center, the Lustgarten Laboratory and Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy have designed a novel type of cell to recognize and fight cancer.
To produce the cells, called Co-STAR (Co-stimulatory Synthetic T-cell receptor and Antigen Receptor) cells, the researchers combined genetic components of four types of cells that the body normally uses to defend against invaders to make ...
Novel genome editing approach restores hearing in adult preclinical models with genetic deafness
2024-07-10
The study also looked at safety of the AAV-mediated genome editing approach and found it had a good safety profile that includes little off-target effect and no detectable long-term integration of the AAV vector in the genome. “Our research suggested minimal potential risk and supports the feasibility of future clinical applications in humans,” said Wenliang Zhu, PhD, and physician-scientist Wan Du, MD, PhD, members of Chen’s lab at Mass Eye and Ear and first authors on the paper.
The study, led by Zheng-Yi Chen, DPhil, an associate scientist in the Eaton-Peabody Laboratories at Mass Eye and Ear (a member of the ...
Rice’s Omid Veiseh elected to the Controlled Release Society College of Fellows
2024-07-10
HOUSTON – (July 10, 2024) – The Controlled Release Society (CRS), the premier international, multidisciplinary society dedicated to the science and technology of drug delivery, has elected Rice University bioengineer Omid Veiseh to its College of Fellows.
The recognition is a prestigious acknowledgement of “outstanding and sustained contributions in the field of delivery science and technology,” according to the organization website.
“I am deeply honored to be elected to the CRS College ...
Bringing quantum tools to high school classrooms
2024-07-10
More than 70 high school students and science teachers gathered at Young Middle School in Arlington this summer to learn about quantum information science (QIS). The annual workshop and camp are part of a national pilot program called Quantum for All led by Karen Jo Matsler, assistant professor in practice and master teacher in the UTeach program at The University of Texas at Arlington.
“Just the word ‘quantum’ scares people, which is why many teachers and school administrators ...
Novel pre-treatment process enhances PFAs removal from drinking water
2024-07-10
In a groundbreaking effort to tackle the pervasive issue of PFAS contamination in drinking water, a research team at New Jersey Institute of Technology has received funding from the Bureau of Reclamation's Desalination and Water Purification Research program.
This highly competitive grant, awarded to only eight projects out of over eighty applicants, supports their innovative project titled "Enhanced Coagulation for the Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances using Hydrophobic Ion Pairing Approach Project."
Arjun Venkatesan, associate ...