(Press-News.org) Markers in the blood that predict whether glaucoma patients are at higher risk of continued loss of vision following conventional treatment have been identified by researchers at UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital.
Over 700,000 people in the UK have glaucoma and it is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. The condition occurs when the cells in the eye that help you see (called retinal ganglion cells) start to die.
The main risk factors for glaucoma are high eye pressure and older age.
Currently, all licenced treatments are designed to lower pressure in the eye – also known as intraocular pressure. However, some patients still continue to lose their sight following treatment.
To help doctors better understand who will lose their vision faster, the new study, published in Nature Medicine, asked whether mitochondrial function, measured in white blood cells, is lower in people with glaucoma than those without glaucoma and if mitochondrial function is associated with the rate at which glaucoma patients lose vision.
Mitochondria are the ‘batteries’ inside cells that produce energy for the cells to function. Cells in the eye use a lot of energy.
The researchers assessed 139 participants who were already receiving treatment to lower intraocular pressure and 50 healthy people acting as a control (comparison) group.
They measured how well cells in the blood use oxygen, how much vision was lost over time and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) levels.
NAD is a molecule in the body that helps cells produce energy and is made from vitamin B3 in the diet.
Firstly, the researchers discovered that certain cells in the blood, known as peripheral blood mononuclear cells, use oxygen differently in people with glaucoma.
The team measured how much oxygen these cells use and found that people whose blood cells used less oxygen tended to lose their vision faster, even if they were being treated to lower intraocular pressure. This measurement explained 13% of the differences in how fast patients lost vision.
Additionally, people with glaucoma were found to have lower levels of NAD in their blood cells compared to people without glaucoma. These lower NAD levels were linked to the lower oxygen use in the blood cells.
Senior author, Professor David (Ted) Garway-Heath (UCL Institute of Ophthalmology and Moorfields Eye Hospital), said: “White blood cell mitochondrial function and NAD levels, if introduced as a clinical test, would enable clinicians to predict which patients are at higher risk of continued vision loss, allowing them to be prioritised for more intensive monitoring and treatment.
“If further research shows that low mitochondrial function or low NAD levels are a cause for glaucoma, then this opens the way for new treatments.
“UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital are currently leading a major clinical trial funded by the Medical Research Council and the National Institute for Health and Care Research, to establish whether high-dose vitamin B3 can boost mitochondrial function and reduce vision loss in glaucoma.*
“We hope that this will open a new avenue for treatment of glaucoma patients which does not depend on lowering the eye pressure.”
The study was supported by Santen SenSyT, Fight for Sight, Glaucoma UK, Rosetrees Trust, Alcon Research Institute and the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and UCL Institute of Ophthalmology.
* UCL News, 2022: Vitamin B3 trialled as glaucoma treatment
END
Biomarkers reveal how patients with glaucoma may respond to treatment
2024-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
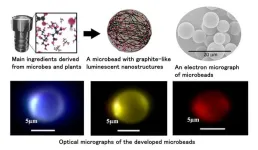
Microbeads with adaptable fluorescent colors from visible light to near-infrared
2024-07-12
1. A research team at NIMS has successfully developed an environmentally friendly, microspherical fluorescent material primarily made from citric acid. These microbeads emit various colors of light depending on the illuminating light and the size of the beads, which suggests a wide range of applications. Furthermore, the use of plant-derived materials allows for low-cost and energy-efficient synthesis.
2. Conventional luminescent devices commonly utilized thin films of compound semiconductors containing metals or sintered inorganic materials with rare earth elements. However, in a circular economy, there ...
Neighborhood disadvantage and prostate tumor RNA expression of stress-related genes
2024-07-12
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, the expression of several stress-related genes in prostate tumors was higher among men residing in disadvantaged neighborhoods. This study is one of the first to suggest associations of neighborhood disadvantage with prostate tumor RNA expression. Additional research is needed in larger studies to replicate findings and further investigate interrelationships of neighborhood factors, tumor biology, and aggressive prostate cancer to inform interventions to reduce disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
Screen media use and mental health of children and adolescents
2024-07-12
About The Study: This secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial found that a short-term reduction in leisure-time screen media use within families positively affected psychological symptoms of children and adolescents, particularly by mitigating internalizing behavioral issues and enhancing prosocial behavior. More research is needed to confirm whether these effects are sustainable in the long term.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jesper Schmidt-Persson, Ph.D., email jesp@kp.dk.
To ...
Mediterranean diet and cardiometabolic biomarkers in children and adolescents
2024-07-12
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that Mediterranean diet-based interventions may be useful tools to optimize cardiometabolic health among children and adolescents.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jose Francisco Lopez-Gil, Ph.D., email josefranciscolopezgil@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.21976)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
A chemical claw machine bends and stretches when exposed to vapors
2024-07-12
Scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia have developed a tiny “claw machine” that is able to pick up and drop a marble-sized ball in response to exposure to chemical vapors.
The findings, published July 12 in the journal Chem, point to a technique that can enable soft actuators—the parts of a machine that make it move—to perform multiple tasks without the need for additional costly materials. While existing soft actuators can be “one-trick ponies” restricted to one type of movement, this novel composite film contorts itself ...
Living in disadvantaged neighborhoods influences stress-related genes, which may contribute to aggressive prostate cancer in African American men
2024-07-12
BALTIMORE, MD, July 12, 2024 — Those living in disadvantaged neighborhoods have significantly higher activity of stress-related genes, new research suggests, which could contribute to higher rates of aggressive prostate cancer in African American men. The study, which was co-led by the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU), was published today in JAMA Network Open.
African American men have a higher incidence of prostate cancer and are more than twice as likely to die from the disease than White men in the U.S. They are often diagnosed with an ...
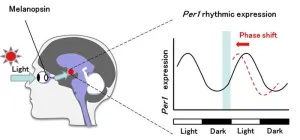
Melanopsin DNA aptamers can regulate input signals of mammalian circadian rhythms by altering the phase of the molecular clock
2024-07-12
Overview:
DNA aptamers of melanopsin that regulate the clock hands of biological rhythms were developed by the Toyohashi University of Technology and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) group.
DNA aptamers can specifically bind to biomolecules to modify their function, potentially making them ideal oligonucleotide therapeutics. We screened the DNA aptamer melanopsin (OPN4), a blue light photopigment in the retina that plays a key role in the use of light signals to reset the phase of circadian rhythms in the central clock.
First, 15 DNA aptamers of melanopsin (Melapts) were identified following eight rounds of Cell-SELEX ...
Challenges and prospects for post-conflict peacebuilding in urban settings
2024-07-12
Wars and conflicts leave devastating destruction in their wake. With so many conflicts now taking place in urban environments, scientists are studying how post-conflict peacebuilding happens in these urban settings. Dahlia Simangan, an associate professor at The IDEC Institute, Hiroshima University, has analyzed the case of Marawi, a city in the Philippines, to better understand the urban environment’s influence on post-siege reconstruction and peacebuilding. This study contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of peacebuilding by integrating conventional peacebuilding components and urban characteristics.
The findings are published ...
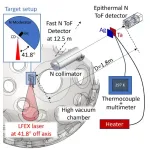
Neutrons give a hot new way to measure the temperature of electronic components
2024-07-12
Osaka, Japan – From LEDs to batteries, our lives are full of electronics, and there is a constant push to make them more efficient and reliable. But as components become increasingly sophisticated, getting reliable temperature measurements of specific elements inside an object can be a challenge.
This is problematic because measuring a device’s temperature is vital for monitoring its performance or designing the materials from which it’s manufactured. Now, in a new study led by Osaka ...
High and low tide cause low and high methane fluxes
2024-07-12
High and low tide cause low and high methane fluxes
Methane, a strong greenhouse gas that naturally escapes from the bottom of the North Sea, is affected by the pressure of high or low tide. Methane emissions from the seafloor can be just easily three times as much or as little, depending on the tide. This is shown by NIOZ oceanographer Tim de Groot, in a publication in Nature Communications Earth and Environment. "Our research shows that you can never rely on one measurement when you want to know how much methane escapes from the seafloor," De Groot emphasizes.
Swamp ...