(Press-News.org)
University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher Thomas Mackie has received a $2.1 million funding award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) to advance the meaningful engagement of communities that are affected by mental health disparities and underrepresented in research partnerships.
The study, entitled “Improving Research Partnership With Engagement Mapping: A Pilot Study to Advance Engagement Science” and co-led by Karen Tabb, a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researcher, is designed to empower community partners to have a greater role in the preparation, implementation, translation and dissemination of research.
Authorized by Congress in 2010, PCORI is an independent, nonprofit organization that funds research to provide patients, their caregivers and clinicians with the evidence-based information needed to make better-informed health care decisions.
The pilot study will test the feasibility of a new engagement approach, called engagement mapping, with three advisory councils at the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School and one advisory council at Postpartum Support International, a nonprofit organization that helps people affected by perinatal mood disorders.
“To advance mental health equity, researchers must find ways to empower the individuals from communities most affected by the mental health care disparities to be partners in our research, both as researchers and as research partners,” says Mackie, professor of health policy and management in the School of Public Health and Health Sciences’ department of health promotion and policy. “Our team will pilot a novel approach to facilitate partnership with individuals from communities who are far too often not meaningfully engaged in research. We will comprehensively review and identify promising practices for research engagement, and then initiate a pilot study to test the feasibility and acceptability of ‘engagement mapping.’”
Engagement mapping will seek out the expertise and judgement of community partners to identify the barriers to research partnerships, co-design and implement strategies responsive to these barriers and then co-evaluate their effectiveness. The pilot study will also identify engagement methods that align with the values and needs of community partners.
The UMass Amherst-University of Illinois Urban-Champaign proposal was selected in response to a PCORI funding announcement aimed at creating an evidence base for developing measures and methods that enhance meaningful engagement in comparative clinical effectiveness research.
Recent years have seen increased knowledge about participatory research involving key stakeholders like patients, caregivers and clinicians as research partners. However, there’s a lack of systematic study on the most effective engagement techniques and a significant gap in evidence regarding the selection of engagement methods tailored for individuals underrepresented in research partnerships, such as communities affected by mental health care disparities.
In reflecting on the motivation for this study, Mackie says, “A member of our advisory council once told us, ‘Nothing about us without us is for us.’ Engagement mapping aims to empower community partners to identify, implement and evaluate strategies that will support their meaningful and impactful engagement in research.”
“This study was selected for PCORI funding for its potential to strengthen patient-centered and stakeholder-driven comparative clinical effectiveness research by providing evidence about specific engagement methods and measures that promote representative engagement of patients and other stakeholders in research,” says Dr. Nakela Cook, PCORI’s executive director. “We look forward to following the study’s progress and working with the University of Massachusetts Amherst to share the results.”
END
Researchers have used gene editing to restore hearing in adult mice with a type of inherited hearing loss. They showed that shutting down a damaged copy of a gene called a microRNA (miRNA) enabled the animals to regain hearing. The approach by a research team supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), reported in Science Translational Medicine, may eventually lead to potential treatments for inherited hearing loss in people.
Zheng-Yi Chen, DPhil., and his colleagues at Mass Eye and Ear in Boston and other institutions studied a rare form of genetic deafness called autosomal dominant deafness-50 (DFNA50). ...
Sant Pau researchers discover a new gene that causes ALS
Researchers from the Neuromuscular Diseases Group and the Dementia Neurobiology Group of the Sant Pau Research Institute (IR Sant Pau) and the Memory Unit of the Sant Pau Hospital, led by neurologist Dr. Ricard Rojas-García, have identified a new mutation in the ARPP21 gene that could be the cause of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), a devastating neurodegenerative disease.
Specifically, it is a shared mutation (c.1586C>T; p.Pro529Leu) in the ARPP21 gene that ...
Long before photosynthesis brought free oxygen into the world, the earth was already populated by numerous organisms. Oxygen was life-threatening for them and therefore they developed completely different metabolic pathways to those we know from plants, animals and humans. Anaerobic bacteria have survived the ages in special, oxygen-free niches, some of them very close to us: as an essential part of the intestinal microbiome, where they are of enormous importance for the well-being of the organism. However, certain anaerobes can ...
Solaris Vita, a startup created by students at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M), has won second place in the "Innovation of the Year" category at Gen-E 2024, the largest European youth entrepreneurship competition, organized by Junior Achievement Europe. This is the first time that a Spanish university team has won this award.
The promoters of Solaris Vita, Miguel Iglesias (Industrial Engineering graduate from UC3M) and Yann Guichard (Economics student at the University), competed ...
Plant cold specialists like the spoonworts have adapted well to the cold climates of the Ice Ages. As cold and warm periods alternated, they developed a number of species that also resulted in a proliferation of the genome. Evolutionary biologists from the universities of Heidelberg, Nottingham, and Prague studied the influence this genome duplication has on the adaptive potential of plants. The results show that polyploids – species with more than two sets of chromosomes – can have an accumulation of structural mutations with signals for a possible local ...
Markers in the blood that predict whether glaucoma patients are at higher risk of continued loss of vision following conventional treatment have been identified by researchers at UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital.
Over 700,000 people in the UK have glaucoma and it is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. The condition occurs when the cells in the eye that help you see (called retinal ganglion cells) start to die.
The main risk factors for glaucoma are high eye pressure and older age.
Currently, all licenced treatments are designed to lower pressure in the eye – also known as intraocular pressure. However, some patients ...
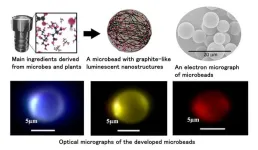
1. A research team at NIMS has successfully developed an environmentally friendly, microspherical fluorescent material primarily made from citric acid. These microbeads emit various colors of light depending on the illuminating light and the size of the beads, which suggests a wide range of applications. Furthermore, the use of plant-derived materials allows for low-cost and energy-efficient synthesis.
2. Conventional luminescent devices commonly utilized thin films of compound semiconductors containing metals or sintered inorganic materials with rare earth elements. However, in a circular economy, there ...
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, the expression of several stress-related genes in prostate tumors was higher among men residing in disadvantaged neighborhoods. This study is one of the first to suggest associations of neighborhood disadvantage with prostate tumor RNA expression. Additional research is needed in larger studies to replicate findings and further investigate interrelationships of neighborhood factors, tumor biology, and aggressive prostate cancer to inform interventions to reduce disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
About The Study: This secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial found that a short-term reduction in leisure-time screen media use within families positively affected psychological symptoms of children and adolescents, particularly by mitigating internalizing behavioral issues and enhancing prosocial behavior. More research is needed to confirm whether these effects are sustainable in the long term.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jesper Schmidt-Persson, Ph.D., email jesp@kp.dk.
To ...
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that Mediterranean diet-based interventions may be useful tools to optimize cardiometabolic health among children and adolescents.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jose Francisco Lopez-Gil, Ph.D., email josefranciscolopezgil@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.21976)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...