SfN establishes James L. Roberts Endowed Fund
2024-07-15
(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C. – The Society for Neuroscience (SfN) has received $128,000 from the estate of James L. Roberts, PhD. With the funds, SfN Council voted to create a new long-term endowed fund, The James L. Roberts Fund, and will use the income from its investments to create and perpetually fund James L. Roberts Trainee Professional Development Awards (TPDAs) beginning at Neuroscience 2024.
“I knew Jimmy Roberts very well. We basically launched neurobiology at Sinai when we co-directed the Fishberg Research Center for Neurobiology at Mount Sinai from 1989–2002,” said incoming SfN President John Morrison. “Jimmy was an outstanding researcher and student mentor, taking great joy in watching his students mature as scientists and people. I cannot think of a better way to honor Jimmy than through support of SfN’s TPDAs. His generosity will ensure future trainees can benefit from his spirit of mentorship in perpetuity.”
The annual contribution by the James L. Roberts Fund will support 5–6 TPDAs every year. As with other funds that become restricted for TPDA in an endowment vehicle, the annual James L. Roberts Fund contribution will be matched by SfN Council, providing an additional 5–6 awards annually. As TPDAs currently represent the Society’s highest fundraising priority, Council is committed to supporting as many early career scientists as possible through this matching initiative.
TPDAs recognize undergraduate and graduate students and postdoctoral scholars who demonstrate scientific merit and excellence in research. The awards are highly competitive as recipients receive a travel stipend to offset the costs of attending Neuroscience 2024, as well as complimentary meeting registration and access to a variety of SfN professional development resources.
James L. Roberts was a 37-year member of SfN. He earned an undergraduate degree from Colorado State University, doctorate from University of Oregon, and fellowship from UC San Francisco. Roberts served on the faculty of Columbia University, Mt. Sinai School of Medicine, University of Texas, and Trinity University, where he retired as Cowles Distinguished Professor of Biology in 2018. He passed away in 2023 at age 72.
The Roberts bequest is the second large bequest to the Society in less than a year. It joins the John I. Simpson Fund and Nancy Rutledge Zahniser Fund as endowments set up in memory of longtime SfN members that support TPDA. SfN welcomes philanthropy from its membership and beyond to support a range of activities and initiatives to advance the neuroscience field. Those interested in advancing neuroscience through estate planning, bequests, or other charitable donations are encouraged to contact SfN’s development team at development@sfn.org or visit the SfN philanthropy webpage.
###
The Society for Neuroscience (SfN) is an organization of nearly 35,000 basic scientists and clinicians who study the brain and the nervous system.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-15
CLEVELAND—The evolution of resistance to diseases, from infectious illnesses to cancers, poses a formidable challenge.
Despite the expectation that resistance-conferring mutations would dwindle in the absence of treatment due to a reduced growth rate, preexisting resistance is pervasive across diseases that evolve—like cancer and pathogens—defying conventional wisdom.
In cancer, it is well known that small numbers of drug-resistant cells likely exist in tumors even before they’re treated. In something of a paradox, before treatment, these mutants have been repeatedly shown to have lower fitness than the surrounding ancestor cells from which they arose. It leads ...
2024-07-15
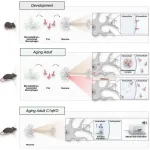
BOSTON, Mass. (July 15, 2024)—A groundbreaking study conducted at the lab of Beth Stevens, PhD, at Boston Children’s Hospital has revealed that an immune protein impacts neuronal protein synthesis in the aging brain. Previous work from the Stevens lab had uncovered that immune cells in the central nervous system, microglia, help prune synapses in the developing brain by tagging synapses with the immune protein C1q. New research led by Nicole Scott-Hewitt, published in Cell, shows that neurons can also internalize C1q. C1q seems to influence protein production inside neurons by interacting with ribosomal proteins, RNA-binding proteins, and ...
2024-07-15
A network of proteins found in the central nervous system could be harnessed to increase the effectiveness and reduce the side effects of popular diabetes and weight-loss drugs, according to new research from the University of Michigan.
The study, appearing today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, focused on two proteins called melanocortin 3 and melanocortin 4 found primarily on the surface of neurons in the brain that play a central role in regulating feeding behavior and maintaining the body's energy balance.
Melanocortin ...
2024-07-15
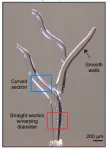
Advances in 3D printing have enabled many applications across a variety of disciplines, including medicine, manufacturing, and energy. A range of different materials can be used to print both simple foundations and fine details, allowing for the creation of structures with tailored geometries.
However, creating structures with micro-scale, precise internal voids and channels still poses challenges. Scaffolds used in tissue engineering, for example, must contain a three-dimensional complex network of conduits that mimic the human vasculature. With traditional additive manufacturing, where the material is deposited layer ...
2024-07-15
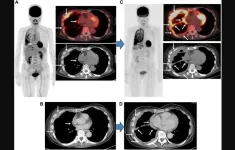
Philadelphia, July 15, 2024 – Building upon groundbreaking research demonstrating how the SARS-CoV-2 virus disrupts mitochondrial function in multiple organs, researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) demonstrated that mitochondrially-targeted antioxidants could reduce the effects of the virus while avoiding viral gene mutation resistance, a strategy that may be useful for treating other viruses. The preclinical findings were recently published in the journal Proceedings ...
2024-07-15
Climate change is causing the ice masses in Greenland and Antarctica to melt. Water from the polar regions is flowing into the world’s oceans –and especially into the equatorial region. “This means that a shift in mass is taking place, and this is affecting the Earth’s rotation,” explains Benedikt Soja, Professor of Space Geodesy at the Department of Civil, Environmental and Geomatic Engineering at ETH Zurich.
“It’s like when a figure skater does a pirouette, first holding her arms close to her body and then stretching ...
2024-07-15
“FDG-PET is generally considered as a useful metabolic evaluation tool, while it is also thought to have an emerging role for assessment of systemic therapy response.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 15, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 20, 2024, entitled, “Comparison of FDG-PET/CT and CT for evaluation of tumor response to nivolumab plus ipilimumab combination therapy and prognosis prediction in patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma.”
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive neoplasm and affected ...
2024-07-15
A new UBC study published recently in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS) has unveiled insights into how microscopic organisms such as marine plankton move through water with different density layers.
Researchers Gwynn Elfring and Vaseem Shaik found that density layers, created by variations in temperature or salinity, influence the swimming direction and speed of tiny particles navigating a liquid.
Pushers and pullers
“There are two different types of microscopic swimmers – ...
2024-07-15
UTICA, NY – The president of SUNY Polytechnic Institute (SUNY Poly), Dr. Winston “Wole” Soboyejo, and postdoctoral researcher, Dr. Tabiri Kwayie Asumadu, have published a revolutionary new paper titled, "Robust Macroscale Superlubricity on Carbon-Coated Metallic Surfaces." This paper explores an innovative approach to reducing friction on metallic surfaces – a significant advancement that could have major real-world impacts.
The study shows that superlubricity – a state with virtually no friction that was once believed to only be achievable at nanoscale – can now be maintained at macroscale for extended time ...
2024-07-15
HOUSTON - (July 15, 2024) - As parents, teachers and pet owners can attest, rewards play a huge role in shaping behaviors in humans and animals. Rewards – whether as edible treats, gifts, words of appreciation or praise, fame or monetary benefits – act as positive reinforcement for the associated behavior. While this correlation between reward and future choice has been used as a well-established paradigm in neuroscience research for well over a century, not much is known about the neural process underlying it, namely how the brain encodes, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] SfN establishes James L. Roberts Endowed Fund