(Press-News.org) Some of the UK’s most recognisable TV doctors are increasingly being “deepfaked” in videos to sell scam products across social media, finds The BMJ today.
Trusted names including Hilary Jones, Michael Mosley and Rangan Chatterjee are being used to promote products claiming to fix high blood pressure and diabetes, and to sell hemp gummies, explains journalist Chris Stokel-Walker.
Deepfaking is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to map a digital likeness of a real-life human being onto a video of a body that isn’t theirs. Reliable evidence on how convincing it is can be hard to come by, but one recent study suggests that up to half of all people shown deepfakes talking about scientific subjects cannot distinguish them from authentic videos.
John Cormack, a retired doctor based in Essex, worked with The BMJ to try and capture a sense of the scale of so-called deepfaked doctors across social media.
“The bottom line is, it's much cheaper to spend your cash on making videos than it is on doing research and coming up with new products and getting them to market in the conventional way,” he says.
The slew of questionable content on social media co-opting the likenesses of popular doctors and celebrities is an inevitable consequence of the AI revolution we’re currently living through, says Henry Ajder, an expert on deepfake technology. “The rapid democratisation of accessible AI tools for voice cloning and avatar generation has transformed the fraud and impersonation landscape.”
“There’s been a significant increase in this kind of activity,” says Jones, who employs a social media specialist to trawl the web for deepfake videos that misrepresent his views and tries to take them down. “Even if you do, they just pop up the next day under a different name.”
A spokesperson for Meta, the company that owns both Facebook and Instagram, on which many of the videos found by Cormack were hosted, told The BMJ: “We will be investigating the examples highlighted by the British Medical Journal. We don’t permit content that intentionally deceives or seeks to defraud others, and we’re constantly working to improve detection and enforcement. We encourage anyone who sees content that might violate our policies to report it so we can investigate and take action.”
Deepfakes work by preying on people’s emotions, writes Stokel-Walker, and when it comes to medical products, that emotional connection with the individual telling you about the wonder drug or magnificent medical product matters all the more.
Someone you don’t know trying to sell you on the virtues of a particular treatment may raise suspicions. But if they’re someone you’ve seen before on social media, television or radio, you’re more likely to believe what they’re saying.
Spotting deepfakes can be tricky too, says Ajder, as the technology has improved. “It’s difficult to quantify how effective this new form of deepfake fraud is, but the growing volume of videos now circulating would suggest bad actors are having some success.”
For those whose likenesses are being co-opted, there’s seemingly very little they can do about it, but Stokel-Walker offers some tips on what to do if you find a deepfake. For instance, take a careful look at the content to make sure your suspicions are well-founded then leave a comment, questioning its veracity. Use the platform’s built-in reporting tools to voice your concerns, and finally report the person who or account that shared the post.
[Ends]
END
Trusted TV doctors “deepfaked” to promote health scams on social media
The BMJ investigates the rise of videos claiming to be UK’s popular media medics
2024-07-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Singing the science: Using karaoke to examine blushing
2024-07-18
A new collaboration between researchers from the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, the University of Amsterdam and the University of Chieti explores the neural substrates of blushing in a MRI scanner.
Most of us know what it feels like to blush. The face becomes warm and red, and we experience self-conscious emotions, such as embarrassment, shyness, shame, and pride. It is perhaps no wonder that Charles Darwin referred to it as “the most peculiar and the most human of all expressions”. But why do we blush, and what ...
Data protection laws reduced breaches but affected firms’ value
2024-07-18
The introduction of new data protection rules significantly reduced breaches by firms but negatively impacted their market value, according to new research by the University of East Anglia (UEA) and University of Texas.
Researchers looked at what happened when the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) started being enforced in 2018. Using its extraterritorial reach, the authors explore variation in US firms’ exposure to the EU GDPR to see how stricter data privacy laws affected their value, ...
Landmark study shows elevated cancer risk for women with endometriosis
2024-07-17
A landmark study from researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (the U), the Spencer Fox Eccles School of Medicine at the U, and Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine found that women with severe endometriosis are 10 times more likely to get ovarian cancer, compared to women who do not have the disease.
Prior studies have shown a causal connection between endometriosis and ovarian cancer. But in using the Utah Population Database—a repository of linked health records housed at Huntsman ...
Lichtenberg earns GSA’s 2024 Donald P. Kent Award
2024-07-17
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) — the nation’s largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to the field of aging — has chosen Peter Lichtenberg, PhD, ABPP, FGSA, of Wayne State University as the 2024 recipient of the Donald P. Kent Award.
This distinguished honor is given annually to a GSA member who best exemplifies the highest standards for professional leadership in gerontology through teaching, service, and interpretation of gerontology to the larger society. It was established in 1973 in memory of Donald P. Kent, PhD, for his outstanding leadership in translating research findings ...
Does the type of workstation you use make a difference in your health and productivity?
2024-07-17
It might be an exaggeration to claim that “sitting is the new smoking,” but significant research indicates that people who are sedentary face more health challenges than their active counterparts.
Office workers who spend most of their eight-hour workdays seated, for example, more often experience symptoms such as daytime exhaustion, hypertension and musculoskeletal discomfort than those who are less sedentary. Although devices such as standing desks have been found to alleviate physical symptoms and increase worker productivity, questions remain regarding the best use of the primary types of workstations—stand-biased, ...
Why the most prescribed chemotherapy drug can cause serious heart damage
2024-07-17
There’s still much to learn about how doxorubicin, a 50-year-old chemotherapy drug, causes its most concerning side effects. While responsible for saving many lives, this treatment sometimes causes cardiac damage that stiffens the heart and puts a subset of patients at risk for future heart failure. To better understand and potentially control such complications, Tufts University School of Medicine and Tufts Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences researchers have isolated the immune cells that become overactive when patients take doxorubicin. The team’s findings appear July 17 in the journal Nature Cardiovascular Research.
Doxorubicin ...
Cohen-Mansfield earns GSA’s 2024 Robert W. Kleemeier Award
2024-07-17
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) — the nation’s largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to the field of aging — has chosen Jiska Cohen-Mansfield, PhD, FGSA, of Tel Aviv University as the 2024 recipient of the Robert W. Kleemeier Award.
This distinguished honor is given annually to a GSA member in recognition for outstanding research in the field of gerontology. It was established in 1965 in memory of Robert W. Kleemeier, PhD, a former president of the Society whose contributions to the quality of life through research in aging were exemplary.
The award presentation will take place at GSA’s ...
Barnes earns GSA’s 2024 James Jackson Outstanding Mentorship Award
2024-07-17
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) — the nation’s largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to the field of aging — has chosen Lisa L. Barnes, PhD, FGSA, of Rush University Medical Center as the 2024 recipient of the James Jackson Outstanding Mentorship Award.
This distinguished honor is given annually and recognizes individuals who have exemplified outstanding commitment and dedication to mentoring minority researchers in the field of aging. It was renamed in 2021 in memory of James Jackson, PhD, FGSA, a pioneering psychologist ...
Although tiny, peatland microorganisms have a big impact on climate
2024-07-17
The Science
Polyphenols are a diverse group of organic compounds produced by plants. These compounds are often toxic to microorganisms. In peatlands, scientists thought that microorganisms avoided this toxicity by degrading polyphenols using an enzyme that requires oxygen. However, when there is little or no oxygen, like after flooding due to climate induced thawing, the enzyme is inactive, and polyphenols accumulate. This inhibits microbes’ carbon cycling. In this study, scientists mined data for thousands of microbial genomes recovered from Stordalen Mire, an Arctic peatland in Sweden. They discovered that these microorganisms used alternative polyphenol-active ...
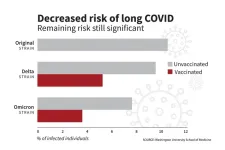
Risk of long COVID declined over course of pandemic
2024-07-17
The risk of developing long COVID has decreased significantly over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to an analysis of data led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Researchers attributed about 70% of the risk reduction to vaccination against COVID-19 and 30% to changes over time, including the SARS-CoV-2 virus’s evolving characteristics and improved detection and management of COVID-19.
The research is published July 17 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“The research on declining rates ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Trusted TV doctors “deepfaked” to promote health scams on social mediaThe BMJ investigates the rise of videos claiming to be UK’s popular media medics