(Press-News.org) Oil drops from underwater oil spills can break into tinier droplets at the surface that remain suspended in the water, according to research from the University of Illinois Chicago. That means cleanups after disasters like the Deepwater Horizon spill may be removing less oil from the environment than was thought.
Because oil is lighter than water, it rises through the ocean after spills, which are usually caused by leaking underwater pipelines or sometimes by natural processes. It was believed that when these oil drops reached the water’s surface, they simply turned into a flat film, forming an oil slick.
A UIC team led by Sushant Anand was the first to look more deeply into the mechanics of how oil goes from being a drop to a slick, and they discovered a different pattern. They found that when oil drops reach the water’s surface, they remain partially submerged for awhile. When the thin film of water that covers the exposed part of the drop breaks, that part of the drop spreads across the water surface into a film. But the part of the drop that was below the surface deforms, breaking off into a smaller “daughter” drop. The process repeats with that smaller droplet, over and over. The research is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
That means some oil from spills remains permanently underwater. This is a problem from an environmental standpoint because oil spill cleanups have focused on the slick that forms above the surface, said Anand, an associate professor in UIC’s College of Engineering and senior author on the paper.
“Unfortunately, underwater oil spills do routinely happen, so understanding the mechanics of oil dispersion is crucial for developing effective cleanup strategies,” Anand said. “Our discovery sheds light on a previously unknown pathway by which oil can spread pollution inside the ocean.” And the smaller an oil droplet is, the harder it is to clean up, he added.
The researchers found that increasing the viscosity of the water can help keep the oil drops intact so the entire drop goes into the oil slick above the surface, making cleanup easier. Perhaps a biodegradable, water-soluble compound could be added at the location of a spill to increase water viscosity and prevent the formation of daughter drops, Anand said.
This process of drops breaking apart isn’t limited to underwater spills in the ocean, he said. Pipelines run under lakes and rivers, too. And an oil spill from a ship has enough force to send the oil underwater before it rises to the surface and breaks up using the same mechanism as oil spills that originate underwater.
Anand said he hopes further research investigates how these tiny droplets impact underwater species. Oil companies, which use models to predict the size and spread of spills, should consider incorporating this information into their calculations, he added.
The other authors of the study, all in the UIC Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering and part of the Anand Research Group, are Varun Kulkarni, Venkata Yashasvi Lolla and Suhas Tamvada.
Written by Emily Stone
END
How pollution may remain in water after oil spill cleanups
2024-07-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
World’s first method: Successful surgery for a rare congenital heart disease “scimitar syndrome”
2024-07-18
Scimitar syndrome, a rare congenital heart disease, involves an anomalous pulmonary venous return where the right pulmonary veins return to the inferior vena cava instead of the left atrium. It is mainly diagnosed in infants, with an estimated prevalence of 1–3 per 100,000 births. Delayed treatment can lead to pulmonary hypertension, right heart failure, respiratory failure, heart arrhythmia, and growth disorders.
This syndrome is characterized by anomalous pulmonary venous drainage to the inferior vena cava, and the usual surgical repair involves re-implanting the right pulmonary veins (scimitar vein) to the left atrium or creating an intra-atrial tunnel to ...
Major computing society endorses efforts to make digital accessibility part of the Americans with Disabilities Act
2024-07-18
The Association for Computing Machinery’s US Technology Policy Committee (USTPC) has released a Statement in Support of Mandatory Comprehensive Digital Accessibility Regulations. The US Department of Justice recently updated the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), a civil rights law that prohibits discrimination based on disability, with requirements for the accessibility of web content and mobile applications. The aim of the revision to the ADA is to ensure that services, programs and activities provided by state and local governments online ...
When you eat may impact your overall health, nutrition experts say
2024-07-18
Philadelphia, July 18, 2024 – Accumulating evidence on the effect of the time of eating in relation to our circadian rhythm and metabolism shows that when we eat may influence our overall health and well-being. A special issue of the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (JAND) on chrononutrition, published by Elsevier, examines the effects of various fasting regimens and covers safety considerations and practical guidance.
The field of chrononutrition is gaining traction as it explores the relationship between temporal eating patterns, circadian rhythms, and metabolism for optimal health.
Guest Editor Krista Varady, PhD, Department of Kinesiology and Nutrition, ...
Researcher receives NASA funding to study ozone pollution
2024-07-18
NORMAN, OKLA. – University of Oklahoma professor Chenghao Wang has received three years of funding through the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Early Career Investigator Program in Earth Science. Wang, an assistant professor in both the OU School of Meteorology and the Department of Geography and Environmental Sustainability, will study compound heat and ozone pollution episodes in urban environments.
Heat waves and air pollution are two increasingly occurring challenges that disproportionately impact urban areas. When multiple stressor events happen simultaneously, these compound events can have more significant impacts than isolated events. ...
New ECDC Director Pamela Rendi-Wagner emphasises importance of restoring and reinforcing public trust in science after pandemic, in editorial for Eurosurveillance
2024-07-18
In an editorial for the scientific journal Eurosurveillance, the incoming ECDC Director Dr Pamela Rendi Wagner outlined her vision for the European Union’s public health agency, highlighting the mounting challenges to public health after the COVID-19 pandemic, including war in Europe, climate change, and increasing social inequalities. She also emphasised the importance of reinforcing and restoring public trust in science.
Current challenges in public health
“War, flooding and the effects of ...
In China, property rights take wrong turn
2024-07-18
In China, Property Rights Take Wrong Turn
Protecting them fueled an economic boom; eroding them risks long-term damage
AUSTIN, Texas — China’s economy, long an engine of world growth, has been sputtering lately. During the second quarter of 2024, it grew at an annual rate of 4.7% — down from an average 7% a year during the past decade. For the next two years, the International Monetary Fund forecasts more of the same.
Analysts have blamed China’s slowdown on short-term factors, such as debt-ridden real estate and a delayed recovery from the COVID-19 ...
Solar farms with stormwater controls mitigate runoff, erosion, study finds
2024-07-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — As the number of major utility-scale ground solar panel installations grows, concerns about their impacts on natural hydrologic processes also have grown. However, a new study by Penn State researchers suggests that excess runoff or increased erosion can be easily mitigated — if these “solar farms” are properly built.
Solar panels are impervious to water, and vast arrays of them, it was feared, could increase the volume and velocity of stormwater runoff similar ...
Drexel team identifies drug-like molecules that show early success in targeting breast cancer brain metastases
2024-07-18
Researchers from Drexel’s College of Medicine have identified new drugs that show early success in shrinking breast cancer tumors that have metastasized in the brain. The discovery marks the first time that targeting a key metabolic enzyme in cancer cells in the brain has shrunk tumors in a mouse model. The findings, which could develop into more effective therapies for breast cancer brain metastases, were recently published in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology.
Brain tumor growth depends on converting an energy source for the brain known as acetate, to acetyl-CoA — a molecule involved in biochemical reactions in carbohydrates, ...
Archivist explores Troy's invisible workers
2024-07-18
While poring over nearly century-old photos documenting the University of Cincinnati’s historic excavation at Troy, archivist Jeff Kramer was struck by just how many people worked behind the scenes for years to contribute to its success.
The archivist and research associate in UC’s Department of Classics created a digital archive of pictures and documents from UC archaeologist Carl Blegen’s influential 1930s project that identified nine periods of reconstruction and evidence of a great battle and fiery devastation that some historians said was suggestive of the ransacking of Troy.
But ...
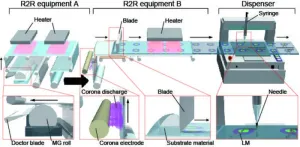
Stretchable electronics might make their way onto the market thanks to roll-to-roll process
2024-07-18
Electronics have evolved over the years to supersede simply enhancing day-to-day life to becoming almost seamlessly integrated with daily life. People have become accustomed to wearable electronics, but what about stretchable ones? There is a growing demand for this type of technology, but the current methods are not easily scalable for mass production to make these devices available to the public. However, mass development may be possible using the roll-to-roll (R2R) process, which prints various layers on a flexible rolled substrate, cutting out the manual nature of the process. By rolling this type of electronic out into the market, the possibility for stretchable electronics and even ...