(Press-News.org) Looking for a Medicare Advantage plan with a five-star quality rating? You’re less likely to find one available to you if you live in a county with higher poverty and unemployment, finds a new study published in JAMA Network Open.
These geographic disparities may be contributing to unequal health outcomes and limiting federal funds from reaching the regions most in need, according to the researchers.
“What this means is that Medicare beneficiaries living in counties with greater social disadvantage have fewer opportunities to choose highly rated Medicare Advantage plans that could be delivering high-quality care,” said Avni Gupta, a health policy researcher who recently earned her PhD in health policy and management from the NYU School of Global Public Health and is now at the Commonwealth Fund.
More than half of all Medicare beneficiaries—nearly 31 million people—enroll in Medicare Advantage plans, rather than choosing traditional Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans, also known as “Part C,” are offered by private health insurance companies that contract with Medicare and typically bundle hospital, outpatient, and prescription drug coverage.
To help consumers compare the quality of Medicare Advantage programs, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) uses a five-star rating system, calculating scores based on nearly 40 indicators.
“Star ratings are meant to capture the performance of Medicare Advantage plans in past years, with better ratings demonstrating higher quality care in areas such as chronic care management, screenings, vaccinations and other preventive services, timely appointments, care coordination, customer service, and handling appeals,” said Gupta, the study’s lead author.
In addition, the star ratings determine the bonuses and rebate payments that insurance companies receive from CMS; larger payments to higher-rated plans can translate into better supplemental benefits for beneficiaries.
With enrollment in Medical Advantage plans growing each year—and in particular, low-income Black and Hispanic adults enrolling at higher rates in recent years—Gupta and her colleagues sought to understand whether quality ratings vary based on where one lives.
Using 2023 Medicare Advantage star ratings—ranging from the highest ratings (4.5 or 5 stars) to lower ratings (less than 3.5 stars)—the researchers mapped the availability of plans in 3,075 US counties. They also looked at county-level characteristics using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Social Vulnerability Index, a calculation of 16 social determinants of health, including poverty, unemployment, education, disability, race and ethnicity, English language proficiency, housing, and access to transportation.
They found that Medicare Advantage plans in the most disadvantaged counties were less likely to be highly rated (4.5 stars or higher) and more likely to have low ratings (3.5 stars or less).
“Our findings imply that beneficiaries who might gain the most from supplemental benefits may only be able to choose from plans that are least likely to have the financial resources to provide these benefits, given that lower star ratings translate to lower bonuses and rebates to insurance plans,” added Gupta. “Such a pattern of star ratings and county-level social vulnerability could exacerbate inequities in health care access, experience, and outcomes.”
The researchers note that Medicare policies that account for area-level vulnerability in the star rating system or incentivize plans serving such areas could help promote equity.
In addition to Gupta, study authors include José Pagán and Diana Silver of the NYU School of Global Public Health, Sherry Glied of NYU’s Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service, and David Meyers of Brown University School of Public Health.
END
Top Medicare advantage plans less available in disadvantaged areas
Limited access to plans with high star ratings in vulnerable counties may exacerbate health disparities
2024-07-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Better carbon storage better carbon storage with stacked geology with stacked geology
2024-07-23
The overarching goal of all carbon capture and storage projects is the same: Keep carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions out of the atmosphere by storing them in the subsurface for good.
One way to do that is to inject the CO2 into a reservoir space that’s covered with a big lid – an impermeable caprock that can keep the gas in place and stop any upward flow in its tracks. That’s the model that petroleum exploration has relied on for decades when searching for oil traps, and it works for both oil and CO2. But according to research led by The University of Texas at Austin’s Bureau of Economic Geology, subsurface ...
Sharp temperature reduction for quantum dots in polymer by highly efficient heat dissipation pathways
2024-07-23
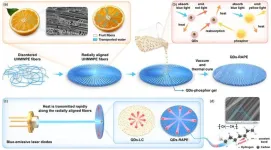
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240036 , discusses sharp temperature reduction for quantum dots in polymer by highly efficient heat dissipation pathways.
Quantum dots (QDs), a kind of luminescent nanocrystals featuring size-tunable emission spectra and superior color purity are widely applied in optoelectronic fields. However, these particles are facing luminous efficiency degradation due to their temperature-sensitive characteristic and the high temperature in optoelectronic ...
UAF researcher creates way to detect elusive volcanic vibrations
2024-07-23
A new automated system of monitoring and classifying persistent vibrations at active volcanoes can eliminate the hours of manual effort needed to document them.
Graduate student researcher Darren Tan at the University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute led development of the system, which is based on machine learning. Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence focused on building systems that learn from data, identify patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
Details about Tan’s automated ...
Lissajous pattern multi-pass cell: Enhancing high sensitivity and simultaneous dual-gas LITES sensing
2024-07-23
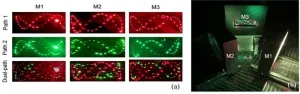
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.240013 , discusses highly sensitive and real-simultaneous CH4/C2H2 dual-gas LITES sensor based on Lissajous pattern multi-pass cell.
Trace gases are atmospheric constituents with a volume fraction of less than 1%. Despite their low concentrations, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, and sulfides in the atmosphere have a significant impact on the environment, closely related to phenomena such as acid rain, greenhouse effects, and ozone layer depletion. Therefore, race gas detection of is crucial for environmental ...
Asexual reproduction usually leads to a lack of genetic diversity. Not for these ants.
2024-07-23
Genetic diversity is essential to the survival of a species. It’s easy enough to maintain if a species reproduces sexually; an egg and a sperm combine genetic material from two creatures into one, forming a genomically robust offspring with two distinct versions of the species’ genome.
Without that combination of different genetic makeups, asexually reproducing species typically suffer from a lack of diversity that can doom them to a limited run on Earth. One such animal should be the clonal raider ant, which produces daughter after genetically identical daughter directly from an unfertilized ovum ...
Mini lungs make major COVID-19 discoveries possible
2024-07-23
Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys, University of California San Diego and their international collaborators have reported that more types of lung cells can be infected by SARS-CoV-2 than previously thought, including those without known viral receptors. The research team also reported for the first time that the lung is capable of independently mustering an inflammatory antiviral response without help from the immune system when exposed to SARS-CoV-2.
This work is especially timely, as cases of COVID-19 are on the rise in the scientists’ hometown of San Diego during a summertime spike. Looking beyond the region, more than half of the states in the country have reported “very ...
Exploratory analysis associates HIV drug abacavir with elevated cardiovascular disease risk in large global trial
2024-07-23
WHAT:
Current or previous use of the antiretroviral drug (ARV) abacavir was associated with an elevated risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in people with HIV, according to an exploratory analysis from a large international clinical trial primarily funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). There was no elevated MACE risk for the other antiretroviral drugs included in the analysis. The findings will be presented at the 2024 International AIDS Conference (AIDS 2024) in Munich, Germany.
The Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in HIV (REPRIEVE) enrolled 7,769 study participants with HIV from 12 countries that found ...
Control of light–matter interactions in two-dimensional materials with nanoparticle-on-mirror structures
2024-07-23
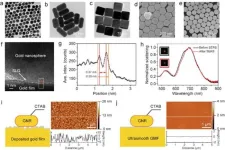
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.230051 , discusses control of light–matter interactions in two-dimensional materials with nanoparticle-on-mirror structures.
With the rapid development of high bit-rate wireless services driven by mobile internet, AI computing, high-definition videos, virtual reality/augmented reality (VAR) applications, and so on, the demand for wireless data rates has grown explosively in the past decades1, 2. Supporting such fast data rate at tens of Gbit/s pushes the carrier frequency to the THz (0.1-10 THz) ...
Does the onset of daylight saving time lead to an unhealthy lifestyle?
2024-07-23
Researchers from North Carolina State University, University of Manitoba, Bern University of Applied Sciences, University of South Carolina, and California Baptist University published a new Journal of Marketing study that explores whether the onset of daylight saving time leads consumers to engage in unhealthy behaviors.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Spring Forward = Fall Back? The Effect of Daylight Saving Time Change on Consumers’ Unhealthy Behavior” and is authored by Ramkumar Janakiraman, Harsha ...
Best Paper awards lack transparency and do not increase equitability
2024-07-23
Research awards are an integral part of the universal “prestige economy” in science, but do they incentivize greater transparency, inclusivity, and openness? This study uses cross-disciplinary data to explore the level of transparency of publicly available award descriptions and assessment criteria, asking whether such awards contribute to or propagate existing reproducibility crises and inequities in science.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002715
Article ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Top Medicare advantage plans less available in disadvantaged areasLimited access to plans with high star ratings in vulnerable counties may exacerbate health disparities