Intelligent compaction: ensuring highway durability with advanced monitoring
2024-07-24
(Press-News.org)
Highway construction often faces challenges in ensuring long-term subgrade performance due to traditional compaction quality control (QC) methods that rely on manual adjustments and sporadic testing. These methods are susceptible to human error, inefficiency, and incomplete assessments. Addressing these issues requires advanced, real-time monitoring systems. Such systems can provide comprehensive and accurate QC, highlighting the need for innovative technologies to improve highway construction standards.
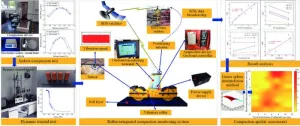
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology Beijing, alongside partners from Hunan and China Renewable Energy Engineering Institute, have published a study (DOI: 10.26599/JIC.2024.9180024) in the Journal of Intelligent Construction on June 20, 2024. The study explores using roller-integrated compaction monitoring (RICM) technology combined with real-time kinematic-Beidou navigation satellite system (RTK-BDS) to enhance compaction quality assessment in highway subgrades. Tested on the Hengyong Highway Project, this innovative approach offers new insights into improving highway construction standards.
The study utilized RICM technology to monitor compaction meter value (CMV) and compaction power per unit volume (E) as real-time indexes for assessing highway subgrade compaction quality. The Hengyong Highway Project case study demonstrated CMV's reliability as a compaction quality indicator, showing a strong correlation with compactness. Integrating RTK-BDS enabled precise real-time monitoring, providing a comprehensive evaluation of the construction area. The Green spline interpolation method further enhanced rapid assessment capability, ensuring swift and uninterrupted evaluations. The results highlighted CMV's superior data stability and lower dispersion compared to other methods, ensuring consistent and high-quality compaction. This innovative approach significantly improves QC in highway construction, preventing defects and enhancing overall highway durability and performance.
A.P. Qinglong Zhang from the University of Science and Technology Beijing stated, "The adoption of RICM technology in combination with RTK-BDS represents a significant advancement in highway construction. This method not only provides real-time, accurate data but also ensures a higher standard of compaction quality, ultimately leading to safer and more durable highways."
The proposed compaction quality assessment method has broad implications for the construction industry. By enabling real-time, comprehensive monitoring, it ensures higher construction quality standards and reduces the risk of defects. This approach can be adapted to various construction projects, enhancing overall infrastructure reliability and safety. The findings pave the way for further research and development in automated, real-time monitoring systems for construction quality control.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52209152), Excellent Youth Team Project for the Central Universities (No. FRF-EYIT-23-01), and Technology Development Project Entrusted by Enterprise and Institution (No. jtgh-jwh2021(008)).
About Journal of Intelligent Construction
Journal of Intelligent Construction (JIC), sponsored by Tsinghua University and the China National Committee on Large Dams, published by Tsinghua University Press (TUP) and exclusively available via SciOpen, is a peer-reviewed journal for publishing original research papers, case studies, reviews and comments regarding the use of novel technologies in all domains of civil engineering, e.g., hydraulic engineering, structural engineering, geotechnical engineering, transportation, and construction management. The journal focuses on the application of advanced theories, methodologies, and tools, such as machine learning, sensors, robotics, 5G, the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, building information modelling, and computational methods, etc., in all stages of the construction life cycle, which makes the process more intelligent and efficient. The journal also covers other essential areas of civil engineering, e.g., planning and design, operation and maintenance, and disaster mitigation.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is an open access resource of scientific and technical content published by Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, identity management, and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-24
Biological treatment methods such as anaerobic digestion, composting, and insect farming are essential for managing organic waste, converting it into valuable resources like biogas and organic fertilizers. However, these processes often face challenges due to their inherent complexity and instability, which can affect efficiency and product quality. Traditional control strategies have limited success in addressing these issues. Therefore, advanced methods like machine learning (ML) are being explored to enhance prediction, optimization, and monitoring of these biological treatments, aiming to improve overall performance and sustainability.
A research team from Tongji University ...
2024-07-24
Relays are extensively utilized in accelerators, satellites, rockets, and various advanced technology sectors. They play crucial roles in signal transmission, long-distance control implementation, and protection circuits, directly impacting the safety of aerospace and defense equipment systems. The selection of electrical contact material in a relay is crucial for its performance. Arc discharge, characterized by high temperature, heat, and energy, is a common occurrence during operation. Consequently, the arc erodes the electric contact material, ...
2024-07-24
Acetic acid, also known as acetate, and other products that can be developed from acetic acid are used in a variety of industries, from food production to medicine to agriculture. Currently, acetate production uses a significant amount of energy and results in harmful waste products. The efficient and sustainable production of acetate is an important target for researchers interested in improving industrial sustainability.
A paper published in Carbon Future on July 9 outlines a method using a polyaniline catalyst with cobalt oxide nanoparticles to produce acetate through carbon dioxide electroreduction.
“The polyaniline catalyst with cobalt ...
2024-07-24
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, today hosts Insilico Medicine Generative AI Action (IMGAIA) webinar. The webinar featured opening remarks by Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, Founder and CEO of Insilico Medicine. During the virtual event, Alex Aliper, PhD, co-founder and president of Insilico Medicine, announced the company’s sustainability initiative. Following this, the session on product launches and updates was delivered by key AI project ...
2024-07-24
KINGSTON, R.I. – July 22, 2024 – A team of researchers at the University of Rhode Island and Nova Southeastern University in Florida have been tracking a 26-foot endangered whale shark – named “Rio Lady” – with a satellite transmitter for more than four years – a record for whale sharks and one of the longest tracking endeavors for any species of shark.
Whale sharks, which live from 80 to 130 years, are the world’s largest fish and third largest creature in the ocean – behind blue and fin whales. The size of a small school bus, they inhabit tropical oceans and ...
2024-07-24
(WASHINGTON, July 24, 2024) – In patients with diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (DLBCL), the two hallmark post-chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T therapy toxicities are extremely rare after two weeks, supporting a shorter, more flexible toxicity monitoring period, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
Currently, three CAR T-cell therapies — axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel), tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel), and lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) — are approved for treating DLBCL, a cancer that affects the white blood cells responsible for producing antibodies. However, patients receiving these therapies are ...
2024-07-24
Information like forest canopy height can be useful in assessing the health of a forest, but current measuring methods are not always feasible for large geographic regions or adaptable to diverse forest types. Monitoring from space can be a solution.
Forests function as more than a place for a quiet retreat: trees intake and absorb carbon dioxide (a major greenhouse gas), a process also known as carbon sequestration, and are essential parts of water regulation, habitat provision, and support much of the world’s terrestrial biodiversity. Quantifying forest structure parameters, ...
2024-07-24
All around the world, scientists are striving towards next-generation energy technologies that can help us move away from fossil fuels. Using hydrogen as an energy carrier and clean energy source is perhaps one of the most promising solutions on the horizon. However, there is a major challenge to overcome before hydrogen economies become a reality: hydrogen gas is remarkably difficult to store and transport safely, which severely limits its applicability across many fields.
Against this backdrop, a research team from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan, and Tokyo University of Science, Japan has been working hard to reach an alternative solution to the hydrogen storage problem. Led by Associate ...
2024-07-24
Exercise is one of the best ways to reduce your risk of heart disease or having a second cardiovascular event, such as a heart attack or stroke.
As more people use wearable technology, such as smartwatches, health care researchers continue to explore whether it can successfully promote physical activity.
That includes customized messages designed to encourage individual patients to be more active in their current location, like walking outside when the weather is nice.
In such a study led by the University of Michigan ...
2024-07-24
DALLAS, July 24, 2024 — In this era of machine learning and artificial intelligence, harnessing large-scale neuroimaging can facilitate new discoveries in neuroscience research.[1]
To that end, the American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service in 2024, has awarded a two-year, $460,000 grant to a consortium of three academic medical centers to work collaboratively and share de-identified imaging data from individuals enrolled in its Get With The Guidelines® – Stroke registry.
A team at Yale University will ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Intelligent compaction: ensuring highway durability with advanced monitoring