(Press-News.org) About The Study: U.S. health care workers are more likely than other workers to carry medical and educational debt, collectively owing more than $150 billion. This study found that medical debt was more prevalent among women, home health and nursing home personnel, uninsured individuals, and those with recent hospitalization. Educational debts disproportionately burdened Black workers and younger workers and those with higher education.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kathryn E.W. Himmelstein, M.D., M.S.Ed., email khimmelstein@mgb.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.1917)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama-health-forum/fullarticle/10.1001/jamahealthforum.2024.1917?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=072624
About JAMA Health Forum: JAMA Health Forum is an international, peer-reviewed, online, open access journal that addresses health policy and strategies affecting medicine, health and health care. The journal publishes original research, evidence-based reports and opinion about national and global health policy; innovative approaches to health care delivery; and health care economics, access, quality, safety, equity and reform. Its distribution will be solely digital and all content will be freely available for anyone to read.
END
Medical and educational indebtedness among health care workers
JAMA Health Forum
2024-07-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US state restrictions and excess COVID-19 pandemic deaths
2024-07-26
About The Study: This cross-sectional study indicates that stringent COVID-19 restrictions, as a group, were associated with substantial decreases in pandemic mortality, with behavior changes plausibly serving as an important explanatory mechanism. These findings do not support the views that COVID-19 restrictions were ineffective. However, not all restrictions were equally effective; some, such as school closings, likely provided minimal benefit while imposing substantial cost.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Christopher J. Ruhm, Ph.D., email ruhm@virginia.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Posttraumatic stress disorder among adults in communities with mass violence incidents
2024-07-26
About The Study: In this survey study of 5,991 participants, presumptive posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) was quite prevalent long after the mass violence incident (MVI) among adults in communities that have experienced an MVI, suggesting that MVIs have persistent and pervasive public health impacts on communities, particularly among those with prior exposure to physical or sexual assault and other potentially traumatic events. Focusing exclusively on direct exposure to MVIs is not sufficient. Incorporating these findings into ...
New understanding of fly behavior has potential application in robotics, public safety
2024-07-26
RENO, Nevada — Why do flies buzz around in circles when the air is still? And why does it matter?
In a paper published online July 26, 2024 by the scientific journal Current Biology, University of Nevada, Reno Assistant Professor Floris van Breugel and Postdoctoral Researcher S. David Stupski respond to this up-until-now unanswered question. And that answer could hold a key to public safety — specifically, how to better train robotic systems to track chemical leaks.
“We don’t currently have robotic systems to track odor or chemical plumes,” van Breugel said. “We don’t know how to efficiently find the ...
Investigating the effect of alemtuzumab in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with inborn errors of immunity
2024-07-26
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) explore the safety and effectiveness of alemtuzumab in an Asian cohort
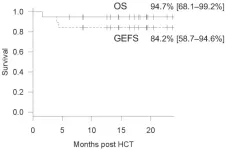
Tokyo, Japan – Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is a commonly used curative therapy for individuals with inborn errors of immunity (IEI). HCT involves introducing stem cells from a compatible donor with the aim of replacing the affected cells in the recipient’s body. Reduced-toxicity conditioning (RTC) is an approach for reducing drug-related toxicities post HCT in patients with IEIs. Alemtuzumab is a humanized anti-CD52 monoclonal antibody that strongly ...
Determining maximum allowable current of an RBS using a directed graph model and greedy algorithm
2024-07-26
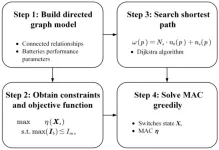
The central principle of the proposed MAC determination method is to connect the batteries within an RBS in parallel to the maximum possible extent, thereby maximizing the output current. To achieve this universally and automatically, the overall process is divided into the 4 steps shown in Fig. 1. First, a directed graph model is established for the subsequent computations. The nodes in the directed graph correspond to the connection points of components in the actual RBS. The edges in the directed graph correspond to the batteries, switches, and external electrical loads in the actual ...
Developed a 21-language, fast and high-fidelity neural text-to-speech technology that works on smartphones
2024-07-26
Highlights
-Developed a 21-language, fast and high-fidelity neural text-to-speech technology
-The developed model can synthesize one second of speech at high speed in only 0.1 seconds using a single CPU core, which is about eight times faster than the conventional methods
-The developed model can realize fast synthesis with a latency of 0.5 seconds on a smartphone without network connection
-The technology is expected to be introduced into speech applications, such as multilingual speech translation and car navigation
Abstract
The Universal Communication Research Institute of the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT, President: TOKUDA Hideyuki, ...
Supporting school re-entry of children with special health care needs post extended hospitalizations
2024-07-26
East Hanover, NJ – July 26, 2024 – Children with special health care needs (CSHCN) often face significant disruptions in their education due to extended hospitalizations. A recent study published online in Disability and Rehabilitation on July 1, 2024, by a multidisciplinary team of Kessler Foundation and Children Specialized Hospital researchers, highlights critical areas needing attention to ensure smoother school re-entries for CSHCN, ensuring they receive the necessary educational support post-hospitalization.
Involving parents, former patients, and rehabilitation ...
Have a seat, doctor: Study suggests eye-level connection makes a difference in hospitals
2024-07-26
Doctors and others who take care of hospitalized patients may want to sit down for this piece of news.
A new study suggests that getting at a patient’s eye level when talking with them about their diagnosis or care can really make a difference. Sitting or crouching at a hospitalized patient’s bedside was associated with more trust, satisfaction and even better clinical outcomes than standing, according to the new review of evidence.
The study’s authors, from the University of Michigan and VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System, note that most of the studies on this topic varied with their interventions and outcomes, and were found to have high risk of bias. Their ...
BRCA1/2: Why men should be screened for the ‘breast cancer gene’
2024-07-26
More and more studies show that men face risks of cancer from BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic mutations that are most often associated with breast and ovarian cancers in women.
According to a July 25 JAMA Oncology review article by experts at Fred Hutch Cancer Center and University of Washington, newly developed national screening guidelines offer hope for identifying the cancer risk of BRCA mutations in men through genetic testing and tailored cancer screening.
“Not enough men are getting genetic testing to see if they carry a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene ...
Researchers develop state-of-the-art device to make artificial intelligence more energy efficient
2024-07-26
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (07/25/2024) — Engineering researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities have demonstrated a state-of-the-art hardware device that could reduce energy consumption for artificial intelligent (AI) computing applications by a factor of at least 1,000.
The research is published in npj Unconventional Computing, a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature. The researchers have multiple patents on the technology used in the device.
With the growing demand of AI applications, researchers have been looking ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
[Press-News.org] Medical and educational indebtedness among health care workersJAMA Health Forum