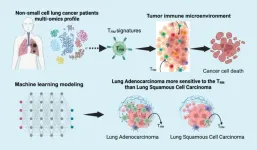
(Press-News.org) (LOS ANGELES, July 30, 2024) – An extensive analytical study performed at the Terasaki Institute and published in Frontiers in Immunology highlights the crucial role of tissue-resident memory T cells and how they influence the immune environment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and their overall prognosis.
Non-small cell lung cancer accounts for ~85% of lung tumors and is a leading cause of death in adults. Tissue-resident memory T cells, a specialized subset of immune cells residing in peripheral tissues, have been suspected of impacting cancer progression. However, it’s still not fully understood how tissue-resident memory T cells affect the tumor immune microenvironment and tumor progression in various non-small cell lung cancer patient populations.
In this comprehensive study, multiple independent datasets from lung cancer patient samples were analyzed. In addition, a machine learning model was developed and validated to predict patient survival, refining an 18-gene risk score that effectively categorizes lung cancer patients into low-risk and high-risk groups. In cancer research, the 18-gene risk score is used to predict disease progression or recurrence chances, which helps create personalized treatment plans. The scores are usually divided into low and high risk, with specific thresholds setting these categories. In this study, patients with high-risk scores exhibited significantly lower overall survival rates than their low-risk counterparts. Distinct Tissue Resident Memory T cell biomarkers were identified that correlate positively with other immune cells within the tumor environment. Moreover, these biomarkers were strongly associated with immune checkpoint and stimulatory genes, directly influencing patient prognosis.
"The study's findings highlight the critical impact of Tissue Resident Memory T cell abundance on immune responses and patient outcomes in lung cancer," said Dr. Xiling Shen, Chief Scientific Officer at Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation. "Our findings not only validate these cells as a prognostic marker but also underscore their potential in guiding personalized treatment strategies, particularly in immunotherapy."
This pioneering research, independently validated by the Cancer Genome Atlas Program and multiple lung cancer patient datasets, provides a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between Tissue Resident Memory T cells and the tumor. It represents a significant step towards advancing precision medicine in lung cancer treatment.
Authors: Aidan Shen, Aliesha Garrett, Cheng-Chi Chao , Dongliang Liu, Chao Cheng, Zhaohui Wang, Chen Qian, Yangzhi Zhu, Junhua Mai, Chongming Jiang
Grant Information: The author(s) declare financial support was received for the
research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is
supported by the National Institutes of Health, United States (NIH)
For more information, please visit Terasaki.org or Contact:
Stewart Han
Email: shan@terasaki.org
Chongming Jiang
Email: tom.jiang@terasaki.org
###
About Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation
The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation is a non-profit research organization dedicated to leveraging cutting-edge technology to address global health challenges. By fostering interdisciplinary collaborations and pushing the boundaries of innovation, TIBI aims to transform healthcare and improve lives worldwide.
END
Recent study reveals key immune cells as critical factors in lung cancer prognosis
T cell study offers new hope for personalized lung cancer treatment
2024-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Accuracy of diagnostic blood tests for Alzheimer’s disease varies
2024-07-30
Neurologists diagnose cognitive impairment with a clinical exam of memory and thinking skills. To determine whether Alzheimer’s disease is the cause of the cognitive impairment, evidence of the specific brain changes that characterize Alzheimer’s must be obtained, typically via a brain scan or spinal tap. Identifying people whose cognitive symptoms are due to Alzheimer’s disease is critical now that new Alzheimer’s therapies are available that could change the course of the illness.
To make diagnosis more convenient for patients, many companies have begun selling Alzheimer’s ...
Ze’ev Ronai steps down as cancer center director at Sanford Burnham Prebys
2024-07-30
Ze’ev Ronai, PhD, is stepping down as director of the National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center at Sanford Burnham Prebys, effective August 1. Cosimo Commisso, PhD, deputy director of the cancer center, will serve as interim head while a national search is conducted for a new cancer center director.
Ronai is moving to Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles where he will focus on translational research.
“During my 20 years at Sanford Burnham Prebys, I’ve had the honor of developing new research directions, institutionally, as well as in my lab,” said Ronai.
“As the director of the cancer ...
FSU researchers identify unique phenomenon in Kagome metal
2024-07-30
In traditional Japanese basket-weaving, the ancient “Kagome” design seen in many handcrafted creations is characterized by a symmetrical pattern of interlaced triangles with shared corners. In quantum physics, the Kagome name has been borrowed by scientists to describe a class of materials with an atomic structure closely resembling this distinctive lattice pattern.
Since the latest family of Kagome metals was discovered in 2019, physicists have been working to better understand their properties and potential applications. A new study led by Florida State University Assistant Professor of ...
Ochsner-Xavier Institute for Health Equity and Research publishes strategic plan
2024-07-30
NEW ORLEANS – The Ochsner-Xavier Institute for Health Equity and Research, or OXIHER, has published its first strategic plan, outlining strategic priorities and achievements since the institute began in 2020.
The strategic plan is available here.
A partnership between Ochsner Health and Xavier University of Louisiana, OXIHER examines health disparities at the community level while educating healthcare providers on creating and nurturing a culture of equity, and training more students for advanced careers in healthcare.
The new plan details OXIHER’s substantial progress in its first three years in addressing ...
Argonne receives U.S. Department of Energy funding for four next-generation clean-energy projects
2024-07-30
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has been awarded funding from DOE’s Office of Technology Transitions for four new projects that will help with commercialization of innovative clean-energy technology for a sustainable future.
Argonne scientists will work to turn their innovative ideas into next-generation technology necessary to build cleaner, more resilient energy systems. These projects build on Argonne’s decades-long role at the forefront of the quest to decarbonize ...
Researchers develop general framework for designing quantum sensors
2024-07-30
Researchers from North Carolina State University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have designed a protocol for harnessing the power of quantum sensors. The protocol could give sensor designers the ability to fine-tune quantum systems to sense signals of interest, creating sensors that are vastly more sensitive than traditional sensors.
“Quantum sensing shows promise for more powerful sensing capability that can approach the fundamental limit set by the law of quantum mechanics, but the challenge lies in being able to direct ...
UBC super-black wood can improve telescopes, optical devices and consumer goods
2024-07-30
Thanks to an accidental discovery, researchers at the University of British Columbia have created a new super-black material that absorbs almost all light, opening potential applications in fine jewelry, solar cells and precision optical devices.
Professor Philip Evans and PhD student Kenny Cheng were experimenting with high-energy plasma to make wood more water-repellent. However, when they applied the technique to the cut ends of wood cells, the surfaces turned extremely black.
Measurements by Texas A&M University’s ...
Repair kit for NASA’s NICER mission heading to space station
2024-07-30
NASA will deliver a patch kit for NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer), an X-ray telescope on the International Space Station, on the agency’s Northrop Grumman 21st commercial resupply mission. Astronauts will conduct a spacewalk to complete the repair.
Located near the space station’s starboard solar array, NICER was damaged in May 2023. The mission team delivered the patch kit to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in May 2024 so it could be prepped and packed for the upcoming resupply mission.
“It’s ...
Mucus-based bioink could be used to print and grow lung tissue
2024-07-30
Lung diseases kill millions of people around the world each year. Treatment options are limited, and animal models for studying these illnesses and experimental medications are inadequate. Now, researchers describe in ACS Applied Bio Materials their success in creating a mucus-based bioink for 3D printing lung tissue. This advance could one day help study and treat chronic lung conditions.
While some people with lung diseases receive transplants, donor organs remain in short supply. As an alternative, medications and other treatments can be used to manage symptoms, but no cure is available for disorders such as chronic obstructive ...
Who is more polarized about AI—the tech community or the general public?
2024-07-30
The tech community is more strongly divided in how they feel about artificial intelligence (AI) than the general public according to a study of Reddit discourse following the launch of ChatGPT.
Researchers from the University of Rochester led by Jiebo Luo, a professor of computer science and the Albert Arendt Hopeman Professor of Engineering, used ChatGPT and natural language processing techniques to analyze the themes and sentiments of 33,912 comments in 388 unique subreddits in the roughly six months following the generative AI tool’s launch in November 2022. The findings appear in Telematics and Informatics.
Reddit is an online social ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
[Press-News.org] Recent study reveals key immune cells as critical factors in lung cancer prognosisT cell study offers new hope for personalized lung cancer treatment