(Press-News.org) URBANA, Ill. -- Elephant conservation is a major priority in southern Africa, but habitat loss and urbanization mean the far-ranging pachyderms are increasingly restricted to protected areas like game reserves. The risk? Contained populations could become genetically isolated over time, making elephants more vulnerable to disease and environmental change.
A recent study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the University of Pretoria in South Africa demonstrates how African conservation managers could create and optimize elephant movement corridors across a seven-country region. The study offers a map showing landscape connections that would support elephants’ habitat needs and allow for more gene flow among populations.
“Other research groups have integrated genetic and spatial data before, but usually it’s done on a more local scale. Ours was the first to combine both types of data for southern African elephants across such a large geographic area,” said lead author Alida de Flamingh, who completed the study as part of her doctoral program in the Department of Animal Sciences, part of the College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences (ACES) at Illinois. She is now a postdoctoral researcher at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology.
Scale is meaningful because African elephants have very large home ranges — roaming up to 11,000 square kilometers, or more than 2.7 million acres — and they often travel long distances out of their way to avoid unsuitable habitat. Capturing that scale in a single analysis was no easy feat.
“This was a massive effort. We went out with our partners in the Conservation Ecology Research Unit at the University of Pretoria to collect non-invasive DNA samples from elephant dung across the whole range,” de Flamingh said. “CERU also contributed data from GPS trackers on 80 collared elephants across nearly 54,000 locations.”
GPS collar data shows how elephants move across the landscape but can’t indicate whether that movement leads to gene flow. Conversely, DNA data documents gene flow, but can’t show how elephants moved to make that happen. Integrating the two data sets required a landscape genetics approach.
“Landscape genetics adapts some ideas from electrical circuit theory to discuss how animals might move and achieve gene flow. Our approach looks at resistances or costs elephants encounter as they move along multiple pathways through the region, accounting for the possibility of losing or gaining individual paths,” said co-author Nathan Alexander, a postdoctoral researcher at the Illinois Natural History Survey. Alexander worked on the project during his doctoral program in the Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences in ACES.
Costs in this case included steep slopes, barren areas with little to no vegetation, densely populated human settlements, and areas far from water. The researchers combined these environmental challenges with DNA data to explain how elephants might navigate their habitat, identifying key routes to maintain gene flow across protected areas.
“We did not find a simple linear relationship where more suitable habitats are less costly. Instead, we found a pronounced nonlinear pattern where the least suitable habitats have the biggest impact on elephant movement or distribution across the landscape,” de Flamingh said. “Intermediate habitats aren't necessarily dictating their movements as much as these really, really unsuitable habitats. That’s positive, if you think about it. They're tolerant of intermediate habitats and can still move through them.”
What qualifies as a “really, really unsuitable” habitat? The researchers identified areas like the vegetation-free Makgadikgadi salt pans in Botswana, as well as densely populated human settlements. Providing connections for elephants that avoid these areas will also reduce human-elephant conflict, a distinct threat to elephants.
De Flamingh said the insights gained from this study can help governmental authorities and NGOs in southern Africa to develop robust conservation initiatives on the ground.
“Southern Africa has the largest number of elephants in all of Africa. So any conservation efforts there, especially those that avoid human-elephant conflict, would protect pretty large populations of elephants,” said senior author Al Roca, an animal sciences professor in ACES. “Our partners at CERU, as well as our funders — the International Fund for Animal Welfare and the African Elephant Conservation Fund of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service — are really critical in those efforts.”
The study, “Integrating habitat suitability modeling with gene flow improves delineation of landscape connections among African savanna elephants,” is published in Biodiversity and Conservation [DOI:10.1007/s10531-024-02910-0]. The paper is dedicated to the memory of co-author Rudi van Aarde, who was instrumental in launching the study as head of CERU, and who passed away while the research was ongoing.
Roca is also affiliated with the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology, the Illinois Natural History Survey, and the School of Information Sciences at Illinois.
END
Elephants on the move: Mapping connections across African landscapes
2024-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Youth mental health-related emergency room trips declined significantly after Illinois ended COVID-19 lockdown
2024-08-06
Social media’s rise to popularity between 2010 and 2020 has been strongly correlated with the nationwide freefall in youth mental health that characterized the 2010s. Lawmakers have put increasing pressure on the U.S. government to take social media regulation more seriously, with cases about platforms like Facebook, Instagram and X rising to the Supreme Court level.
But despite the ubiquity of social media, scientists at Northwestern Medicine and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that in Illinois, youth emergency room visits and hospitalizations for depression and anxiety decreased ...
How plants become bushy, or not
2024-08-06
or many plants, more branches means more fruit. But what causes a plant to grow branches? New research from the University of California, Davis shows how plants break down the hormone strigolactone, which suppresses branching, to become more “bushy.” Understanding how strigolactone is regulated could have big implications for many crop plants.
The study was published August 1 in Nature Communications.
“Being able to manipulate strigolactone could also have implications beyond plant architecture, including on a plant’s resilience to drought and pathogens,” said senior author Nitzan Shabek, an associate professor in the UC Davis Department of ...
Research spotlight: Identifying potential new protein targets for melanoma therapeutics
2024-08-06
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Some proteins, such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1), can stop the immune system from attacking cancer cells and, therefore, support the growth of cancer. Therapies targeting these proteins can be highly effective, but tumors can become resistant.
We applied a method to detect proteins on a single–cell level to uncover human carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) patterns in melanoma. We found that increased ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $5.2 million to top clinical investigators
2024-08-06
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $5.2 million to top clinical investigators
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named six new Damon Runyon Clinical Investigators. The recipients of this prestigious award are outstanding, early-career physician-scientists conducting patient-oriented cancer research at major research centers under the mentorship of the nation's leading scientists and clinicians.
The Clinical Investigator Award program was designed to increase the number of physicians capable of translating scientific discoveries into new treatments for cancer patients. Each Awardee will receive $600,000 over three years, ...
Good outcomes 10 years after surgery for ectopic bone in thoracic spine
2024-08-06
August 6, 2024 — Thoracic ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (TOPLL) is a rare condition associated with ectopic bone formation in the thoracic spine. A long-term follow-up study from Japan shows significant and lasting improvement in outcomes with posterior decompression and fixation surgery for patients with T-OPLL, reports The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Surgical treatment of T-OPLL is effective in improving neurological function, quality ...
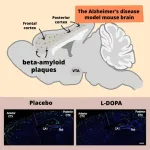
Dopamine treatment alleviates symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-08-06
A new way to combat Alzheimer’s disease has been discovered by Takaomi Saido and his team at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan. Using mice with the disease, the researchers found that treatment with dopamine could alleviate physical symptoms in the brain as well as improve memory. Published in the scientific journal Science Signaling on August 6, the study examines dopamine’s role in promoting the production of neprilysin, an enzyme that can break down the harmful plaques in the brain that are the ...
Do your supplements contain potentially hepatoxic botanicals?
2024-08-06
Millions of Americans consume supplements that contain potentially hepatoxic botanical ingredients, according to a study from University of Michigan researchers.
Over a 30-day period, 4.7% of the adults surveyed in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2017 to 2020 took herbal and dietary supplements containing at least one of the botanicals of interest: turmeric; green tea; ashwagandha; black cohosh; garcinia cambogia; and red yeast rice containing products.
The resulting paper, “Estimated Exposure ...
No room for nuance in polarized political climate: SFU study
2024-08-06
Sometimes you just can’t win, and that goes double for people navigating the increasingly polarized political landscape in the United States.
Having nuanced opinions of politics in the U.S. turns out to be a very lonely, and unpopular, road, according to a recent study from a research team that includes assistant professor Aviva Phillipp-Muller from Simon Fraser University’s Beedie School of Business.
Published in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, the study found that people who express ambivalence about political topics – ranging from COVID-19 mask mandates, immigration and the death ...
What happens to your brain when you drink with friends?
2024-08-06
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 6, 2024) – Grab a drink with friends at happy hour and you’re likely to feel chatty, friendly and upbeat. But grab a drink alone and you may experience feelings of depression. Researchers think they now know why this happens.
“Social settings influence how individuals react to alcohol, yet there is no mechanistic study on how and why this occurs,” said Kyung-An Han, Ph.D., a biologist at The University of Texas at El Paso who uses fruit flies to study alcoholism.
Now, Han and a team of UTEP faculty and students have taken a key step in understanding the neurobiological process behind social drinking and how it boosts ...
University of Houston researchers create new treatment and vaccine for flu and various coronaviruses
2024-08-06
A team of researchers, led by the University of Houston, has discovered two new ways of preventing and treating respiratory viruses. In back-to-back papers in Nature Communications, the team - from the lab of Navin Varadarajan, M.D. Anderson Professor of William A. Brookshire Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering - reports the development and validation of NanoSTING, a nasal spray, as a broad-spectrum immune activator for controlling infection against multiple respiratory viruses; and the development of NanoSTING-SN, a pan-coronavirus nasal vaccine, that can protect against infection and disease by all members of the coronavirus family.
NanoSTING ...