(Press-News.org) Forests absorb carbon by capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, making forest carbon stocks an important resource against climate change. In research published in Ecology and Evolution, investigators examined existing tree regeneration patterns to develop an indicator of potential changes to future carbon stocks across forests in the northeastern and midwestern United States.
The scientists’ comparison of carbon stock predictions from tree and seedling composition suggested that 29% of plots were poised to lose carbon based on seedling composition, 55% were poised for replacement of carbon stocks, and 16% were poised to gain carbon. Forests predicted to lose carbon tended to be on steeper slopes, at lower latitudes, and in rolling upland environments.
The findings may help managers identify areas that are most vulnerable to losing carbon storage capacity so that they can prioritize these areas when developing strategies to increase tree regeneration and secure resilient forest carbon stocks.
“It is important to take tree seedlings into account when we are thinking about long-term forest carbon storage because tree seedlings shape the future of our forests,” said corresponding author Lucas B. Harris, PhD, of the University of Vermont. “We hope that our work generates discussion about how to manage tree regeneration to promote resilient and carbon-rich forests in the context of threats such as climate change and invasive species.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ece3.70077
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
Ecology and Evolution is a broad open access journal welcoming all research in ecology, evolution, and conservation science. We are an author-friendly journal, providing a forum for evidence-based views. This means we aim to review all submissions, and look for reasons to publish, not reject. We welcome submissions across taxa, and consider a range of formats, including original research articles, reviews, hypotheses and Registered Reports. We also offer novel categories of papers with Nature Notes and Academic Practice in Ecology and Evolution.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
How well will different US forests remove atmospheric carbon in the future?
2024-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Medical issues experienced by women and children after returning from Hamas captivity
2024-08-07
Among the 250 individuals who were kidnapped during the Hamas terror attack on Israeli towns in October 2023, 19 children and 7 women were released and admitted to Schneider Children's Medical Center of Israel after approximately 50 days in captivity, during a cease-fire deal. A new study published in Acta Paediatrica reports on the physical and psychological state of these returnees upon their return.
The most common clinical findings included significant weight loss, psychological trauma, complications of poor hygiene (such as head lice), and complications of recent shrapnel injuries. Tests revealed that returnees also often had ...
Do dieticians have weight biases towards themselves and others?
2024-08-07
In a survey-based study, UK dietitians exhibited significant weight stigma, both towards themselves and towards others.
The study in the Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics involved an online survey completed in 2022 by 402 registered dietitians aged 20–70 years old. Most respondents reported personally experiencing weight stigma prior to (51%) and after becoming (59.7%) registered dieticians, and nearly a quarter (21.1%) felt that their weight influenced their own ability to perform as a dietitian.
Weight stigma was experienced across the weight spectrum. Participants reported explicit (or conscious) weight bias attitudes, moderate beliefs that obesity is ...
Can nanomaterials enhance plant tolerance to high soil salt levels?
2024-08-07
Soil salt concentrations above the optimal threshold for plant growth can threaten global food security by compromising agricultural productivity and crop quality. An analysis published in Physiologia Plantarum examined the potential of nanomaterials—which have emerged over the past decade as a promising tool to mitigate such “salinity stress”—to address this challenge.
Nanomaterials, which are tiny natural or synthetic materials, can modulate a plant’s response to salinity stress ...
Study on planet-warming contrails “a spanner in the works” for aviation industry
2024-08-07
Modern commercial aircraft flying at high altitudes create longer-lived planet-warming contrails than older aircraft, a new study has found.
The result means that although modern planes emit less carbon than older aircraft, they may be contributing more to climate change through contrails.
Led by scientists at Imperial College London, the study highlights the immense challenges the aviation industry faces to reduce its impact on the climate. The new study also found that private jets produce more contrails than previously thought, ...
Sea lion camera crews help researchers explore previously unmapped ocean habitats
2024-08-07
The world’s seabeds are little explored, and the knowledge we have is patchy. Using remotely operated underwater vehicles to learn about seabeds is expensive, requires certain weather conditions, and is difficult in deep, remote, and offshore habitats.
To circumvent these challenges, researchers in Australia have now enlisted endangered Australian sea lions (Neophoca cinerea) to carry cameras. The resulting videos allowed the researchers to identify previously unmapped benthic habitats used by the sea lions on the continental shelf. They published their results in Frontiers in Marine Science.
“Using ...
Superbugs spread to family members of recently hospitalized patients
2024-08-07
ARLINGTON, Va. (August 7, 2024) — Family members of patients recently discharged from the hospital may have a higher risk of getting an antibiotic-resistant infection, often called a superbug, even if the patient was not diagnosed with the same infection, suggesting hospitals play a role in the community spread of resistant bacteria, according to study in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
When recently hospitalized patients were diagnosed with the superbug — Methicillin-resistant ...
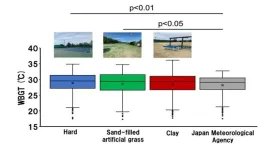
Preventing heat stroke in tennis: insights into the heat environments of tennis courts
2024-08-07
With rising global temperatures due to global warming, the risk of heat strokes has increased and is expected to grow even further. This is particularly troubling for athletes participating in competitive sports. In tennis, multiple matches are played daily, lasting up to five hours. Playing such matches in sweltering conditions could be highly detrimental.
The Tokyo Olympic Games in 2021 faced extremely hot conditions with many players calling for appropriate countermeasures. Consequently, the International Tennis Federation (ITF) formulated and issued the “Extreme Weather Policy” at the Tokyo Olympics to manage matches based ...
Dozing at the wheel? Not with these fatigue-detecting earbuds
2024-08-07
Everyone gets sleepy at work from time to time, especially after a big lunch. But for people whose jobs involve driving or working with heavy machinery, drowsiness can be extremely dangerous — if not outright deadly. Drowsy driving contributes to hundreds of fatal vehicle accidents in the U.S. each year, and the National Safety Council has cited drowsiness as a critical hazard in construction and mining.
To help protect drivers and machine operators from the dangers of drifting off, engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have created prototype earbuds that can detect the signs of drowsiness ...
FDA approves new therapy for glioma patients for first time in decades
2024-08-07
Boston – Vorasidenib has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for patients with Grade 2 gliomas with IDH1 or IDH2 mutations.
Based on evidence from the INDIGO clinical trial, a global phase 3, double-blinded, randomized clinical trial, vorasidenib more than doubled progression-free survival and delayed the need for treatment with radiation and chemotherapy for patients with Grade 2 IDH-mutant glioma after surgery to remove the tumor. INDIGO was the first phase 3 clinical trial of a molecularly targeted therapy for IDH-mutant glioma.
“The INDIGO trial ...
Think about banning kitchen worktop favourite to ward off incurable lung disease, urge doctors
2024-08-07
It may now be time to ban artificial stone—a firm favourite for kitchen worktops in the UK— to ward off the incurable lung disease caused by its manufacturing and fitting, say a team of doctors in the journal Thorax after treating the first 8 cases of artificial stone silicosis reported in the UK.
Silicosis is caused by breathing in crystalline silica dust, and millions of people around the world are at risk of developing it as a result of their jobs in mining, quarrying, stone-cutting ...