(Press-News.org) An activity pattern in certain genes responsible for building proteins known as spleen tyrosine kinases can predict which melanoma patients are likely to have severe side effects from immunotherapy designed to treat the most deadly skin cancer, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, the latest experiments focused on checkpoint inhibitors, drugs that have in the last decade become a mainstay of treating melanoma. This form of skin cancer kills nearly 10,000 Americans annually.
The drugs work by blocking molecules (checkpoints) that sit on the surface of immune T cells and stop them from attacking cancer cells like they would invading viruses or bacteria. While the immune system normally uses checkpoints to recognize and protect healthy cells, cancer cells are able to hijack and turn off immune cell surveillance, evading detection. Immunotherapy drugs like nivolumab and ipilimumab are designed to block checkpoints, making cancer cells more “visible” again to T cells.
However, more than a third of melanoma patients given checkpoint inhibitors develop side effects so severe that they compromise their quality of life and ability to continue therapy. Side effects most often involve some form of inflammation, a sign of an overactive immune response. Patients can experience severe skin rashes, diarrhea, or hyperthyroidism. More severe side effects can include liver toxicity, colitis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
In the new study, publishing in the journal Clinical Cancer Research online Aug. 8, researchers found that even before treatment began in their test subjects, the activity of genes controlling the production of spleen tyrosine kinases predicted 83 percent of melanoma patients who eventually developed severe side effects from combined immunotherapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab.
Moreover, the researchers found that this heightened gene signature, as evidenced by the production of spleen tyrosine kinases, or the SYK pathway, did not interfere with the effectiveness of therapies in preventing recurrence of melanoma. The impact was connected only to side effects.
“Our study results show that increased gene activity in the spleen tyrosine kinase pathway could be the basis of a possible blood test that identifies melanoma patients most susceptible to having severe side effects from immunotherapy, and well before they start treatment,” said study co-lead investigator Kelsey Monson, PhD.
“Predictive information of this kind is critically important to oncologists and patients to help guide their immunotherapy decisions, to either minimize these side effects by taking additional precautions or choose alternative immunotherapies,” said study co-senior investigator Tomas Kirchhoff, PhD. Kirchhoff is an associate professor in the Department of Population Health at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and a member of Perlmutter Cancer Center.
For the study, researchers analyzed immune system cell samples from 212 men and women with melanoma participating in a national multicenter trial called CheckMate-915. The trial was designed to test whether combined therapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab worked better than single therapy with nivolumab in preventing postsurgical recurrence of melanoma. All immune cell samples were taken prior to the start of immunotherapy. Both drugs are manufactured by the pharmaceutical company Bristol Myers Squibb, which sponsored the CheckMate-915 trial, and provided the patient specimens and data used in the analysis.
When researchers looked at what genes were more active than others in patients who experienced side effects from their immunotherapy, they found a specific pattern among 24 genes tied to the production of spleen tyrosine kinases. Further statistical analyses showed that increased or decreased activity (transcription) of only five of these genes — CD22, PAG1, CD33, HNRNPU, and FCGR2C — along with age and stage severity of their melanoma served as the best predictors of who would experience immunotherapy side effects.
Study co-senior investigator Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD, says that the SYK pathway has previously been linked to other autoimmune diseases, including lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and colitis, disorders marked by immune system attack on healthy cells. He also points out that immunotherapy side effects were also most common in areas affected by these autoimmune diseases, including the skin, colon, and liver.
Weber, the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Professor of Oncology in the Department of Medicine at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, says the team next plans to investigate if an activated SYK pathway is predictive of side effects in patients treated with ipilimumab alone or with other combination immunotherapies. Weber also serves as deputy director of NYU Langone’s Perlmutter Cancer Center.
“If our future research can explain how an activated spleen tyrosine kinase pathway leads to increased risk of side effects from immunotherapy, then it could also potentially help us to design better cancer immunotherapies and potentially other treatments for autoimmune diseases,” said Kirchhoff.
Funding for the study was provided by National Institutes of Health grants P50CA225450, F99CA274650, and R01CA227505, with additional support from Melanoma Research Alliance grant MRA-686192.
Weber owns equity in Altor BioScience, Biond Biologics, and CytomX Therapeutics. He has also received honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Genentech, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, GlaxoSmithKline, Eisai, Altor BioScience, Amgen, Roche, Ichor Medical Systems, Celldex Therapeutics, CytomX Theraputics, Nektar, Novartis, SELLAS, WindMIL Therapeutics, and Takeda. Weber has been a paid consultant or advisor to Celldex, Ichor Medical Systems, Biond Biologics, Altor BioScience, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Genentech, Roche, Amgen, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Daiichi Sankyo, AbbVie, Eisai, CytomX Therapeutics, Nektar, Novartis, SELLAS, WindMIL Therapeutics, and Takeda. He has also received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Daiichi Sankyo, Roche, Celldex Therapeutics, Amgen, Merck, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Novartis, WindMIIL Therapeutics, and Takeda. All of these arrangements are being managed in accordance with the policies and practices of NYU Langone Health.
Besides Kirchhoff and Weber, other NYU Langone researchers involved in this study are co-lead investigator Robert Ferguson, and co-investigators Joanna Handzlik, Jiahan Xiong, Sasha Dagayev, Leah Morales, Vylyny Chat, Anabelle Bunis, Chaitra Sreenivasaiah, Yongzhao Shao, and Iman Osman. Other study co-investigators are Sonia Dolfi and Daniel Tenney at Bristol Myers Squibb in Princeton, NJ.
END
Distinct pattern in protein production can predict severe side effects from skin cancer treatment
2024-08-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lens-free fluorescence instrument detects deadly microorganisms in drinking water
2024-08-08
WASHINGTON — Researchers have shown that a fluorescence detection system that doesn’t contain any lenses can provide highly sensitive detection of deadly microorganisms in drinking water. With further development, the new approach could provide a low-cost and easy-to-use way to monitor water quality in resource-limited settings such as developing countries or areas affected by disasters. It could also be useful when water safety results are needed quickly, such as for swimming events, a concern highlighted during the Paris Olympics.
“In developing countries, unsafe water sources ...
Individualized cancer therapy demonstrates safety and sustained immune responses
2024-08-08
For decades, researchers have worked to develop therapies that can prime the immune system to recognize and attack proteins on the surface of tumor cells. However, success has been limited due to the technological challenge of engineering therapies that provide specific enough “training” to the immune system to identify a given patient’s neoantigens. Now, investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, have evaluated an ...
Eating disorder risks elevated among women with PCOS
2024-08-08
WASHINGTON—Women with the common reproductive and metabolic condition polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) face a greater risk of developing bulimia, binge eating disorder and disordered eating, according to new research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
PCOS affects roughly one in eight women. Women who have the condition face an increased risk of developing metabolic problems such as diabetes, reproductive issues such as infertility, and psychological issues including anxiety and depression.
Women are diagnosed when they have at least two of the three ...
The first universal principles for designing solid-state batteries developed by Korean researchers
2024-08-08
A Korean research team has presented the first universal design principles for solid-state batteries, signaling a paradigm shift in battery design research that previously lacked standard benchmarks.
Dr. Jinsoo Kim from the Ulsan Advanced Energy Technology R&D Center of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) and Professor Sung-Kyun Jung's research team from the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) have jointly developed a design principles and a versatile design toolkit for implementing high-energy-density solid-state batteries and have completed performance verification.
With ...
Alcohol use in older adults doubles risk of brain bleeds from falls
2024-08-08
Nationally, falls remain the leading cause of both fatal and non-fatal injuries in older adults and are the leading cause of traumatic brain injury. In 2021, falls led to the deaths of 36,500 older adults in the United States and 3,805 older Floridians. While some studies have hypothesized that alcohol use contributed to these outcomes, there are few studies which have examined this issue.
As such, little is known about the association between the frequency of alcohol use and the severity of injuries sustained after a fall in older adults. A study by Florida Atlantic University’s Schmidt College of Medicine and collaborators, is one of the first to examine the relationship ...
Insilico Medicine received IND approval and orphan drug designation from FDA for ISM6331, an AI-designed TEAD inhibitor targeting solid tumors and mesothelioma
2024-08-08
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., Aug 8, 2024 --- Insilico Medicine ("Insilico"), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven biotechnology company, today announced ISM6331, potential best-in-class pan-TEAD inhibitor, has received the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Investigational New Drug (IND) clearance for the treatment of mesothelioma, following the grant of Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) in June 2024. It brings the total number of IND-approved molecules of Insilico to nine.
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the mesothelium, a thin layer of tissue that covers most of the ...
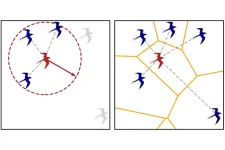
Are birds flying atoms?
2024-08-08
A crowd or a flock of birds have different characteristics from those of atoms in a material, but when it comes to collective movement, the differences matter less than we might think. We can try to predict the behavior of humans, birds, or cells based on the same principles we use for particles. This is the finding of a new study published in the Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, JSTAT, conducted by an international team that includes the collaboration of MIT in Boston and CNRS in France. The study, based on the physics ...
New study is helping to understand and achieve species elements in the Kunming–Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework
2024-08-08
Experts provide clarity on key terms for urgent species recovery actions to support the implementation of the Global Biodiversity Framework.
The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) is a landmark agreement ratified in 2022 by Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity that outlines ambitious goals to combat biodiversity decline.
The Framework states outcomes for species to be achieved by 2050 in Goal A and establishes a range of targets to reduce pressures on biodiversity and halt biodiversity loss ...
Unlocking the secrets of salt stress tolerance in wild tomatoes
2024-08-08
As our climate changes and soil salinity increases in many agricultural areas, finding crops that can thrive in these challenging conditions is crucial. Cultivated tomatoes, while delicious, often struggle in salty soils. Their wild cousins, however, have evolved to survive in diverse and often harsh environments. A recent study delved into the genetic treasure trove of wild tomatoes to uncover secrets of salt tolerance that could be used to develop resilient crop varieties.
A team of researchers focused on Solanum pimpinellifolium, the closest wild relative of our beloved cultivated tomato. These tiny, ...
Detecting climate change using aerosols
2024-08-08
Climate change is one of the most significant environmental challenges of present times, leading to extreme weather events, including droughts, forest fires, and floods. The primary driver for climate change is the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere due to human activities, which trap heat and raise Earth’s temperature. Aerosols (such as particulate matter, PM2.5) not only affect public health but also influence the Earth's climate by absorbing and scattering sunlight and altering cloud properties. Although future climate change predictions are being reported, it is possible that the impacts of climate change could be more severe than predicted. ...