(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, Mass., Aug 8, 2024 --- Insilico Medicine ("Insilico"), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven biotechnology company, today announced ISM6331, potential best-in-class pan-TEAD inhibitor, has received the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Investigational New Drug (IND) clearance for the treatment of mesothelioma, following the grant of Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) in June 2024. It brings the total number of IND-approved molecules of Insilico to nine.
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the mesothelium, a thin layer of tissue that covers most of the internal organs, primarily caused by exposure to asbestos. As an aggressive and fatal disease, Mesothelioma tends to spread along surfaces, nerves, and blood vessels inside the body, the median survival of the disease after diagnosis is only 9 to 12 months. Traditional treatments, including surgery and radiotherapy, often fail to provide long-term benefits, highlighting the urgent need for innovative treatment options.
"We are thrilled to receive the FDA's ODD designation and approval to initiate clinical evaluation of ISM6331." says Sujata Rao, MD, Chief Medical Officer of Insilico Medicine. "The preclinical development of ISM6331 not only demonstrates the AI-driven approach to innovative drug discovery and development, but also showcases the best-in-class capabilities of Insilico's R&D team. We will move forward with patient enrollment in the US as soon as possible and look forward to advancing ISM6331 for patients in high unmet medical needs with mesothelioma and other Hippo pathway related tumors."
ISM6331 is a potent non-covalent small molecule inhibitor with a novel scaffold targeting the transcriptional enhanced associate domain (TEAD) protein family, which are considered to be key regulators of the Hippo pathway, and play an important role in tumor progression, metastasis, cancer metabolism, immunity and drug resistance.
The development of ISM6331 was significantly accelerated by AI, where Chemistry42, Insilico’s generative chemistry engine, yielded 3 promising hit series in the first round of compound generation. After that, Chemistry42 provided additional information about affinity and novelty scores, assisting researchers in the molecular optimization leading to the ISM6331.
In preclinical studies, ISM6331 shows broad anti-tumor effect in multiple cell lines and potent efficacy at low doses in animal models, as well as a high safety margin and favorable ADMET profiles. The promising data further motivated Insilico to nominate ISM6331 as a preclinical candidate for the program in June 2023. Insilico is committed to advancing the clinical translation of the program and accelerating the delivery of to meet unmet medical needs.
"About 10% of cancer patients are affected by abnormalities in the Hippo signaling pathway. By effectively targeting the TEAD family, ISM6331 provides a strategic approach. The potential applications are vast, including the promising enhancement of chemotherapy efficacy, bolstering tumor immunity, improving small molecule targeting, and overcoming current drug resistance challenges", says Feng Ren, Ph.D., Co-CEO and Chief Scientific Officer of Insilico Medicine. "We remain committed to harnessing the power of AI to push the boundaries of medical science, offering new hope and potential therapies for patients with rare and challenging conditions."
Previously, ISM6331 was granted Orphan Drug Designation by the FDA for the treatment of mesothelioma. The designation would qualify ISM6331 for certain benefits and incentives, including seven years of marketing exclusivity following the regulatory approval of the designated indication, potential tax credits for certain activities, eligibility for orphan drug grants, and the waiver of certain administrative fees. The FDA's Orphan Drug Designation program supports the development and evaluation of drugs that address rare diseases which affect fewer than 200,000 people in the United States.
In 2016, Insilico first described the concept of using generative AI for the design of novel molecules in a peer-reviewed journal, which laid the foundation for the commercially available Pharma.AI platform. Since then, Insilico keeps integrating technical breakthroughs into Pharma.AI platform, which is currently a generative AI-powered solution spanning across biology, chemistry and clinical development. Powered by Pharma.AI, Insilico has nominated 18 preclinical candidates in its comprehensive portfolio of over 30 assets since 2021 and has received IND approval for 9 molecules.
During the recent Insilico Medicine Generative AI Action (IMGAIA) webinar, updates on the Pharma.AI platform were presented, highlighting its latest features, including Biology42: PandaOmics Box hardware for confidential computing, Precious-3 GPT for virtual data generation and biomedical research, and Science42: DORA for drafting scientific documents. These enhancements underline Insilico’s commitment to pioneering breakthroughs responsibly and sustainably. Those who are interested in trial versions of the abovementioned platforms are encouraged to contact BD@insilicomedicine.com.
About Insilico Medicine
Insilico Medicine, a global clinical stage biotechnology company powered by generative AI, is connecting biology, chemistry and clinical trials analysis using next-generation AI systems. The company has developed AI platforms that utilize deep generative models, reinforcement learning, transformers and other modern machine learning techniques for novel target discovery and the generation of novel molecular structures with desired properties. Insilico Medicine is developing breakthrough solutions to discover and develop innovative drugs for cancer, fibrosis, immunity, central nervous system diseases, infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, and aging-related diseases.
www.insilico.com
END
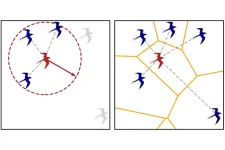
A crowd or a flock of birds have different characteristics from those of atoms in a material, but when it comes to collective movement, the differences matter less than we might think. We can try to predict the behavior of humans, birds, or cells based on the same principles we use for particles. This is the finding of a new study published in the Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, JSTAT, conducted by an international team that includes the collaboration of MIT in Boston and CNRS in France. The study, based on the physics ...
Experts provide clarity on key terms for urgent species recovery actions to support the implementation of the Global Biodiversity Framework.
The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) is a landmark agreement ratified in 2022 by Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity that outlines ambitious goals to combat biodiversity decline.
The Framework states outcomes for species to be achieved by 2050 in Goal A and establishes a range of targets to reduce pressures on biodiversity and halt biodiversity loss ...
As our climate changes and soil salinity increases in many agricultural areas, finding crops that can thrive in these challenging conditions is crucial. Cultivated tomatoes, while delicious, often struggle in salty soils. Their wild cousins, however, have evolved to survive in diverse and often harsh environments. A recent study delved into the genetic treasure trove of wild tomatoes to uncover secrets of salt tolerance that could be used to develop resilient crop varieties.
A team of researchers focused on Solanum pimpinellifolium, the closest wild relative of our beloved cultivated tomato. These tiny, ...
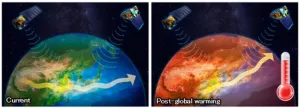
Climate change is one of the most significant environmental challenges of present times, leading to extreme weather events, including droughts, forest fires, and floods. The primary driver for climate change is the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere due to human activities, which trap heat and raise Earth’s temperature. Aerosols (such as particulate matter, PM2.5) not only affect public health but also influence the Earth's climate by absorbing and scattering sunlight and altering cloud properties. Although future climate change predictions are being reported, it is possible that the impacts of climate change could be more severe than predicted. ...
According to the attention-based view, a firm’s actions and growth performance are directly influenced by its attentional allocation to specific issues. The consequences of organizational attention are reflected in the firm’s strategic decision-making and adaptability. However, existing literature is limited in its exploration of how a firm’s attentional uniqueness impacts its behavior and performance. Notably, attentional uniqueness refers to how the firm’s attentional allocation diverges from competitors in the same industry.
To address the above-mentioned knowledge gap, Associate Professor Takumi ...
The deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA, the molecular system that carries the genetic information of living organisms, can transcribe and amplify information using its two helical strands. Creating such artificial molecular systems that match or surpass DNA in functionality is of great interest to scientists. Double-helical foldamers are one such molecular system.
Helical foldamers are a class of artificial molecules that fold into well-defined helical structures like helices found in proteins and nucleic acids. They have garnered considerable attention as stimuli-responsive switchable molecules, tuneable chiral materials, and cooperative supramolecular systems due to their chiral and ...
A saliva test can more accurately indicate the severity of recurrent respiratory infections in children than the standard blood test. If saliva contains too few broadly protective antibodies, a child is more likely to suffer from pneumonia episodes. This is reported by researchers from Radboudumc Amalia Children's Hospital and UMC Utrecht Wilhelmina Children's Hospital in the European Respiratory Journal. Saliva testing provides valuable information for treatment and is more comfortable for children.
About ...
Research Highlights:
Researchers found repeated one-minute bursts of high-intensity interval training were more effective than traditional, moderate continuous exercise for improving the body’s aerobic fitness after a stroke.
Fitness level improvements doubled in participants in the high-intensity interval training group compared to those in the moderate intensity exercise group.
Researchers found the level of fitness changes in the high intensity interval training group were associated with improved survival and lower risk of stroke-related ...
Pathological abnormalities associated with motor neurone disease have been identified using a new technique developed at the University of Birmingham.
The method will help scientists better understand the changes in the brain that lead to motor neurone disease (MND) and could eventually yield insights that will help with the development of new treatments. The abnormalities were identified in a collaboration between the University of Birmingham and the University of Sheffield and published today [8 Aug] in Nature Communications.
Motor neurone disease, also known ...
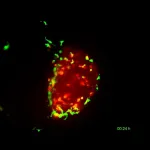
Using zebrafish “Avatars”, an animal model developed by the Cancer Development and Innate Immune Evasion lab at the Champalimaud Foundation (CF), led by Rita Fior, Mayra Martínez-López – a former PhD student at the lab now working at the Universidad de las Américas in Quito, Ecuador – and colleagues studied the initial steps of the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine’s action on bladder cancer cells. Their results, which are published today (August 1, 2024) in the journal Disease Models and Mechanisms, show that macrophages – the first line of ...