(Press-News.org) Researchers have uncovered a surprising way bacteria defend themselves: when a bacterium is infected, bacterial enzymes that copy genetic information from RNA into DNA synthesize genes whose protein products help shut down cell growth. This prevents further viral spread in the neighboring bacterial population. The results highlight the potential for other “hidden” genes, like the one found here, to be unearthed in different biological contexts. Bacteria defend themselves from viral infection using diverse immune systems, some of which target and degrade foreign DNA, while others, including defense-associated reverse transcriptase (DRT) systems, take advantage of DNA synthesis. But how the latter approach leads to antiviral defense – including through DNA products produced – remains largely unknown. Focusing on a DRT system from the bacteria K. pneumoniae, Stephen Tang and colleagues discovered that when K. pneumoniae cells were infected with a phage, the DRT2 reverse transcriptases used RNA templates to synthesize a new gene, which the authors dubbed “neo.” Using mass spectrometry, the authors detected Neo peptides in phage-infected cells. The peptides’ presence halted cell growth and restricted viral spread, they say. “It is the Neo protein, we propose,” say the authors, “that acts as the effector arm of the immune system by rapidly arresting cell growth and inducing programmed dormancy, thus protecting the larger bacterial population from the spread of phage.”
END
Surprise: infected bacteria fight back with “hidden” genes that halt cell growth, slow viral spread
2024-08-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Early prenatal exposure to famine increases Type 2 diabetes risk in adulthood, shows study of historical Ukraine event
2024-08-08
Prenatal exposure to famine significantly increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in adulthood, according to a new study of people impacted by the 1932-1933 Holodomor famine in Ukraine. While the immediate and short-term effects of famines on mortality and morbidity are well-documented, deciphering famines’ long-term health consequences – as this study did – has been more difficult. Previous research has suggested a link between prenatal nutrition and adult health ...
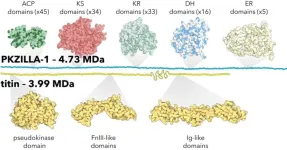
Marine algae use massive enzymes of unprecedented size to biosynthesize fish-killing toxins
2024-08-08
Marine algae Prymnesium parvum use massive enzymes dubbed PKZILLAs – some of the largest proteins ever to be identified in nature – to make large and complex prymnesin neurotoxins responsible for mass fish kills during harmful algal blooms worldwide, researchers report. “The discovery and initial characterization of the prymnesin PKZILLA gigasynthases now elucidates the long-standing question about how microalgae biosynthesize their giant polyketide polyether molecules,” write the authors. It also expands ...
Record-breaking 1.2-kilometer drill core unveils new insights into Earth's mantle
2024-08-08
A record-breaking 1268-meter drill core into Earth’s mantle, collected from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge in the North Atlantic, has provided a deep and detailed mineralogical glimpse of the oceanic mantle. The findings reveal new insights into mantle composition, Earth’s deep geology, and the potential biogeochemical conditions involved in the origins of life. Understanding the Earth’s mantle is crucial for comprehending important details of the Earth system, including terrestrial magmatism, crust formation, and the cycling ...
American College of Cardiology issues guide for managing in-patient heart failure
2024-08-08
The American College of Cardiology has issued updated guidance on managing patients hospitalized for heart failure (HF) to provide a decision-making pathway that tailors therapy to clinical trajectory to better manage disease. The updated Expert Consensus Decision Pathway incorporates the latest evidence to provide guidance for clinicians to use at the point of care in conjunction with the 2022 ACC/AHA Heart Failure Guideline.
Heart failure refers to several conditions that can affect the way the heart works, its structure or both. Over time, heart failure makes ...
Type 2 diabetes cases more than doubled seven decades after exposure to famine
2024-08-08
Researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and at the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine used the setting of the man-made Ukrainian Holodomor famine of 1932-1933 to examine the relation between prenatal famine and adult Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). They studied 128,225 Type 2 diabetes cases diagnosed between 2000-2008 among 10,186,016 male and female Ukrainians born between 1930 and 1938.
Individuals who were exposed in early gestation to the famine had a more than two-fold likelihood of developing Type 2 diabetes compared to those ...
Millions of years for plants to recover from global warming
2024-08-08
In brief:
Disruption of the functioning of vegetation due to warming can lead to the failure of climate regulating mechanisms for millions of years.
Vegetation changes can alter the planet’s climate equilibrium.
Geological and climatic history provide insight into the effects of global warming today.
Scientists often seek answers to humanity’s most pressing challenges in nature. When it comes to global warming, geological history offers a unique, long-term perspective. Earth’s geological ...
The long-lasting impact of war on global diabetes prevalence
2024-08-08
[Vienna, August 7 2024] — The ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine has led to severe humanitarian crises, including widespread food shortages. According to the United Nations World Food Programme, an estimated 11 million Ukrainians—about one-third of the population—were at risk of hunger in 2023. This crisis, exacerbated by supply chain disruptions and extreme weather events, could increase diabetes prevalence not only in Ukraine but globally, argue Peter Klimek and Stefan Thurner from the Complexity Science Hub in a commentary published in the journal Science.
Malnutrition during early pregnancy is known to elevate diabetes ...
Potential new approach to enhancing stem-cell transplants
2024-08-08
August 8, 2024—(BRONX NY)—A discovery by a three-member Albert Einstein College of Medicine research team may boost the effectiveness of stem-cell transplants, commonly used for patients with cancer, blood disorders, or autoimmune diseases caused by defective stem cells, which produce all the body’s different blood cells. The findings, made in mice, were published today in the journal Science.
“Our research has the potential to improve the success of stem-cell transplants and expand their use,” explained Ulrich Steidl, ...
Largest protein yet discovered builds algal toxins
2024-08-08
While seeking to unravel how marine algae create their chemically complex toxins, scientists at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography have discovered the largest protein yet identified in biology. Uncovering the biological machinery the algae evolved to make its intricate toxin also revealed previously unknown strategies for assembling chemicals, which could unlock the development of new medicines and materials.
Researchers found the protein, which they named PKZILLA-1, while studying how a type of algae called Prymnesium parvum makes its toxin, which is responsible for massive fish kills.
“This is the Mount Everest of proteins,” ...
Researchers show nanovoids improve material performance
2024-08-08
Voids or pores have usually been viewed as fatal flaws that severely degrade a material's mechanical performance and should be eliminated in manufacturing.
However, a research team led by Prof. JIN Haijun from the Institute of Metal Research (IMR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed that the presence of voids is not always hazardous. Instead, voids can be beneficial if they are added "properly" to the material.
The team demonstrated that a metal with a large number of nanoscale voids shows improved ...