(Press-News.org) As the Paris Olympics captured the world’s attention this month, it proved apparent that winning medals often hinged on the success of teamwork.
While such an approach clearly works in sports, new research suggests teamwork is not always the desired method … especially for young scientists trying to find an academic job.
“We found that if your team size in your discipline is large, your prospects for an academic career go down,” said Donna Ginther, the Roy A. Roberts Distinguished Professor of Economics at the University of Kansas.
Her paper titled “The rise of teamwork and career prospects in academic science” reveals individuals who finish their doctorate in situations where the average team in their field is larger have worse career options. The results demonstrate that academic science has not adjusted its reward structure (which is largely individual) in response to team science. It appears in Nature Biotechnology.
“The number of authors on papers in our discipline has changed,” she said. “In econ, when I graduated, there were single-author papers. Now it’s often three to five -- so it’s essentially doubled. In science fields in particular, it’s grown a lot. And when the National Institutes of Health budget doubled, papers increased by about one author.”
Co-written with Mabel Andalón, Catherine de Fontenay and Kwanghui Lim of the University of Melbourne, this research combined data on career outcomes from the Survey of Doctorate Recipients with publication data that measured research size from ISI Web of Science. It also incorporated a regression on career outcomes at the individual level to control for any changes in the characteristics of young scientists (such as whether the scientists obtained their doctorate from a top-ranked school).
“The questions we asked were if the average team size gets larger, what does it affect? Then how does it affect your career?” Ginther said.
“My co-author Catherine de Fontenay and Kwanghui Lim developed a theoretical model where if you have large teams, it’s unclear who contributed what to the paper. That makes the signal of your scientific ability noisy. But if there are just two authors, it’s pretty clear you both did a lot of work. Then the signal of your contribution is clear.”
As a result, it’s hard to discern and give individuals credit for their contribution … and that affects their next job and whether they get research funding.
“All of the phenomena we’re seeing about the length of time it takes from the time you get your Ph.D., until you get your first academic job, until you get your first R01 -- that can be explained by this growth in team size,” she said.
Ginther recently spent six months on sabbatical in Australia, which led to a research partnership with her University of Melbourne colleagues.
“I have a whole body of work on early career scientists,” she said. “For this paper, I really liked the model we used and the intuition behind the result. The world is big and complex, and teams are an important part of it. You can’t be this kind of solitary intellectual. Teamwork is something you must be able to navigate.”
Now in her 22nd year at KU, Ginther specializes in labor economics. She is also the director of the Institute for Policy & Social Research, an interdisciplinary campus center for faculty and students doing funded work in the social and behavioral sciences.
The economist believes her findings can be applied to other professions beyond academia.
“I’d be very curious to look at the military because you always operate in teams. How does the size of your team or the composition of your team affect your career?” she said.
Ultimately, Ginther emphasizes the key takeaway of this latest research is how money is correlated with team size.
“To the extent we can make more groups of scientists that are smaller, this could lead to a policy change that is supported by our work,” she said. “Having more smaller teams may be better than mega teams, both in terms of scientific discovery and career outcomes.”
END
Larger teams in academic research worsen career prospects, study finds
2024-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Newly discovered ability of comammox bacteria could help reduce nitrous oxide emissions in agriculture
2024-08-14
An international research team led by the Centre for Microbiology and Environmental Systems Science (CeMESS) at the University of Vienna has discovered that comammox bacteria, first identified by them in 2015, can grow using guanidine, a nitrogen-rich organic compound, as their sole energy and nitrogen source. This unique ability opens new avenues for targeted cultivation of these enigmatic microbes and could also provide a key to reducing agricultural nitrous oxide emissions. The research findings were recently published as an article in the prestigious journal Nature.
Nitrification, the conversion of ammonia via nitrite to nitrate, is ...
Cybersecurity flaws could derail high-profile cycling races
2024-08-14
High-end bicycles used for high-profile road races such as the Tour de France are vulnerable to cybersecurity attacks targeting the bike’s wireless gear shifting system.
In recent years, bicycle manufacturers have adopted wireless gear-shifting technology, which gives riders better control over changing gears. The technology is not vulnerable to the physical issues that plague mechanical systems. However, the way the wireless systems were built created critical cybersecurity vulnerabilities, which a team of computer scientists from the University of California ...
How bread dough gave rise to civilization
2024-08-14
A major international study has explained how bread wheat helped to transform the ancient world on its path to becoming the iconic crop that today sustains a global population of eight billion.
“Our findings shed new light on an iconic event in our civilisation that created a new kind of agriculture and allowed humans to settle down and form societies,” said Professor Brande Wulff, a wheat researcher at KAUST (King Abdullah University of Science and Technology) and one of the lead ...
Revealing the mysteries within microbial genomes
2024-08-14
A new technique developed at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) will make it much easier for researchers to discover the traits or activities encoded by genes of unknown function in microbes, a key step toward understanding the roles and impact of individual species.
The approach, called barcoded overexpression bacterial shotgun library sequencing, or Boba-seq, is described in a paper published August 5 in Nature Communications.
“There is so much genetic dark matter – ...
Consumer-grade insecticide sprays fail to control cockroaches, study shows
2024-08-14
Annapolis, MD; August 14, 2024—A common variety of consumer insecticide sprays is mostly ineffective and of "little to no value" in eliminating cockroach infestations, a new study shows.
Residual insecticides are designed to be sprayed on surfaces where cockroaches are likely to appear, exposing them to the toxic ingredient when they move across the surface later. But laboratory testing by researchers at the University of Kentucky and Auburn University shows that the residues have little effect on German cockroaches (Blattella germanica), ...
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers find possible inaccuracies in crash-reported child passenger injuries
2024-08-14
Philadelphia, August 14, 2024 – Researchers from the Center for Injury Research and Prevention (CIRP) at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) found discrepancies between crash reports and hospital data that might paint an incomplete or inaccurate picture of how crashes impact the safety of child passengers. Enhancing the quality of injury data reported in crash reports can aid researchers in assessing the effectiveness of various transportation safety strategies for children. The findings were recently published by ...
Ontario Institute for Cancer Research announces awards for eight research teams developing innovative ways to diagnose and treat cancer
2024-08-14
August 14, 2024, TORONTO — A new round of awards from the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR) will jumpstart eight promising studies that could change how cancers are diagnosed and treated.
OICR announced the results of its Pre-Clinical Acceleration Team Awards — part of the Institute’s Clinical Translational Pathway, which helps advance new discoveries so they can benefit people affected by cancer.
The winning research teams are based across Ontario and are tackling some of the most common and hardest to treat cancers. They are developing solutions to find cancer earlier, diagnose it more ...
People with COPD, asthma have higher risk of health problems from increased wildfire activity, smoke
2024-08-14
MIAMI (August 14, 2024) – Communities impacted by increased wildfire activity and smoke can use a population health-based action plan to help alleviate health risks, particularly for those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, according to a new perspective article. The article is published in the July 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, ...
Early life exposure to common chemical permanently disrupts gut microbiome
2024-08-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Early life exposure to ‘forever chemicals’ in the environment permanently disrupts the gut microbiome in mice, contributing to the development of metabolic disease in later life, according to new research led by Penn State. The results, published today (Aug. 14) in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, suggest that human exposure to these chemicals during early childhood may be contributing to the recent epidemic of metabolic disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes among adults.
The researchers focused specifically on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran ...
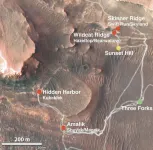
Rocks collected on Mars hold key to water and perhaps life on the planet. Bring them back to Earth.
2024-08-14
Over the course of nearly five months in 2022, NASA's Perseverance rover collected rock samples from Mars that could rewrite the history of water on the Red Planet and even contain evidence for past life on Mars.
But the information they contain can't be extracted without more detailed analysis on Earth, which requires a new mission to the planet to retrieve the samples and bring them back. Scientists hope to have the samples on Earth by 2033, though NASA's sample return mission may be delayed.
"These samples are the reason why our mission was flown," said paper ...