(Press-News.org)
Esophageal cancer, a highly aggressive malignancy originating in the esophageal epithelium, poses significant public health challenges in China, where it ranks sixth in incidence and fifth in mortality among cancers. The country's large population contributes to over half of the global cases and deaths from esophageal cancer. This cancer's poor prognosis is often due to late diagnosis, as early-stage esophageal cancer is typically asymptomatic, leading to diagnoses at more advanced stages. The geographical distribution of high-risk areas in China, such as the southern side of the Taihang Mountains, the Dabie Mountains, and northern Sichuan, underscores the need for focused screening efforts. Since 2005, China's national public health initiatives have emphasized endoscopic screening in over 110 high-risk areas, yielding significant outcomes, although the overall decline in incidence and mortality rates remains gradual.
Goals of Screening for Esophageal Cancer
The primary goal of esophageal cancer screening is early detection, particularly of early-stage cancer or esophageal intraepithelial neoplasia. Early identification facilitates timely intervention and treatment, significantly improving patient survival rates and quality of life. Research indicates that early diagnosis can increase the five-year survival rate to over 95%, demonstrating the critical importance of screening. Screening programs have been shown to reduce the incidence and mortality rates of upper gastrointestinal cancers significantly, underscoring the potential benefits of early detection.
Risk Factors and Screening Target Population
In China, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the predominant type of esophageal cancer, with several risk factors contributing to its incidence. These include smoking, alcohol consumption, consumption of hot or red foods, poor oral hygiene, and insufficient intake of fresh fruits and vegetables. Additional factors such as family history, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, gastric mucosal atrophy, and a history of head and neck SCC further increase the risk. Although esophageal adenocarcinoma is less common in China, it is associated with risk factors like smoking, obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and Barrett's esophagus. Given these risk factors and China's demographic profile, screening is recommended for individuals aged forty and above, particularly those in high-incidence areas or with specific high-risk characteristics.
Current Status of Screening Methods
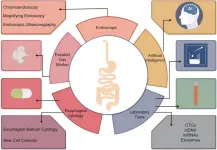
Current screening methods for esophageal cancer in China include endoscopy, exfoliative cytology, and biomarker detection. Traditional endoscopic techniques, such as white-light endoscopy, have been the mainstay of screening. However, advanced technologies like chromoendoscopy, magnifying endoscopy, and endoscopic ultrasound are gaining traction. These techniques offer enhanced visualization of mucosal surfaces and can improve the accuracy of early cancer detection. Despite their advantages, these methods are not widely adopted at the grassroots level due to high costs and technical complexities.
Emerging Technologies and Future Directions
Innovations in esophageal cancer screening include artificial intelligence-assisted methods, which enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis. The use of artificial intelligence in analyzing cytological samples collected by advanced esophageal cell collectors represents a significant improvement over traditional methods. Additionally, new endoscopic technologies, such as magnetic capsule endoscopy and confocal laser microscopy, are being explored for their potential to improve patient comfort and screening accuracy. However, these technologies are currently limited by high costs and a lack of comprehensive prospective studies.
Conclusions
Esophageal cancer remains a major public health concern in China, necessitating effective screening strategies. The continuous development and implementation of advanced screening technologies are crucial for improving early detection rates and patient outcomes. With ongoing advancements and reduced research and development costs, these new technologies are expected to become more widely accessible, providing more efficient and convenient screening options for esophageal cancer in China.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2835-3315/CSP-2024-00012
The study was recently published in the Cancer Screening and Prevention.
Cancer Screening and Prevention (CSP) publishes high-quality research and review articles related to cancer screening and prevention. It aims to provide a platform for studies that develop innovative and creative strategies and precise models for screening, early detection, and prevention of various cancers. Studies on the integration of precision cancer prevention multiomics where cancer screening, early detection and prevention regimens can precisely reflect the risk of cancer from dissected genomic and environmental parameters are particularly welcome.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
Nakkash & Griffin Engaging Virginia Youth & Community In Designing LGBTQ+ Inclusive Vaping Prevention Interventions
Rima Nakkash, Professor, Global and Community Health, College of Public Health, and Kenneth Griffin, Professor, Global and Community Health, College of Public Health, received funding for the project: “Engaging Virginia youth and community in designing LGBTQ+ Inclusive Vaping Prevention Interventions.”
The researchers are developing evidence-based vaping prevention interventions tailored for LGBTQ+ youth in Virginia, informed by input from youth and stakeholders in this community.
Nakkash and Griffin ...
Cuellar Examining Negotiated Rates For Behavioral Health & Primary Care Providers
Alison Cuellar, Associate Dean of Research, College of Public Health; Professor, Health Administration and Policy, received funding for the project: “Examining Negotiated Rates for Behavioral Health and Primary Care Providers.” The goal of the study is to inform future Medicaid policy by examining differences in how much payers reimburse for medical services in Virginia.
Cuellar is a Co-Investigator on the project with ...
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening and routine supplementation for iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia in pregnant persons to prevent adverse maternal and infant health outcomes. Iron deficiency is the leading cause of anemia during pregnancy. According to survey data from 1999 to 2006, overall estimated prevalence of iron deficiency during pregnancy is near 18% and increases across the three trimesters of pregnancy. An estimated 5% of pregnant ...
Serous effusion, defined as the excessive accumulation of fluid in body cavities such as the pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal spaces, is a critical diagnostic challenge in pathology. Cytological evaluation of serous fluids provides vital information for detecting underlying etiologies, such as malignancy, and helps in evaluating tumor stages and customizing treatment plans. To address inconsistencies in the diagnostic criteria and nomenclature used in fluid cytology reporting, the International Academy of Cytology and the American Society of Cytopathology introduced The International ...
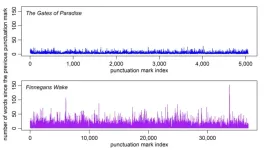
WASHINGTON, Aug. 20, 2024 – Statistical analysis of classic literature has shown that the way punctuation breaks up text obeys certain universal mathematical relationships. James Joyce’s tome “Finnegans Wake,” however, famously breaks the rules of normal prose through its unusual, dreamlike stream of consciousness. New work in chaos theory, published in the journal Chaos, from AIP Publishing, takes a closer look at how Joyce’s challenging novel stands out, mathematically.
Researchers have compared the distribution of punctuation marks in various experimental novels to determine the underlying order of “Finnegans Wake.” ...
About The Study: In this disproportionality study of an adverse drug reaction database, researchers identified a disproportionality signal of suicidal ideation with semaglutide, but not for liraglutide, particularly among patients with co-reported antidepressant use, a proxy for affective disorders (a notable exclusion criteria of premarketing clinical trials). A detected signal of semaglutide-associated suicidal ideation warrants urgent clarification.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Georgios Schoretsanitis, ...
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, approximately 50% of cancer survivors experienced cancer-related financial hardship, with a disproportionate number of survivors who were younger, were Medicare or Medicaid beneficiaries, were socioeconomically disadvantaged, and had advanced disease. Social vulnerability was independently associated with increasing levels of financial hardship, emphasizing the central role one’s community may play in cancer survivorship and the compounding financial detriments of residing in a socially vulnerable community.
Corresponding ...
Patients who overdose on opioids and have a pulse are often given naloxone (Narcan) by first responders, a common life-saving measure.
However, emergency medical service (EMS) agencies have different protocols for administering naloxone, so there is little evidence to support its use in patients without a pulse who experienced opioid-associated out of hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA).
A recent study by UC Davis Health researchers set out to assess the effects of giving naloxone administration by paramedics to patients with OHCA.
The study, published in Jama Network Open, ...
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian found that a self-guided cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) app, called Maya, significantly reduced anxiety in young adults struggling with mental health challenges. The decrease in anxiety symptoms was clinically and statistically significant at six weeks and continued at the 12-week follow-up period with improvement levels similar to anxiety medication studies.
The study, published Aug. 20 in JAMA Network Open, looked at how young adults ages ...
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology announced today the winners of its annual awards. Colleagues and other leaders in the field nominated the winners for making significant contributions to biochemistry and molecular biology as well as to the training and support of emerging scientists.
The recipients will give talks about their work at the society’s 2025 annual meeting slated for April 12–15 in Chicago.
In addition to cash prizes ranging from $2,000 to $35,000, each awardee will receive a plaque and transportation expenses to the annual meeting.
Learn more about the ASBMB awards.
Herbert Tabor ...