(Press-News.org) East Hanover, NJ – August 21, 2024 – Kessler Foundation researchers have published a new clinical study investigating the effects of robotic postural stand training combined with spinal cord epidural stimulation (Stand-scES) on trunk control in individuals with high-level spinal cord injury (SCI). The open access article, “Effects of Robotic Postural Stand Training with Epidural Stimulation on Sitting Postural Control in Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury: A Pilot Study” (doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154309) was published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine on July 24, 2024.
Improvement of trunk postural control, and particularly trunk stability, is recognized as one of the key rehabilitative goals as well as one of the top priorities indicated by individuals living with SCI. As per the study results, the robotic postural stand training protocol with Stand-scES led to relevant trunk control improvements in the upright standing position. However, it did not promote statistically significant changes or large effects in any of the sitting trunk control outcomes considered for analysis in a population of high-level motor complete SCI individuals.
According to lead author Enrico Rejc, PhD, consulting researcher in the Tim and Caroline Reynolds Center for Spinal Stimulation at the Foundation, “Our study indicates that while robotic postural stand training with epidural stimulation significantly enhances trunk control during standing tasks, this improvement does not automatically extend to sitting. This posture-specific response underscores the complexity of motor recovery in individuals with high-level spinal cord injuries.”
Future studies should investigate, prospectively, whether, and to what extent, posture specificity plays a role in determining activity-based training-induced neural plasticity and motor recovery, asserted Dr. Rejc. “The lack of significant changes in sitting trunk control following this standing-focused training suggests that rehabilitation strategies should be tailored to target specific postures,” he said, adding, “Future research should explore combined training approaches to address both sitting and standing postural challenges in this population. This approach may provide a positive balance between specificity and variability of the sensory-motor inputs for motor recovery.”
The study included the methodological approach, where six participants with cervical or high-thoracic motor complete SCI underwent approximately 80 sessions of robotic postural stand training with Stand-scES. The training included dynamic and static standing tasks with trunk perturbations but did not involve specific sitting exercises.
This research was supported by the New York State Spinal Cord Injury Research Board under Grants C31290GG and C37719GG, Kessler Foundation, the Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation, and the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust.
About Kessler Foundation
Kessler Foundation, a major nonprofit organization in the field of disability, is a global leader in rehabilitation research. Our scientists seek to improve cognition, mobility, and long-term outcomes, including employment, for adults and children with neurological and developmental disabilities of the brain and spinal cord including traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and autism. Kessler Foundation also leads the nation in funding innovative programs that expand opportunities for employment for people with disabilities. For more information, visit KesslerFoundation.org.
Press Contact at Kessler Foundation:
Deborah Hauss, DHauss@kesslerfoundation.org
Stay Connected with Kessler Foundation
X (formerly known as Twitter) | Facebook | YouTube | Instagram | SoundCloud
END
Kessler Foundation scientists investigate effects of robotic postural stand training combined with spinal cord epidural stimulation
Article reveals improved trunk control in standing but no significant impact on sitting outcomes for high-level, motor-complete individuals with SCI
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New center to improve robot dexterity selected to receive up to $52 million
2024-08-21
PITTSBURGH - Carnegie Mellon University will be a core partner in a new multi-institutional collaboration that has received $26 million from the National Science Foundation to launch an Engineering Research Center (ERC) dedicated to revolutionizing the ability of robots to amplify human labor.
Nine Carnegie Mellon University faculty members, with expertise ranging from Softbotics, engineering, and computer science to psychology, and diversity and inclusion, will help to develop highly dexterous robotic hands, user-friendly interfaces, ...
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification’s regulatory role in acute and chronic leukemia
2024-08-21
Epigenetics, the modification of chromosomes without altering DNA sequences, serves as a crucial regulatory mechanism for gene expression. Among the various epigenetic marks, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications on RNA have gained significant attention in recent years for their role in various biological processes, including cancer development and progression. This article reviews the latest advances in understanding the role of m6A modifications in leukemia, a heterogeneous group of hematological malignancies.
Role of m6A Modification in Leukemia
m6A Writers and Erasers
m6A modifications ...
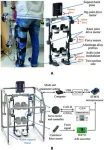
Revolutionary rehab robotics: A new leap in adaptive gait training
2024-08-21
In an era where technology increasingly merges with healthcare to enhance patient outcomes, a groundbreaking study conducted by Fuyang Yu and his colleagues introduces an innovative approach to lower limb rehabilitation. Their research, published in Cyborg Bionic Systems, outlines the development of a lower limb rehabilitation robot designed to significantly improve the safety and effectiveness of gait training through a novel method based on human-robot interaction force measurement.
Rehabilitation robots are ...
Targeted cancer cell therapy may slow endometrial cancer
2024-08-21
There may be a way to slow the growth of endometrial cancer through targeted cancer cell therapy, according to new research from the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
This year, around 65,000 women are expected to be diagnosed with endometrial cancer, the most common cancer of the female reproductive organs. An increased risk in development for multiple human cancers is associated with mutations in the PTEN protein, which normally regulates cell division and growth. The mutation allows cells to multiply uncontrollably.
Using mice models, Krystina Dunston, research lab manager and NextGen Precision Health researchers Tae Hoon Kim and Jae-Wook Jeong, studied the ...
Hepatic disease: a camu-camu fruit extract to reduce liver fat
2024-08-21
Québec City, August 21, 2024 – A research team from Université Laval has shown the benefits of camu-camu on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which affects over seven million people in Canada. This exotic fruit reduces liver fat levels.
Over 12 weeks, thirty participants took either camu-camu extract or a placebo at different times in this randomized clinical trial. Participants underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine fat levels in the liver. Scientists observed a 7.43% reduction in liver lipids when study participants took camu-camu extract. With the ...
Quenching the intense heat of a fusion plasma may require a well-placed liquid metal evaporator
2024-08-21
Inside the next generation of fusion vessels known as spherical tokamaks, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) envisioned a hot region with flowing liquid metal that is reminiscent of a subterranean cave. Researchers say evaporating liquid metal could protect the inside of the tokamak from the intense heat of the plasma. It’s an idea that dates back several decades and is tied to one of the Lab’s strengths: working with liquid metals.
“PPPL’s expertise in using liquid metals, ...
The power of face time: Insights from zebra finch courtship
2024-08-21
A new study on songbirds sheds light on the power of social interaction to facilitate learning, insights that potentially apply to human development.
McGill University researchers discovered that zebra finches deprived of early social experiences could still form strong bonds with a partner later in life. Once placed into cohabitation with a male, females that had never heard a mating song before could quickly develop a preference for his melody.
The findings, published in Proceedings of the Royal Society ...
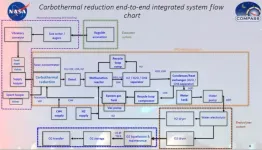
Near-term NASA Mars and lunar in situ propellant production: complexity versus simplicity
2024-08-21
First, lunar ISPP is analyzed from aspects of lunar resources, near-term lunar processes, carbothermal process, polar ice, and reduction of iron oxides. There are basically 4 potential lunar resources: (1) Silicates in regolith containing typically >40% oxygen. (2) Regolith containing FeO for hydrogen reduction. FeO content may vary from 5% to 14%, leading to recoverable oxygen content in the 1 to 3% range. (3) Imbedded atoms in regolith from solar wind (typically parts per million). (4) Water ice in regolith pores in permanently shadowed craters near the poles (unknown percentage but ...
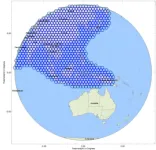
An active multi-beam antenna design method and its application for the future 6G satellite network
2024-08-21
First, the payload requirements and problems faced by traditional multi-beam antenna are described. The user beam of the VHTS payload system mainly uses Ka-band multi-beam antenna for a large range of area coverage, and the number of beams in the coverage area is not less than 500, usually using 7-color frequency reuse scheme(Fig. 2). At present, the spaceborne multi-beam antenna technology applied to high-throughput communication satellites is usually divided into multi-aperture multi-beam antenna and passive multi-feed ...
EMBARGOED NEJM Catalyst TOC, August 21, 2024
2024-08-21
Contact NEJM Group Media Relations (mediarelations@nejm.org) if you’d like to receive full-text articles and author contact information for the articles listed below.
Embargoed Until 9 AM ET on Wednesday, August 21
The African American Transplant Access Program: Mitigating Disparities in Solid Organ Transplantation
D. Simpson
The Journey to an Incentive-Based Health Equity Quality Index (Embargo lifted August 14)
E. Cheng
A Physician-Created Platform to Speed Clinical Decision-Making and Referral Workflow
E. Cunningham
How a Robust Community ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
[Press-News.org] Kessler Foundation scientists investigate effects of robotic postural stand training combined with spinal cord epidural stimulationArticle reveals improved trunk control in standing but no significant impact on sitting outcomes for high-level, motor-complete individuals with SCI