(Press-News.org) New York, NY (August 27, 2024) – The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) Catalyst Award program has awarded a $4 million, five-year grant to Prashant Rajbhandari, PhD, Assistant Professor of Medicine (Endocrinology, Diabetes and Bone Disease) at the Mount Sinai Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism Institute, to investigate a new frontier in understanding metabolic diseases like obesity and type 2 diabetes.
While much is known about how organs like the liver, fat tissue, and pancreas contribute to these conditions, Dr. Rajbhandari and his team are turning their focus to an overlooked player—the mammary gland. Their project is designated by the NIDDK as a High-Risk, High-Reward Research program.
“By using advanced technologies and machine learning that analyze single cells and proteins, the team and I hope to identify specific hormones produced by the mammary gland, which we call ‘mammokines,’” said Dr. Rajbhandari. “We believe mammokines could play a critical role in how the mammary gland communicates with different organs during breastfeeding and pregnancy and may influence obesity and diabetes in both mothers and offspring. Understanding these interactions might lead to new treatments or biomarkers for these diseases, particularly in women.”
The grant is part of the National Institutes of Health Director's Pioneer Award (DP1) mechanism. The DP1 mechanism was established to support an elite group of individual investigators who exhibit exceptional creativity and who are exploring bold and highly innovative research projects. The results of these projects have the potential to greatly impact areas relevant to the mission of NIDDK.
Dr. Rajbhandari’s study will explore how the mammary glands, particularly the cells lining the milk ducts, influence the body’s overall metabolic health. This research is inspired by the well-documented benefits of breastfeeding, which reduces the risk of diabetes and obesity for both mothers and their children. However, obesity can interfere with the normal function of the mammary gland, potentially impacting both maternal and child health.
This groundbreaking work could reveal how the mammary gland acts as an endocrine organ, potentially affecting the liver, pancreas, and fat tissue. The team will explore how these processes occur in both mice and humans, providing insights into the physiological impact of disrupted endocrine communication.
“This cutting-edge research represents a unique opportunity to make a critical impact on the fight against some of the most prevalent health issues of our time,” said Dr. Rajbhandari. “Obesity and diabetes affect millions worldwide, yet many of the mechanisms behind these diseases remain poorly understood. By investigating how mammokines affect organs like the liver and pancreas, this project could reveal entirely new pathways, potentially transforming the lives of countless lactating and non-lactating individuals.”
This innovative research aims to advance our understanding of metabolic health in women and may pave the way for new approaches to treating obesity and diabetes. The findings could also have implications for public health recommendations, especially regarding breastfeeding and maternal care.
###
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with 48,000 employees working across eight hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 11 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2024-2025.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.
END
LOUISVILLE, Ky. – The University of Louisville’s groundbreaking Green Heart Louisville Project has found that people living in neighborhoods where the number of trees and shrubs was more than doubled showed lower levels of a blood marker of inflammation than those living outside the planted areas. General inflammation is an important risk indicator for heart disease and other chronic diseases.
The Christina Lee Brown Envirome Institute launched the first-of-its-kind project in 2018 in partnership with The Nature ...
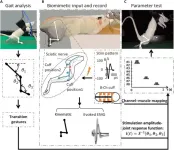
A research paper by scientists at Beijing Institute of Technology presented a sciatic nerve stimulation method that will aid in lower extremity standing and stepping.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 04 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, used the electrical nerve stimulation method and achieved muscle control via different sciatic nerve branches to facilitate the regulation of lower limb movements during stepping and standing.
Peripheral nerve stimulation is an effective neuromodulation method in patients with lower extremity movement disorders caused by stroke, spinal cord injury, or other diseases. ...
A finding by a McGill-led team of neuroscientists could open doors to new treatments for a range of psychiatric and neurological disorders attributed to dysfunctions in specific dopamine pathways.
For those struggling with a psychiatric disorder such as schizophrenia, addiction or ADHD, or with neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease or Alzheimer’s, there might be good news ahead. The neuroscientists have discovered that a small group of dopamine neurons in the striatum play a crucial role in balancing several essential brain functions, including those related to reward, cognition and movement.
Dopamine ...
Whether between galaxies or within doughnut-shaped fusion devices known as tokamaks, the electrically charged fourth state of matter known as plasma regularly encounters powerful magnetic fields, changing shape and sloshing in space. Now, a new measurement technique using protons, subatomic particles that form the nuclei of atoms, has captured details of this sloshing for the first time, potentially providing insight into the formation of enormous plasma jets that stretch between the stars.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) created ...
Crime films, action films, comedies, or documentaries? A person's favourite film genre reveals a lot about how their brain works. This is the finding of a new study led by the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) that compared data on film preferences with recordings of the brain activity of around 260 people. Fans of action films and comedies reacted very strongly to negative emotional stimuli, while participants who favoured documentaries or crime films and thrillers had a significantly weaker reaction. The results were published in the journal "Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience".
Films are ...
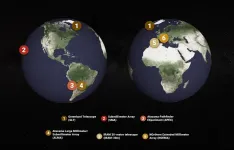
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration has conducted test observations achieving the highest resolution ever obtained from the surface of the Earth, by detecting light from the centers of distant galaxies at a frequency of around 345 GHz.
When combined with existing images of supermassive black holes at the hearts of M87 and Sgr A at the lower frequency of 230 GHz, these new results will not only make black hole photographs 50% crisper but also produce multi-color views of the region immediately outside the boundary of these cosmic beasts.
The new detections, led by scientists from the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA) that ...
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration has conducted test observations, using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and other facilities, that achieved the highest resolution ever obtained from the surface of Earth [1]. They managed this feat by detecting light from distant galaxies at a frequency of around 345 GHz, equivalent to a wavelength of 0.87 mm. The Collaboration estimates that in future they will be able to make black hole images that are 50% more detailed than was possible before, bringing the region immediately outside the boundary of nearby supermassive black holes into sharper focus. They will also ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A proposed artificial intelligence tool to support clinician decision-making about hospital patients at risk for sepsis has an unusual feature: accounting for its lack of certainty and suggesting what demographic data, vital signs and lab test results it needs to improve its predictive performance.
The system, called SepsisLab, was developed based on feedback from doctors and nurses who treat patients in the emergency departments and ICUs where sepsis, the body’s overwhelming response to an infection, is most ...
At the MIT Press, we believe that everyone deserves access to scholarship. Our dedication to this mission remains strong as we head into the fourth funding cycle for Direct to Open (D2O), our model for open access monographs. Libraries and consortia can commit to support the program through November 30, 2024.
“Direct to Open is a game changer,” said Amy Brand, Director and Publisher at the MIT Press. “We know that open scholarship benefits authors, readers, and the academy at large. This is why we ...
A study finds an increased risk of developing a productive SARS-CoV-2 infection in obese people. Obesity is known to predict worse outcomes and higher mortality for those with COVID-19. Masanori Aikawa and colleagues sought to determine if obesity also affected the likelihood of getting ill in the first place. To investigate, the authors analyzed electronic medical records for 687,813 patients from the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, including 72,613 individuals with suspected SARS-CoV-2 exposure, 18,447 of whom tested positive. The authors limited their data to a timeframe before vaccination became widespread in Massachusetts, to avoid the possible confounding ...