(Press-News.org) Researchers map 50,000 of DNA’s mysterious ‘knots’ in the human genome
Innovative study of DNA’s hidden structures may open up new approaches for treatment and diagnosis of diseases, including cancer.
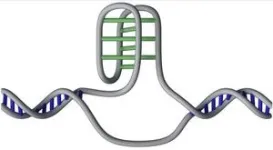
DNA is well-known for its double helix shape. But the human genome also contains more than 50,000 unusual ‘knot’-like DNA structures called i-motifs, researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research have discovered.
Published today in The EMBO Journal is the first comprehensive map of these unique DNA structures, shedding light on their potential roles in gene regulation involved in disease.
In a landmark 2018 study, Garvan scientists were the first to directly visualise i-motifs inside living human cells using a new antibody tool they developed to recognise and attach to i-motifs. The current research builds on those findings by deploying this antibody to identify i-motif locations across the entire genome.
“In this study, we mapped more than 50,000 i-motif sites in the human genome that occur in all three of the cell types we examined,” says senior author Professor Daniel Christ, Head of the Antibody Therapeutics Lab and Director of the Centre for Targeted Therapy at Garvan. “That’s a remarkably high number for a DNA structure whose existence in cells was once considered controversial. Our findings confirm that i-motifs are not just laboratory curiosities but widespread – and likely to play key roles in genomic function.”
Curious DNA i-motifs could play a dynamic role in gene activity
I-motifs are DNA structures that differ from the iconic double helix shape. They form when stretches of cytosine letters on the same DNA strand pair with each other, creating a four-stranded, twisted structure protruding from the double helix.
The researchers found that i-motifs are not randomly scattered but concentrated in key functional areas of the genome, including regions that control gene activity.
“We discovered that i-motifs are associated with genes that are highly active during specific times in the cell cycle. This suggests they play a dynamic role in regulating gene activity,” says Cristian David Peña Martinez, a research officer in the Antibody Therapeutics Lab and first author of the study.
“We also found that i-motifs form in the promoter region of oncogenes, for instance the MYC oncogene, which encodes one of cancer’s most notorious ‘undruggable’ targets. This presents an exciting opportunity to target disease-linked genes through the i-motif structure,” he says.
I-motifs hold promise for new type of therapies and diagnostics
“The widespread presence of i-motifs near these ‘holy grail’ sequences involved in hard-to-treat cancers opens up new possibilities for new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. It might be possible to design drugs that target i-motifs to influence gene expression, which could expand current treatment options,” says Associate Professor Sarah Kummerfeld, Chief Scientific Officer at Garvan and co-author of the study.
Professor Christ adds that mapping i-motifs was only possible thanks to Garvan’s world-leading expertise in antibody development and genomics. “This study is an example of how fundamental research and technological innovation can come together to make paradigm-shifting discoveries,” he says.
--ENDS--
This research was supported by funding from the National Health and Medical Research Council.
Professor Daniel Christ is a Conjoint Professor at St Vincent's Clinical School, Faculty of Medicine and Health, UNSW Sydney. Associate Professor Sarah Kummerfeld is a Conjoint Associate Professor at St Vincent's Clinical School, Faculty of Medicine and Health, UNSW Sydney.
END
Researchers map 50,000 of DNA’s mysterious ‘knots’ in the human genome
Innovative study of DNA’s hidden structures may open up new approaches for treatment and diagnosis of diseases, including cancer.
2024-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can fungi turn food waste into the next culinary sensation?
2024-08-29
Chef-turned-chemist Vayu Hill-Maini has a passion: to turn food waste into culinary treats using fungi.
One of his collaborators is Rasmus Munk, head chef and co-owner of the Michelin two-star restaurant Alchemist in Copenhagen, who serves a dessert — orange-colored Neurospora mold grown on rice — inspired by Hill-Maini.
For the past two years, Hill-Maini has worked with a team of chefs at Blue Hill at Stone Barns, a Michelin two-star restaurant in Pocantico Hills, New York, to generate tasty morsels from Neurospora mold grown on grains and pulses, including the pulp left over from making oat ...
Women with endometriosis at greater associated risk of heart attack and stroke
2024-08-29
London, United Kingdom – 29 Aug 2024: According to research presented at ESC Congress 2024,1 women with endometriosis have a 20% greater risk of significant cardiac outcomes compared with women without endometriosis.
“For decades, cardiovascular disease (CVD) has been thought of as a man’s disease and risk factors have been considered from the male perspective, for example, including erectile dysfunction in guidelines on CVD risk assessment.2 Yet, 1 in 3 women die from CVD and 1 in 10 women suffer from ...
Catching up on sleep on weekends may lower heart disease risk by up to 20%
2024-08-29
London, United Kingdom – 29 August 2024: The demands of the working week, often influenced by school or work schedules, can lead to sleep disruption and deprivation. However, new research presented at ESC Congress 2024 shows that people that ‘catch up’ on their sleep by sleeping in at weekends may see their risk of heart disease fall by one-fifth.
“Sufficient compensatory sleep is linked to a lower risk of heart disease,” said study co-author Mr Yanjun Song of the State Key Laboratory ...
Quitting smoking nearly halves heart attack risk, cutting down does little
2024-08-29
London, United Kingdom – 29 August 2024: According to research presented today at ESC Congress 2024,1 patients with stable coronary artery disease who quit smoking at any timepoint after their diagnosis reduced their risk of a major event by almost 50%. In contrast, there was minimal impact on cardiovascular risk in patients who reduced their smoking habits.
The international CLARIFY registry (prospeCtive observational LongitudinAl RegIstry oF patients with stable coronary arterY ...
Children contribute to group projects when there are clear and common goals
2024-08-29
Children can work together to reach a target that benefits a whole group even if it is at a personal cost to themselves, a new study has shown.
Researchers invited groups of six to 10-year-olds to take part in a game where they were each given containers of water and could decide how much of it to offer into a common pool.
If the group contributed a certain amount of water it resulted in benefits for the whole group, but children also obtained benefits for any water they kept.
At the same time, the ...
Dine on DNA: Compounds from nucleic acids in food show anticancer effects
2024-08-29
When people eat, they ingest the nucleic acids that reside in all living things. The compounds in these acids could inhibit the growth of cancer cells, according to findings published in PLOS ONE by Osaka Metropolitan University Associate Professor Akiko Kojima-Yuasa of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology and colleagues.
Consuming nucleic acids found in food has been shown to boost the immune system and prevent some diseases. The nucleotides and nucleosides that result from digesting the acids are largely responsible for these beneficial effects.
Professor ...
MCG scientists working to understand why men with prostate cancer are at higher risk of Alzheimer’s
2024-08-29
AUGUSTA, Ga. (Aug. 29, 2024) – Researchers at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University are searching for a better way to understand why many men with prostate cancer end up with Alzheimer’s disease, and whether it’s the standard hormone therapy treatment or an overactive immune response that actually contributes to the problem.
The hormone therapy, androgen deprivation therapy, known as ADT, treats the cancer by reducing testosterone, which the cancer needs to grow. But androgen is a key regulator of amyloid metabolism and when it’s removed from the equation, more amyloid is left to form the plaques that are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s.
“We ...
Ancient sea cow attacked by a crocodile and sharks sheds new light on prehistoric food chains
2024-08-29
A new study describing how a prehistoric sea cow was preyed upon by not one, but two different carnivores – a crocodilian and a shark – is revealing clues into both the predation patterns of ancient creatures and the wider food chain millions of years ago.
Published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, the findings mark one of the few examples of a creature being preyed upon by different animals during the Early to Middle Miocene epoch (23 million to 11.6 million years ago).
Predation marks in the skull indicate that the dugongine sea cow, ...
Georgia Tech neuroscientists explore the intersection of music and memory
2024-08-29
By Jerry Grillo
The soundtrack of this story begins with a vaguely recognizable and pleasant groove. But if I stop writing and just listen for a second, the music reveals itself completely. In Freddie Hubbard’s comfortable, lilting trumpet solo over Herbie Hancock’s melodic, repetitive piano vamping, I recognize “Cantaloupe Island.” Then, with my fingers again poised at the keyboard, Freddie and Herbie fade into the background, followed by other instrumental music: captivating — but not distracting — sonic nutrition, feeding my concentration and productivity.
Somewhere, I think, Yiren Ren is studying, focused on her ...
Waging war on ‘superbugs’ in aged care
2024-08-29
There’s an urgent need for more careful antibiotic management to protect older people living in residential aged care from the dangerous spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria or ‘superbugs’, researchers from Flinders University and SAHMRI warn.
A new study published in the well-respected Journal of Infection, explores the link between the widespread use of antibiotics in residential aged care and the resulting antibiotic resistant bacteria in the gut that can be passed on to other residents.
“Commonly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
[Press-News.org] Researchers map 50,000 of DNA’s mysterious ‘knots’ in the human genomeInnovative study of DNA’s hidden structures may open up new approaches for treatment and diagnosis of diseases, including cancer.