Persistent neighborhood poverty and breast cancer outcomes
JAMA Network Open
2024-08-29
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: The findings of this study of women ages 18 or older diagnosed with stage I to III breast cancer between 2010 and 2018 suggest that residing in persistently impoverished neighborhoods is associated with poor tumor characteristics and increased mortality.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Samilia Obeng-Gyasi, MD, MPH, email samilia.obeng-gyasi@osumc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27755)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27755?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=082924
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-29
About The Study: Inhaler prescriptions filled by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services beneficiaries in 2022 resulted in an estimated 1.15 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions, equivalent to 226,960 homes’ yearly electricity use. Metered-dose inhalers were responsible for nearly all inhaler-related emissions, with the largest contribution arising from short-acting β-agonist medications. Although dry-powder and soft-mist inhalers had substantially lower emissions, they accounted for a disproportionate amount of spending, representing nearly two-thirds ...
2024-08-29
How are rodents able to navigate pitch-black subway tunnels or other dark environments so adeptly, despite not being able to rely on vision?
With the assistance of a novel motion simulator, researchers at Bar-Ilan University in Israel have discovered that rats rely on airflow to navigate their surroundings. When they move, the flow of air relative to their bodies provides crucial information, complementary to their sense of balance, to perceive their own motion in space. This might explain their agility in the dark as they scurry through pipes and tunnels, ...
2024-08-29
PHILADELPHIA – A new tool for monitoring immune health patterns over time has revealed how a pair of checkpoint inhibitor therapies works together to recruit new cancer-fighting T cells with every infusion. Findings from the use of the new tool, developed by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine and Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center (ACC), were published today in Cancer Cell. The study challenges fundamental assumptions about how a common immunotherapy ...
2024-08-29
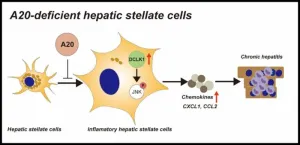
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) determine how a protein called A20 can regulate the inflammatory response to suppress chronic hepatitis
Tokyo, Japan – Many individuals worldwide suffer from chronic liver disease (CLD), which poses significant concerns for its tendency to lead to hepatocellular carcinoma or liver failure. CLD is characterized by inflammation and fibrosis. Certain liver cells, called hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), contribute to both these characteristics, but how they are specifically involved in the inflammatory response is not ...
2024-08-29
The Microbiology Society, one of the largest microbiology societies in Europe, is pleased to announce a new three year Publish and Read offering with German consortium ZB Med – Information Centre for Life Sciences, available to its 400 member institutions and 2,000 hospitals. This agreement was established in partnership with HARRASSOWITZ, the Society’s representative agency in Germany.
From 2025, member institutions can join this consortium-wide Publish and Read agreement to enjoy discounted pricing. For participating institutions, the ...
2024-08-29
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, implement modifications to their high-speed atomic force microscopy that simultaneously improve resolution and speed, while enabling direct measurements of 3D structures to provide conclusive evidence of a contested hydration layer forming as calcite dissolves.
Understanding the dissolution processes of minerals can provide key insights into geochemical processes. Attempts to explain some of the observations during the dissolution of calcite (CaCO3) have led to the hypothesis that a hydration layer forms, although this has been contested. Hydration layers are also ...
2024-08-29
A new study has found an answer for a long-lasting question in aging research - Is Alzheimer’s disease-dementia a form of accelerated aging or is there a different path that can lead us to healthier brain aging? In an international effort, the researchers mapped 1.65 million cells from 437 aging brains, and uncovered distinct paths of cellular change in the aging brains, with one leading to Alzheimer’s disease and the other to an alternative form brain aging. They also point to specific cell signatures predicted to advance disease once they appear in the aging ...
2024-08-29
Toronto- August 27, 2024 - JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Advancing Digital Health: Real-World Implementation and Strategic Insights from Industry-Driven Innovation” in JMIR Medical Informatics, a leading peer-reviewed journal indexed in PubMed with a unique focus on clinical informatics and the digitization of care processes.
The health care landscape is transforming rapidly, driven by technological innovation and the pressing need for more efficient, accessible and patient-centric health care solutions.
Yet, the health IT industry grapples with ...
2024-08-29
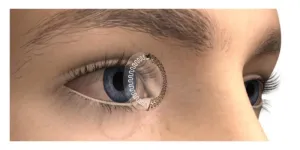
LOS ANGELES, August 29, 2024 — Yangzhi Zhu, Ph.D., Assistant Professor at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), has been awarded the prestigious 2024 NARSAD Young Investigator Grant for his groundbreaking work on a lab-on-a-contact lens (LoCL) system. This innovative technology is designed to monitor mental health by providing real-time, non-invasive tracking of panels of key biomarkers, from the wearer’s tears.
Mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, affect nearly a billion ...
2024-08-29
A recent case report published in Cyborg Bionic Systems details the diagnosis of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (iNPH) using multimodality diagnostic approaches, highlighting significant advancements in medical diagnostics and patient care. The study conducted by a team of researchers from Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin, China, presents a comprehensive case study of a 68-year-old male patient diagnosed with iNPH, showcasing the effectiveness of these advanced diagnostic techniques.
iNPH is a condition characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) causing ventricular dilation, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Persistent neighborhood poverty and breast cancer outcomes
JAMA Network Open