(Press-News.org) Chemists at the University of Amsterdam have developed a method to furnish a range of molecules with a trifluoromethyl group attached to a sulphur, nitrogen or oxygen atom. Their procedure, which has just been published in Science, avoids the use of PFAS reagents. It thus provides an environmentally friendly synthesis route for pharmaceutical and agrochemical compounds that rely on the presence of the trifluoromethyl group.
The straightforward and effective method was developed at the Flow Chemistry group at the Van ‘t Hoff Institute for Molecular Sciences led by Prof. Timothy Noël, in cooperation with researchers in Italy, Spain and the UK, both from academia and industry. Applying the principles of flow chemistry, where reactions take place in closed systems of small tubes, makes for safe and controlled chemistry. It also offers greater versatility and flexibility over more common procedures using traditional chemical glassware.
Environmentally more friendly
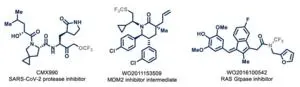
Many pharmaceutical compounds (such as anti-depressants) as well as agrochemical compounds (such as pesticides) benefit from the presence of a trifluoromethyl (-CF3) group. It enhances hydrophobicity and increases metabolic stability, thus improving efficacy and lowering the required dose or concentration.
To introduce the fluorine atoms in these molecules, their synthesis often requires bespoke fluorinated reagents. Many of these are among the family of PFAS compounds and thus will face future legislation. The synthesis protocol now presented in the Science paper provides a viable alternative since it only requires caesium fluoride salt as the fluorine source. Such PFAS-free synthesis of fluorinated agents can provide an environmentally more friendly option for the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds, which motivated scientists from AstraZeneca to participate in the research.
In addition, the new synthesis protocol enables coupling of the CF3 group through a sulphur (S), nitrogen (N) or oxygen (O) atom. Such fluorinated motifs confer unique features to drug molecules and agrochemicals, impacting their lipophilicity, oxidation resistance, and acid-base properties.
Integrated flow system
The Science paper presents a versatile microfluidic flow module for generating reactive N–, S– and O–CF3 anions. These are prepared in a packed bed flow reactor containing the caesium fluoride salt. Appropriate (S, O or N containing) precursors are then led through this reactor. They are fluorinated with high efficiency due to the high surface area of the salt in the packed bed as well and the improved mixing of the organic intermediates. Importantly, this approach also offers enhanced safety as all formed intermediates are contained within the microfluidic system.
Another important feature of the system is the integration of the anion generating module with a downstream reaction module. There, the N–, S– or O–CF3 anions react with appropriate substrates to achieve pharmaceutical and agrochemical active ingredients as the desired end products.
Implementation in an academic and industrial context
In combination, the anion generator module and the downstream reactor provide a streamlined platform for the derivatization of molecules bearing N–, S– and O–CF3 motifs. This innovative approach is poised to impact the development of new pharmaceutical drugs by enhancing their properties while improving safety and sustainability in their production processes. In their Science paper, the researchers report the combination of various anions with a range of substrates, resulting in multiple fluorinated products with relevance to pharmaceutical and agrochemical syntheses. In many cases the research team was able to report very satisfactory yields. Moreover, the operational parameters (e.g. reaction times) offer a good prospect for actual implementation in an academic as well as an industrial context.
END
PFAS-free synthesis of fluorinated pharmaceutical and agrochemical compounds
2024-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
School of Dentistry researchers develop innovative sleep apnea model to find answers to chronic pain
2024-08-29
Scientists at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) School of Dentistry created a first of its kind sleep apnea model for studying chronic pain. A study published July 30 in Science Signaling, explains the mechanism behind persistent pain related to obstructive sleep apnea.
More than 100 million people worldwide are affected by obstructive sleep apnea. This health condition causes a person to stop breathing numerous times while they are sleeping. Reduced sleep time and sleep quality can lead to numerous health problems including chronic pain, which is diagnosed at a much higher rate ...
Plastic surgery patients who use marijuana also have elevated nicotine levels
2024-08-29
August 29, 2024 — Marijuana use is common among patients considering plastic surgery and is associated with elevated nicotine levels on laboratory tests, reports a paper in the September issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"We found that patients who report marijuana use also have elevated urine nicotine and cotinine levels ...
Machine learning predicts which patients will continue taking opioids after hand surgery
2024-08-29
August 29, 2024 — A machine learning algorithm performs well in predicting the risk of persistent opioid use after hand surgery, reports a study in the August issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"We found that a machine learning model performs well in identifying hand surgery patients who are more likely to become persistent opioid users," comments ASPS ...
$15.5 million NIH award funds development of national network to include nursing home residents in clinical trials
2024-08-29
INDIANAPOLIS – A team led by research scientists from the Indiana University School of Medicine and Regenstrief Institute has received funding expected to total $15.5 million from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Aging to establish a national network structure to include more nursing home residents in clinical trials.
Even though clinical trials are critical to the development and testing of medical therapies and treatments including drugs and care models, individuals living in nursing homes are rarely included in clinical research studies.
The new five-year award will fund ...
What’s in the microbiome of the foods we eat?
2024-08-29
Microbes are part of the food we eat and can influence our own microbiome, but we know very little about the microbes in our foods. Now, researchers have developed a database of the “food microbiome” by sequencing the metagenomes of 2,533 different foods. They identified 10,899 food-associated microbes, half of which were previously unknown species, and showed that food-associated microbes account for around 3% of the adult and 56% of the infant gut microbiome on average. The study published August 29 in the journal ...
Scientists discover how starfish get ‘legless’
2024-08-29
Researchers at Queen Mary University of London have made a groundbreaking discovery about how starfish manage to survive predatory attacks by shedding their own limbs. The team has identified a neurohormone responsible for triggering this remarkable feat of self-preservation.
Autotomy, the ability of an animal to detach a body part to evade predators, is a well-known survival strategy in the animal kingdom. While lizards shedding their tails are a familiar example, the mechanisms behind this process remain largely mysterious.
Now, scientists have unveiled a key piece of the puzzle. By studying the common European starfish, ...
Hormone therapy and biological aging in postmenopausal women
2024-08-29
About The Study: Postmenopausal women with historical hormone therapy (HT) use were biologically younger than those not receiving HT, with a more evident association observed in those with low socioeconomic status. The biological aging discrepancy mediated the association between HT and decreased mortality. Promoting HT in postmenopausal women could be important for healthy aging.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Chenglong Li, PhD, email chenglongli@bjmu.edu.cn.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.30839)
Editor’s ...
Persistent neighborhood poverty and breast cancer outcomes
2024-08-29
About The Study: The findings of this study of women ages 18 or older diagnosed with stage I to III breast cancer between 2010 and 2018 suggest that residing in persistently impoverished neighborhoods is associated with poor tumor characteristics and increased mortality.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Samilia Obeng-Gyasi, MD, MPH, email samilia.obeng-gyasi@osumc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27755)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Greenhouse gas emissions and costs of inhaler devices in the US
2024-08-29
About The Study: Inhaler prescriptions filled by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services beneficiaries in 2022 resulted in an estimated 1.15 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions, equivalent to 226,960 homes’ yearly electricity use. Metered-dose inhalers were responsible for nearly all inhaler-related emissions, with the largest contribution arising from short-acting β-agonist medications. Although dry-powder and soft-mist inhalers had substantially lower emissions, they accounted for a disproportionate amount of spending, representing nearly two-thirds ...
Novel motion simulator reveals key role of air flow in rodent navigation
2024-08-29
How are rodents able to navigate pitch-black subway tunnels or other dark environments so adeptly, despite not being able to rely on vision?
With the assistance of a novel motion simulator, researchers at Bar-Ilan University in Israel have discovered that rats rely on airflow to navigate their surroundings. When they move, the flow of air relative to their bodies provides crucial information, complementary to their sense of balance, to perceive their own motion in space. This might explain their agility in the dark as they scurry through pipes and tunnels, ...