(Press-News.org) CAMBRDIGE, MA – In order to train more powerful large language models, researchers use vast dataset collections that blend diverse data from thousands of web sources.
But as these datasets are combined and recombined into multiple collections, important information about their origins and restrictions on how they can be used are often lost or confounded in the shuffle.
Not only does this raise legal and ethical concerns, it can also damage a model’s performance. For instance, if a dataset is miscategorized, someone training a machine-learning model for a certain task may end up unwittingly using data that are not designed for that task.
In addition, data from unknown sources could contain biases that cause a model to make unfair predictions when deployed.
To improve data transparency, a team of multidisciplinary researchers from MIT and elsewhere launched a systematic audit of more than 1,800 text datasets on popular hosting sites. They found that more than 70 percent of these datasets omitted some licensing information, while about 50 percent had information that contained errors.
Building off these insights, they developed a user-friendly tool called the Data Provenance Explorer that automatically generates easy-to-read summaries of a dataset’s creators, sources, licenses, and allowable uses.
“These types of tools can help regulators and practitioners make informed decisions about AI deployment, and further the responsible development of AI,” says Alex “Sandy” Pentland, an MIT professor, leader of the Human Dynamics Group in the MIT Media Lab, and co-author of a new open-access paper about the project.
The Data Provenance Explorer could help AI practitioners build more effective models by enabling them to select training datasets that fit their model’s intended purpose. In the long run, this could improve the accuracy of AI models in real-world situations, such as those used to evaluate loan applications or respond to customer queries.
“One of the best ways to understand the capabilities and limitations of an AI model is understanding what data it was trained on. When you have misattribution and confusion about where data came from, you have a serious transparency issue,” says Robert Mahari, a graduate student in the MIT Human Dynamics Group, a JD candidate at Harvard Law School, and co-lead author on the paper.
Mahari and Pentland are joined on the paper by co-lead author Shayne Longpre, a graduate student in the Media Lab; Sara Hooker, who leads the research lab Cohere for AI; as well as others at MIT, the University of California at Irvine, the University of Lille in France, the University of Colorado at Boulder, Olin College, Carnegie Mellon University, Contextual AI, ML Commons, and Tidelift. The research is published today in Nature Machine Intelligence.
Focus on finetuning
Researchers often use a technique called fine-tuning to improve the capabilities of a large language model that will be deployed for a specific task, like question-answering. For finetuning, they carefully build curated datasets designed to boost a model’s performance for this one task.
The MIT researchers focused on these fine-tuning datasets, which are often developed by researchers, academic organizations, or companies and licensed for specific uses.
When crowdsourced platforms aggregate such datasets into larger collections for practitioners to use for fine-tuning, some of that original license information is often left behind.
“These licenses ought to matter, and they should be enforceable,” Mahari says.
For instance, if the licensing terms of a dataset are wrong or missing, someone could spend a great deal of money and time developing a model they might be forced to take down later because some training data contained private information.
“People can end up training models where they don’t even understand the capabilities, concerns, or risk of those models, which ultimately stem from the data,” Longpre adds.
To begin this study, the researchers formally defined data provenance as the combination of a dataset’s sourcing, creating, and licensing heritage, as well as its characteristics. From there, they developed a structured auditing procedure to trace the data provenance of more than 1,800 text dataset collections from popular online repositories.
After finding that more than 70 percent of these datasets contained “unspecified” licenses that omitted much information, the researchers worked backward to fill in the blanks. Through their efforts, they reduced the number of datasets with “unspecified” licenses to around 30 percent.
Their work also revealed that the correct licenses were often more restrictive than those assigned by the repositories.
In addition, they found that nearly all dataset creators were concentrated in the global north, which could limit a model’s capabilities if it is trained for deployment in a different region. For instance, a Turkish language dataset created predominantly by people in the U.S. and China might not contain any culturally significant aspects, Mahari explains.
“We almost delude ourselves into thinking the datasets are more diverse than they actually are,” he says.
Interestingly, the researchers also saw a dramatic spike in restrictions placed on datasets created in 2023 and 2024, which might be driven by concerns from academics that their datasets could be used for unintended commercial purposes.
A user-friendly tool
To help others obtain this information without the need for a manual audit, the researchers built the Data Provenance Explorer. In addition to sorting and filtering datasets based on certain criteria, the tool allows users to download a data provenance card that provides a succinct, structured overview of dataset characteristics.
“We are hoping this is a step, not just to understand the landscape, but also help people going forward to make more informed choices about what data they are training on,” Mahari says.
In the future, the researchers want to expand their analysis to investigate data provenance for multimodal data, including video and speech. They also want to study how terms of service on websites that serve as data sources are echoed in datasets.
As they expand their research, they are also reaching out to regulators to discuss their findings and the unique copyright implications of fine-tuning data.
“We need data provenance and transparency from the outset, when people are creating and releasing these datasets, to make it easier for others to derive these insights,” Longpre says.
END
Study: Transparency is often lacking in datasets used to train large language models
Researchers developed an easy-to-use tool that enables an AI practitioner to find data that suits the purpose of their model, which could improve accuracy and reduce bias.
2024-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New ESC Hypertension Guidelines recommend intensified BP targets and introduce a novel elevated blood pressure category to better identify people at risk for heart attack and stroke
2024-08-30
London, UK, 30 August 2024: Updated ESC Guidelines on the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension include a new elevated blood pressure category, more ambitious and intensive treatment targets, and, for the first time, recommendations on the use of renal denervation to treat various forms of hypertension. The Guidelines have been produced by an international panel of experts that include co-Chairpersons Professor Bill McEvoy of the University of Galway, Ireland, and Professor Rhian Touyz of McGill University, Canada.
Elevated blood pressure and hypertension are by far the most common and important risk ...
New ESC Guidelines combine peripheral arterial and aortic diseases for first time, emphasising interconnectivity of whole arterial system
2024-08-30
London, UK, 30 August 2024: The 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of peripheral arterial and aortic diseases (PAAD) evaluate these vascular diseases together as part of same cardiovascular system, appreciating that patients with aortic diseases are at risk of having peripheral vascular diseases and vice versa. The Guidelines are aimed at cardiologists, but were coordinated for alignment with guidelines for surgeons by EACTS and endorsed by VASCERN and ESVM.
“These updated guidelines have been introduced now due to significant advancements and shifts in our understanding and management of aortic and peripheral ...
New Chronic Coronary Syndrome (CCS) Guidelines expand diagnostic tools and ways to prevent major adverse events and enhance quality of life
2024-08-30
London, UK, 30 August 2024: The 2024 ESC Guidelines on the management of chronic coronary syndromes (CCS) include a focus on both larger and smaller blood vessels of the heart; new models to estimate chances of blocked large arteries (so-called obstructive coronary artery disease); optimal selection and sequence of tests; drugs and interventions to prevent disease complications and improve symptoms, and the fundamental role of patient involvement.
“The new guidelines prompt cardiologists to rethink chronic coronary syndromes ...
Atrial fibrillation guidelines focus on shared and equal care, patient empowerment, comorbidities, evidence-based management and dynamic re-evaluation
2024-08-30
London, UK, 30 August 2024: The 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation, developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), contain a number of new approaches and treatment-specific recommendations to help manage the surging numbers of patients with AF worldwide.
“Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most commonly encountered heart conditions, with a broad impact on all health services across primary, secondary and tertiary care,” says Guidelines Chair Professor Isabelle C. Van Gelder, University Medical Centre Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands. “The prevalence ...
Two thirds of deaths related to high BMI are due to cardiovascular diseases - ESC Clinical Consensus Statement on Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease
2024-08-30
London, United Kingdom – 30 August 2024: The ESC Clinical Consensus Statement on Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease, presented at this year’s ESC Congress (London, UK, 30 August to 2 September) summarises current evidence on the epidemiology and aetiology of obesity; the interplay between obesity, cardiovascular risk factors and cardiac conditions; the clinical management of patients with cardiac disease and obesity; and weight loss strategies including lifestyle changes, interventional procedures, and anti-obesity medications with particular focus ...
Prehospital pulse-dose glucocorticoid in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
2024-08-30
About The Study: In patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, treatment with prehospital pulse-dose glucocorticoid did not reduce final infarct size after 3 months. However, the trial was likely underpowered as the final infarct size was smaller than anticipated. The glucocorticoid group had improved acute parameters compared with placebo.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jasmine Melissa Madsen, MD, email jasmine.melissa.madsen.01@regionh.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2024.2298)
Editor’s ...
Effects of sacubitril/valsartan on all-cause hospitalizations in heart failure
2024-08-30
About The Study: In this post hoc pooled analysis of 13,194 patients with chronic heart failure (HF) in the PARADIGM-HF and PARAGON-HF randomized clinical trials, sacubitril/valsartan significantly reduced hospitalization for any reason, with benefits most apparent in patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction below normal. This reduction appeared to be principally driven by lower rates of cardiac and pulmonary hospitalizations.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, email mvaduganathan@bwh.harvard.edu.
To ...
Promising antibiotic candidates discovered in microbes deep in the Arctic Sea
2024-08-30
Antibiotics are the linchpin of modern medicine: without them, anyone with open wounds or needing to undergo surgery would be at constant risk of dangerous infections. Yet we continue to face a global antibiotics crisis, as more and more resistant strains of bacteria are evolving, while the rate of discovery of fundamentally new antibiotics has been much slower.
But there is reason for hope: 70% of all currently licensed antibiotics have been derived from actinobacteria in the soil, and most environments on Earth have not yet ...
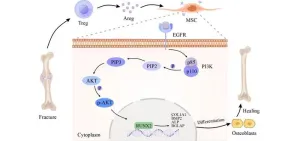
A distinct “repair” role of regulatory T cells in fracture healing
2024-08-30
The study uncovers a unique reparative function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the process of fracture healing, a discovery that adds a new dimension to our understanding of the immune response in tissue regeneration. Tregs, a subset of T cells known for their role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity, are now shown to play a critical part in the intricate interplay between the immune system and bone repair.
Fracture healing is a complex process that involves a sequence of events, including inflammation, repair, and remodeling. While the initial ...
Dancing galaxies make a monster at the cosmic dawn
2024-08-30
Astronomers have spotted a pair of galaxies in the act of merging 12.8 billion years ago. The characteristics of these galaxies indicate that the merger will form a monster galaxy, one of the brightest types of objects in the Universe. These results are important for understanding the early evolution of galaxies and black holes in the early Universe.
Quasars are bright objects powered by matter falling into a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy in the early Universe. The most accepted theory is that when two gas-rich galaxies merge to form a single larger galaxy, the gravitational interaction of the two galaxies causes gas to fall towards the supermassive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Study: Transparency is often lacking in datasets used to train large language modelsResearchers developed an easy-to-use tool that enables an AI practitioner to find data that suits the purpose of their model, which could improve accuracy and reduce bias.