(Press-News.org) Investigators involved in a multicenter study co-led by Cedars-Sinai discovered a pathway by which immune cells prevent the lungs’ protective barrier from healing after viral infections like COVID-19. The findings, published in Nature may lead to new therapeutic treatment options.
The COVID-19 pandemic revealed how viral infections can cause long-lasting effects—a condition called long COVID. Also known as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2, long COVID has left a devastating trail of people who continue to live with long-term debilitation after infection. One such manifestation is scarring of the lungs—a condition known as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 pulmonary fibrosis.
Those with long COVID can present with a broad constellation of symptoms, including post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 pulmonary fibrosis, which can cause severe difficulty breathing that requires oxygen supplementation. Patients with the most severe breathing difficulty may also need a lung transplant. Without additional treatment options, many patients are often left with long-term disability and life-threatening complications.
“This study sought to understand the pathways that led to abnormal repair in the lungs that produced a scar-forming environment,” said Peter Chen, MD, co-corresponding author of the study, the Medallion Chair in Molecular Medicine and the interim chair of the Department of Medicine at Cedars-Sinai. “Our findings may lead to therapeutic strategies to prevent fibrotic lung disease after viral illnesses.”
Investigators established models of post-viral lung disease and used molecular profiling and imaging to identify immune cells called CD8+ T cells as a driving factor in preventing lung healing and repair post-infection. Moreover, the investigators used post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 pulmonary fibrosis patient cohorts to validate the abnormal immunologic pathways, corroborating the animal model work.
“Although we based the work on post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 pulmonary fibrosis, other viral pandemics in the past have also revealed that ability to cause lung scarring after infection—like swine flu,” said Jie Sun, PhD, co-corresponding author of the study and professor of Medicine at the University of Virginia School of Medicine. “The research and broader medical field must be prepared and better understand how to prevent adverse outcomes stemming from these viruses.”
Chen and Sun say these findings—and similar studies—could provide novel information into the pathobiology of other forms of lung fibrosis.
Other Cedars-Sinai authors include Tanyalak Parimon, Changfu Yao and Alberto Marchesvsky. Additional authors include Harish Narasimhan, Su Cheon, Wei Qian, Sheng’en Shawn Hu, Chaofan Li, Nick Goplen, Yue Wu, Xiaoqin We, Young Min Son, Elizabeth Fink, Gislane de Almeida Santos, Jinyi Tang, Lyndsey Muehling, Glenda Canderan, Alexandra Kadl, Abigail Cannon, Samuel Young, Riley Hannan, Grace Bingham, Mohammed Arish, Arka Sen Chaudhari, Jun sub Im, Cameron L.R. Mattingly, Patcharin Pramoonjago, Jeffrey Sturek, Jacob E. Kohlmeier, Yun Michael Shim, Judith Woodfolk, and Chongzhi Zang.
The study was in part supported by the US National Institutes of Health grants AI147394, AG069264, AI112844, HL170961, AI176171 and AI154598 to J.S, R01HL132287, R01HL167202, and R01HL132177 to Y.M.S, R35HL150803 to J.E.K., Emory Center of Excellence for Influenza Research and Response grant 75N93019R0028 to J.E.K., F31HL164049-01A1 to C.L.R.M., and F31HL170746 and T32AI007496 to H.N.
END
Immune cells prevent lung healing after viral infection
Investigators from Cedars-Sinai and University of Virginia identify pathways responsible for pulmonary fibrosis after viral infection
2024-09-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
KERI overcomes from overseas dependence on drive system technology for machine tools!
2024-09-04
Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) has succeeded in domestically developing the ‘CNC driving system’ technology, a core component of machine tools—often referred to as "Mother Machines," the machines that make other machines.
The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system is an electronic module that processes numerical information via a computer and automatically controls all functions of machine tools, including position, speed, and rotation of a machine tool. In a computer, it plays a role similar to that of a CPU.
A major challenge ...
Digital Science unveils Papers Pro: Revolutionizing scholarly research with advanced AI-powered features
2024-09-04
Digital Science today announces the launch of Papers Pro, an AI-enhanced premium version of its acclaimed reference manager, Papers.
As part of the ReadCube suite of literature solutions, Papers Pro is designed to make researchers and students more productive in their daily tasks by integrating cutting-edge AI tools to transform how they discover, organize, read, annotate, share and cite research materials.
Search and discovery has always been a core part of the Papers workflow. The launch of Papers Pro introduces new search capabilities, powered by Dimensions, one of the world’s largest ...
PCORI offers up to $100 million for new research promoting healthy children and youth
2024-09-04
Sept. 4, 2024
WASHINGTON, D.C. – The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) today began inviting proposals through eight new funding opportunities, including three PCORI Funding Announcements (PFAs) for patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER). One PFA is offering up to $100 million to support CER studies promoting healthy children and youth, a demographic representing more than a third of the U.S. population and facing a range of mental and physical health challenges.
“These ...
Newly discovered gene may influence longevity
2024-09-04
It turns out that a particular gene has a great influence on longevity, a new study from the University of Copenhagen concludes. This may pave the way for new treatment.
Sleep, fasting, exercise, green porridge, black coffee, a healthy social life …
There is an abundance of advice out there on how to live a good, long life. Researchers are working hard to determine why some people live longer than others, and how we get the most out of our increasingly long lives.
Now researchers from the Center for Healthy Aging, Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine at the University of Copenhagen have made a breakthrough. They have discovered that ...
SwRI signs MOU with Blade Energy Partners to support carbon dioxide sequestration research
2024-09-04
SAN ANTONIO — September 4, 2024 — Southwest Research Institute has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Blade Energy Partners, establishing a new research collaboration focused on advancing carbon dioxide storage technology to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) refers to the practices of capturing CO2 from its industrial sources or the atmosphere, transport it using pipelines and other means, using it as alternative fuel or other industrial applications, and storing it for later use. The drive to meet net-zero greenhouse gas emissions goals and ...
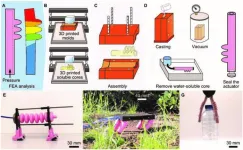
Integrated design and fabrication of pneumatic soft robot actuators in a single casting step
2024-09-04
A research paper by scientists at University of Coimbra proposed an integrated approach targeting the design and fabrication of pneumatic soft actuators in a single casting step. Molds and sacrificial water-soluble hollow cores are printed using fused filament fabrication.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 17 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, presented an integrated process for the design and fabrication of soft robot actuators in a single casting. The author proved the availability, versatility, and effectiveness of the proposed methods, contributing to accelerating the design and fabrication of soft robots.
Bio-inspired soft robots have already shown the ability to handle ...
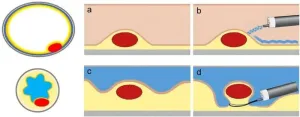
Underwater resection of neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract
2024-09-04
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract are a rare and heterogeneous group of malignancies arising from the neuroendocrine cell system. These tumors are more commonly encountered in the stomach, appendix, small bowel, rectum, and pancreas. Over the past few decades, the incidence of GI NETs has increased due to improved diagnostic capabilities and an aging population. The management of these tumors requires a careful assessment of various factors, including the site, size, grading, depth of invasion, and local lymphadenopathy, as they significantly impact prognosis and treatment ...
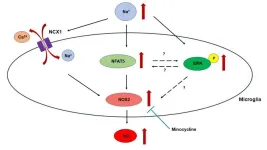
Microglial responses to hypernatremia: new insights into brain health
2024-09-04
Microglia are the brain’s immune cells known to play a vital role in maintaining neural function and responding to potential threats. However, when the brain is subjected to hyperosmotic stress—a condition characterized by elevated extracellular sodium levels, the microglial response can become exaggerated, leading to potentially harmful effects. Understanding the mechanisms behind this heightened response is crucial for the treatment of hypernatremia-induced neurological dysfunctions.
To ...
Breaking the link between obesity and atrial fibrillation with a new cellular target
2024-09-04
A cellular link between obesity and atrial fibrillation — a heart condition that afflicts over 33 million people worldwide — presents a promising target for new therapies, researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago report.
Obesity is among the leading causes of atrial fibrillation, an irregular heart rhythm that can lead to heart failure and stroke. But scientists still don’t know how high levels of body fat cause this heart condition.
In a new study published in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, UIC researchers identified a cellular pathway essential to obesity-induced ...
New research has potential to speed up forensic analysis in sexual assault cases
2024-09-04
A team of researchers has developed a radical new technique for analyzing evidence in sexual assault cases. The new approach could streamline the forensics pipeline and reduce delays in the processing of DNA evidence.
The research is described in a paper published today in the journal Advanced Science.
There are almost half a million sexual assaults in Canada every year with many more going unreported. The new approach could mitigate one of the reasons victims are reluctant to report assaults: the perception that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
[Press-News.org] Immune cells prevent lung healing after viral infectionInvestigators from Cedars-Sinai and University of Virginia identify pathways responsible for pulmonary fibrosis after viral infection