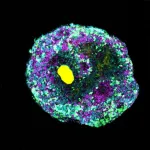
(Press-News.org) A new molecular engineering technique can precisely influence the development of organoids. Microbeads made of specifically folded DNA are used to release growth factors or other signal molecules inside the tissue structures. This gives rise to considerably more complex organoids that imitate the respective tissues much better and have a more realistic cell mix than before. An interdisciplinary research team from the Cluster of Excellence “3D Matter Made to Order” with researchers based at the Centre for Organismal Studies and the Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University, the university’s BioQuant Center as well as the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg developed the technique.
Organoids are miniature, organ-like tissue structures derived from stem cells. They are used in basic research to gain new insights into human development or to study the development of diseases. “Until now it wasn’t possible to control the growth of such tissue structures from their interior,” states Dr Cassian Afting, a Physician Scientist at the Centre for Organismal Studies (COS). “Using the novel technique, we can now determine precisely when and where in the growing tissue key developmental signals are released,” emphasizes Tobias Walther, a biotechnologist and doctoral candidate at the Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University (ZMBH) and the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg.
The interdisciplinary research team of biologists, physicians, physicists, and materials scientists constructed microscopically small beads of DNA that can be “loaded” with proteins or other molecules. These microbeads are injected into the organoids and release their cargo when exposed to UV light. This allows the release of growth factors or other signal molecules at any given time and location within the developing tissue.
The researchers tested the process on retinal organoids of the Japanese rice fish medaka by precisely inserting microbeads loaded with a Wnt signal molecule into the tissue. For the first time, they were able to induce retinal pigment epithelial cells – the outer layer of the retina – to form adjacent to neural retinal tissue. Previously, adding Wnt to the culture media would induce pigment cells but suppress neural retina development. “Thanks to the localized release of signaling molecules, we were able to achieve a more realistic mix of cell types, thereby more closely mimicking the natural cell composition of the fish eye than with conventional cell cultures,” explains Prof. Dr Kerstin Göpfrich, a researcher in the field of synthetic biology at the ZMBH and the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research.
According to the scientists, the DNA microbeads can be flexibly adapted to transport many different signal molecules in various types of cultivated tissue. “This opens up new possibilities for engineering organoids with improved cellular complexity and organization,” states Prof. Dr Joachim Wittbrodt, who directed the research work together with Prof. Göpfrich. “More sophisticated organoid models could accelerate research on human development and disease and potentially lead to better organoid-based drug research,” states the Heidelberg developmental biologist, whose research group is located at the COS.
The new technique for creating more complex organoids was developed in the Cluster of Excellence “3D Matter Made to Order”, which is operated jointly by Heidelberg University and the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology. The research work was funded by the European Research Council (ERC) within the framework of an ERC Starting Grant for Kerstin Göpfrich, and the German Research Foundation. A paper with the research results was published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
END
New molecular engineering technique allows for complex organoids
Interdisciplinary research team uses DNA microbeads to control the development of cultivated tissue
2024-09-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How the brain's inner chamber governs our state of consciousness
2024-09-09
In hospital operating rooms and intensive care units, propofol is a drug of choice, widely used to sedate patients for their comfort or render them fully unconscious for invasive procedures.
Propofol works quickly and is tolerated well by most patients when administered by an anesthesiologist. But what is happening inside the brain when patients are put under and what does this reveal about consciousness itself?
Investigators at U-M who are studying the nature of consciousness have successfully used the drug to identify the intricate brain geometry behind the unconscious state, offering an unprecedented ...
Can coping with a cancer diagnosis contribute to psychological and cardiovascular problems in family members?
2024-09-09
New research suggests that a family member’s cancer diagnosis may increase first-degree relatives’ and spouses’ risks of developing psychological and cardiovascular illnesses. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Having a family member diagnosed with cancer can be a stressful and traumatic experience for the entire family. Because stress influences not only mental health but also cardiovascular health, investigators explored whether a cancer diagnosis contributes ...
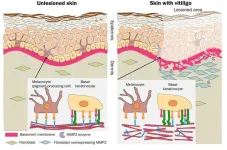
Loss of skin’s pigment-producing cells could be related to basement membrane disruption
2024-09-09
Skin pigmentation disorders affect people across the world. One of them, vitiligo, is said to have a worldwide incidence of 1-2%. What causes the loss of pigmentation in vitiligo has long been unclear, but an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has uncovered clues to the mechanism behind the disorder.
In findings published in The Journal of Pathology, Graduate School of Medicine Specially Appointed Associate Professor Lingli Yang, the corresponding author, and researchers including Specially Appointed Professor Ichiro ...
Developed proprietary quantum error correction technology beyond the world's leading quantum computing companies
2024-09-09
Solving the problem of error is essential for the practical application of quantum computing technologies that surpass the performance of digital computers. Information input into a qubit, the smallest unit of quantum computation, is quickly lost and error-prone. No matter how much we mitigate errors and improve the accuracy of qubit control, as the system size and computation scale increase, errors accumulate and algorithms become impossible to perform. Quantum error correction is a way to solve this problem. As the race for global supremacy in quantum technology intensifies, most major companies and research groups leading the development of quantum ...
AI will surpass human brains once we crack the ‘neural code’
2024-09-09
Humans will build Artificial Intelligence (AI) which surpasses our own capabilities once we crack the ‘neural code’, says an AI technology analyst.
Eitan Michael Azoff, a specialist in AI analysis, argues that humans are set to engineer superior intelligence with greater capacity and speed than our own brains.
What will unlock this leap in capability is understanding the ‘neural code’, he explains. That’s how the human brain encodes sensory information, and how it ...
RSV vaccination in older adults with health conditions is cost-effective
2024-09-09
Targeting vaccination programs for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) to older adults with underlying health conditions is a cost-effective way to reduce disease, according to a new modelling study https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240452 in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
RSV infections cause major illness, especially in infants and older adults, and rates of infection increase with age. There are now vaccines available to prevent disease caused by RSV in adults, and vaccination campaigns may reduce the incidence in older adults and associated ...
Melanoma incidence and mortality trends in Sweden
2024-09-09
About The Study: The findings of this cohort study showed a significant recent downward trend in both melanoma incidence and melanoma mortality in the age group 30 to 49 years in Sweden. The reasons for these declines are unclear but may include UV protection, public health campaigns, changing population demographics, and the introduction of effective melanoma treatment. None of these possibilities were evaluated; further study is needed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hildur Helgadottir, MD, PhD, email hildur.helgadottir@sll.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Breaking the trend: Skin cancer incidence in young adults declines
2024-09-09
The risk of skin cancer, malignant melanoma, now appears to be decreasing in Sweden - at least in those under 50, according to a new study.
“We can see a trend break in young adults around 2015 where the incidence curves are falling,” says first author Hildur Helgadottir, senior consultant and associate professor of oncology at the Department of Oncology-Pathology, Karolinska Institutet.
She and her research colleagues have analyzed data from the Swedish Melanoma Registry and followed melanoma incidence and mortality for different age segments over time. This means that they have compared individuals in a certain age range at one ...
ChatGPT outperformed trainee doctors in assessing complex respiratory illness in children
2024-09-09
The chatbot ChatGPT performed better than trainee doctors in assessing complex cases of respiratory disease in areas such as cystic fibrosis, asthma and chest infections in a study presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Congress in Vienna, Austria [1].
The study also showed that Google’s chatbot Bard performed better than trainees in some aspects and Microsoft’s Bing chatbot performed as well as trainees.
The research suggests that these large language models (LLMs) could be used to support trainee doctors, nurses and general practitioners to triage patients more quickly and ease pressure on health services.
The ...
Night owls are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes – and it’s not just because of an unhealthy lifestyle, Dutch study finds
2024-09-09
Night owls have a higher BMI, larger waists, more hidden body fat and are almost 50% more likely to develop type 2 diabetes (T2D) than those who go to bed earlier, new research to be presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid, Spain (9-13 September), has found.
Lead researcher Dr Jeroen van der Velde, of Leiden University Medical Centre, Leiden, Netherlands, says: “Previous studies have indicated that a late chronotype – preferring to go to bed late and wake up later – is associated with an unhealthy lifestyle. Late chronotypes are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
[Press-News.org] New molecular engineering technique allows for complex organoidsInterdisciplinary research team uses DNA microbeads to control the development of cultivated tissue