(Press-News.org) The world has not hit the brakes on methane emissions, a powerful driver of climate change. More than 150 nations have pledged to slash by 30% this decade under a global methane pledge, but new research shows global methane emissions over the past five years have risen faster than ever.
The trend “cannot continue if we are to maintain a habitable climate,” the researchers write in a Sept. 10 perspective article in Environmental Research Letters published alongside data in Earth System Science Data. Both papers are the work of the Global Carbon Project, an initiative chaired by Stanford University scientist Rob Jackson that tracks greenhouse gas emissions worldwide.
Atmospheric concentrations of methane are now more than 2.6 times higher than in pre-industrial times – the highest they’ve been in at least 800,000 years. Methane emission rates continue to rise along the most extreme trajectory used in emission scenarios by the world’s leading climate scientists.
The current path leads to global warming above 3 degrees Celsius or 5 degrees Fahrenheit by the end of this century. “Right now, the goals of the Global Methane Pledge seem as distant as a desert oasis,” said Jackson, who is the Michelle and Kevin Douglas Provostial Professor in the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability and lead author of the Environmental Research Letters paper. “We all hope they aren’t a mirage.”
More methane from fossil fuels, agriculture, and waste
Methane is a short-lived but highly potent greenhouse gas that comes from natural sources like wetlands and human or “anthropogenic” sources such as agriculture, fossil fuels, and landfills. During the first 20 years after release, methane heats the atmosphere nearly 90 times faster than carbon dioxide, making it a key target for limiting global warming in the near term.
Despite growing policy focus on methane, however, total annual methane emissions have increased by 61 million tons or 20% over the past two decades, according to the new estimates. Increases are being driven primarily by growth of emissions from coal mining, oil and gas production and use, cattle and sheep ranching, and decomposing food and organic waste in landfills.
“Only the European Union and possibly Australia appear to have decreased methane emissions from human activities over the past two decades,” said Marielle Saunois of the Université Paris-Saclay in France and lead author of the Earth System Science Data paper. “The largest regional increases have come from China and southeast Asia.”
In 2020, the most recent year for which complete data are available, nearly 400 million tons or 65% of global methane emissions came directly from human activities, with agriculture and waste contributing about two tons of methane for every ton from the fossil fuel industry. According to the researchers, human-caused emissions continued to increase through at least 2023.
Assessing pandemic impacts
Our atmosphere accumulated nearly 42 million tons of methane in 2020 – twice the amount added on average each year during the 2010s, and more than six times the increase seen during the first decade of the 2000s.
Pandemic lockdowns in 2020 reduced transport-related emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), which typically worsen local air quality but prevent some methane from accumulating in the atmosphere. The temporary decline in NOx pollution accounts for about half of the increase in atmospheric methane concentrations that year – illustrating the complex entanglements of air quality and climate change.
“We’re still trying to understand the full effects of COVID lockdowns on the global methane budget,” said Jackson. “COVID changed nearly everything – from fossil fuel use to emissions of other gases that alter the lifetime of methane in the atmosphere.”
Quantifying humans’ influence on methane from wetlands and waterways
The Global Carbon Project scientists have made an important change in their latest accounting of global methane sources and “sinks,” which include forests and soils that remove and store methane from the atmosphere.
In previous assessments, they categorized all methane from wetlands, lakes, ponds, and rivers as natural. But the new methane budget makes a first attempt to estimate the growing amount of emissions from these types of sources that result from human influences and activities.
For instance, reservoirs built by people lead to an estimated 30 million tons of methane emitted per year, because newly submerged organic matter releases methane as it decomposes. “Emissions from reservoirs behind dams are as much a direct human source as methane emissions from a cow or an oil and gas field,” said Jackson, who published a new book about methane and climate solutions titled Into the Clear Blue Sky: The Path to Restoring Our Atmosphere (Scribner) in July.
The scientists estimate that about a third of wetland and freshwater methane emissions in recent years were influenced by human-caused factors including reservoirs and emissions increased by fertilizer runoff, wastewater, land use, and rising temperatures.
After a summer when severe weather and heat waves have given a glimpse of the extremes predicted in our changing climate, the authors write, “The world has reached the threshold of 1.5C increases in global average surface temperature, and is only beginning to experience the full consequences.”
Jackson is also a senior fellow at the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment and Precourt Institute for Energy. Other Stanford co-authors include Earth system science postdoctoral scholars Xueying Yu and Mengze Li, and Earth system science professor Steven J. Davis. Additional study authors are affiliated with Université Paris-Saclay, CSIRO and the Global Carbon Project, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center’s Biospheric Sciences Laboratory, Yale School of the Environment, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC), and the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature in Kyoto, Japan.
This research was supported by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, UNEP’s International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO), the Australian Government’s National Environmental Science Programme’s Earth Systems and Climate Change Hub, and Future Earth.
END
Methane emissions are rising faster than ever
2024-09-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study to explore novel marker in interstitial lung disease prognosis
2024-09-10
Researchers at the University of Exeter and clinical radiopharmaceutical company Serac Healthcare Ltd are researching a new molecular imaging marker which could help to detect disease progression sooner.
The novel imaging agent 99mTc-maraciclatide has been used to scan the first patient with the aim of evaluating the marker’s potential for predicting interstitial lung disease in a Phase II study titled ‘PRospective Evaluation of Interstitial Lung Disease progression with quantitative CT’ ...
Experimenting with different vapes could be crucial to help people quit smoking
2024-09-10
New research from the University of East Anglia (UEA) found that more than a third of quitters who were given a vape in A&E experimented with different devices bought from shops or online
People who smoke and had little experience with vapes were particularly receptive to an opportunistic approach in a medical setting
The study found that some quitters reduced their vaping significantly within a few months, showing that not everyone who uses an e-cigarette becomes dependent on vaping long-term
Peer-reviewed – Observational Study- People
Experimenting with commercially ...
Long-term exercisers have 'healthier' belly fat
2024-09-10
People with obesity who are long-time exercisers have healthier belly fat tissue and can store fat there more effectively than nonexercisers with obesity, according to a new study from a team of researchers at the University of Michigan.
The research team also grew fat tissue in the lab from cells collected from both exercisers and nonexercisers, and cells from the exercisers developed into a tissue that stored fat more effectively.
"Our findings indicate that in addition to being a means to expend calories, exercising regularly for several months to years seems to modify your fat tissue ...
Gene therapy effective in hereditary blindness
2024-09-10
Bothnia dystrophy is a form of hereditary blindness, prevalent in the region Västerbotten in Sweden. A new study at Karolinska Institutet published in Nature Communications shows that gene therapy can improve vision in patients with the disease.
Bothnia dystrophy occurs mainly in the region Västerbotten in Sweden, but the disease has also been identified in other parts of the world. The disease leads to progressive visual impairment due to the destruction of the visual cells in the retina. It is caused by an inherited genetic mutation ...
Report: Conscientiousness, not willpower, is a reliable predictor of success
2024-09-10
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — According to two psychologists, the field of psychological science has a problem with the concept of self-control. It has named self-control both a “trait” — a key facet of personality involving attributes like conscientiousness, grit and the ability to tolerate delayed gratification — and a “state,” a fleeting condition that can best be described as willpower. These two concepts are at odds with one another and are often confused, the authors report.
“Self-control is a cherished quality. People who have lots of it are celebrated and seen as morally righteous,” wrote University of Toronto psychology professor Michael Inzlicht ...
Advancing prison safety
2024-09-10
The lead article in the current issue of The Criminologist, written by Nancy Rodriguez, University of California Irvine professor of criminology, law and society, shines a light on the lack of prison violence metrics that could help advance safety.
“For the 800,000 persons currently confined and the 200,000 state and federal correctional officers who work within U.S. prisons, the threat of violence is a routine feature of daily life,” she writes. “Accounts from incarcerated persons and staff detail the ever-present threats ...
Towards a better understanding of epigenetics and dynamic gene silencing and reactivation
2024-09-10
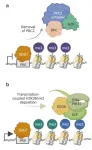
Ikoma, Japan – One of the most fascinating discoveries in biology is that cells have mechanisms for dynamically regulating genetic expression. This ability to promote or restrict the transcription of specific genes without altering the DNA sequences themselves is essential to all forms of life, from single-cell organisms to the most complex plants and animal species.
While our understanding of these so-called epigenetic mechanisms is far from complete, remarkable progress has been made in this field with the understanding of the role of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2). PRC2 is a protein that, in many plants, binds to specific DNA sequences called polycomb ...
Artificial muscles propel a robotic leg to walk and jump
2024-09-09
Inventors and researchers have been developing robots for almost 70 years. To date, all the machines they have built – whether for factories or elsewhere – have had one thing in common: they are powered by motors, a technology that is already 200 years old. Even walking robots feature arms and legs that are powered by motors, not by muscles as in humans and animals. This in part suggests why they lack the mobility and adaptability of living creatures.
A new muscle-powered robotic leg is not only more energy efficient than a conventional one, it can also perform high jumps and fast movements as well as detect and react to obstacles – ...
Researchers develop reaction-induced molybdenum carbides for efficient carbon dioxide conversion
2024-09-09
Molybdenum (Mo) carbides, known for their unique electronic and structural properties, are considered promising alternatives to noble metal catalysts in heterogeneous catalysis. However, traditional methods for preparing Mo carbides suffer from complex processes, stringent synthesis conditions, challenging crystal regulation, and high energy consumption. Additionally, Mo carbides are susceptible to oxidation and deactivation, which poses a significant barrier to their widespread application.
In a study published in Nature Chemistry, a research group led by Prof. SUN Jian from the Dalian Institute ...
Researchers identify factor that drives prostate cancer-causing genes
2024-09-09
For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
EMBARGOED for release at 5 a.m. ET Sept. 9, 2024
Researchers identify factor that drives prostate cancer-causing genes
Factor previously known to play a role in advanced cancer is fundamental in early stages of cancer development
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — Researchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center have uncovered a key reason why a typically normal protein goes awry and fuels ...