(Press-News.org)
Ikoma, Japan – One of the most fascinating discoveries in biology is that cells have mechanisms for dynamically regulating genetic expression. This ability to promote or restrict the transcription of specific genes without altering the DNA sequences themselves is essential to all forms of life, from single-cell organisms to the most complex plants and animal species.
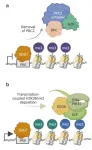
While our understanding of these so-called epigenetic mechanisms is far from complete, remarkable progress has been made in this field with the understanding of the role of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2). PRC2 is a protein that, in many plants, binds to specific DNA sequences called polycomb response elements (PREs) and applies a chemical mark to nearby histones (the structural support of DNA in the nucleus). Known as “trimethylation of H3K27 (H3K27me3),” this chemical modification prevents nearby genes from being converted into RNA and, in turn, into proteins, effectively silencing them. Despite this knowledge, however, scientists haven’t yet understood how genes silenced by PRC2 can be turned back on.
In a recent study published in eLife, a research team from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) in Japan sought to find answers to this puzzle. Led by Nobutoshi Yamaguchi, the team conducted extensive experiments on genetically modified Arabidopsis thaliana plants, revealing key parts of the complex epigenetic orchestra that goes on within these and many other organisms.
The researchers mostly focused on Set Domain-containing Protein 7 (SDG7), which is known to regulate the methylation of proteins in the cell cytosol (intracellular fluid). Preliminary experiments revealed that SDG7 is also present in the cell nucleus, which prompted the team to investigate further.
After an extensive series of analyses and measurements on mutant A. Thaliana cultures, the researchers uncovered a new role for SDG7. It turns out this protein also binds to PREs, competing with PRC2. Moreover, SDG7 can actually displace PRC2, preventing it from leaving the H3K27me3 mark. On top of this, SDG7 adds an active histone mark itself via the methylation of H3K36. After H3K36 methylation is in place, the protein pair SDG8 and Polymerase Associated Factor 1 (PAF1) spread this active mark across the gene’s body, resulting in efficient gene activation.
In a way, the histone sites H3K27 and H3K36 can be interpreted as a “switch” that can dynamically turn on and turn off the expression of specific genes. “This simple and elegant antagonistic molecular switch between H3K27 and H3K36 methylation is ideally suited for epigenetic reprogramming during plant development,” highlights Yamaguchi. “Since switching between H3K27 and H3K36 methylation has been seen in many flowering plants, the competitive mechanism between SDGs and PRC2 at PREs may be conserved across many plant species during for controlling development.”
This study sheds light on the intricate epigenetic mechanisms that countless species of plants and animals may rely on, potentially paving the way for future breakthroughs in the agricultural, horticultural, and farming fields. “We believe our findings will be of broad general interest to plant biologists and epigeneticists, given the widespread role of epigenetic regulation in gene expression during development and environmental responses,” concludes Yamaguchi.
###
Resource
Title: Arabidopsis SDG proteins mediate Polycomb removal and transcription-coupled H3K36 methylation for gene activation
Authors: Yicong Wang, Masato Abe, Yuka Kadoya, Takeru Saiki, Kanae Imai, Xuejing Wang, Taiko Kim To, Soichi Inagaki, Takamasa Suzuki, Tetsuji Kakutani, Toshiro Ito, Nobutoshi Yamaguchi
Journal: eLife
DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.100905.1
Information about the Plant Stem Cell Regulation and Floral Patterning Laboratory can be found at the following website: https://bsw3.naist.jp/eng/courses/courses112.html
About Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST)
Established in 1991, Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) is a national university located in Kansai Science City, Japan. In 2018, NAIST underwent an organizational transformation to promote and continue interdisciplinary research in the fields of biological sciences, materials science, and information science. Known as one of the most prestigious research institutions in Japan, NAIST lays a strong emphasis on integrated research and collaborative co-creation with diverse stakeholders. NAIST envisions conducting cutting-edge research in frontier areas and training students to become tomorrow's leaders in science and technology.
END
Inventors and researchers have been developing robots for almost 70 years. To date, all the machines they have built – whether for factories or elsewhere – have had one thing in common: they are powered by motors, a technology that is already 200 years old. Even walking robots feature arms and legs that are powered by motors, not by muscles as in humans and animals. This in part suggests why they lack the mobility and adaptability of living creatures.
A new muscle-powered robotic leg is not only more energy efficient than a conventional one, it can also perform high jumps and fast movements as well as detect and react to obstacles – ...
Molybdenum (Mo) carbides, known for their unique electronic and structural properties, are considered promising alternatives to noble metal catalysts in heterogeneous catalysis. However, traditional methods for preparing Mo carbides suffer from complex processes, stringent synthesis conditions, challenging crystal regulation, and high energy consumption. Additionally, Mo carbides are susceptible to oxidation and deactivation, which poses a significant barrier to their widespread application.
In a study published in Nature Chemistry, a research group led by Prof. SUN Jian from the Dalian Institute ...
For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
EMBARGOED for release at 5 a.m. ET Sept. 9, 2024
Researchers identify factor that drives prostate cancer-causing genes
Factor previously known to play a role in advanced cancer is fundamental in early stages of cancer development
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — Researchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center have uncovered a key reason why a typically normal protein goes awry and fuels ...
A new molecular engineering technique can precisely influence the development of organoids. Microbeads made of specifically folded DNA are used to release growth factors or other signal molecules inside the tissue structures. This gives rise to considerably more complex organoids that imitate the respective tissues much better and have a more realistic cell mix than before. An interdisciplinary research team from the Cluster of Excellence “3D Matter Made to Order” with researchers based at the Centre for Organismal Studies and the Center ...
In hospital operating rooms and intensive care units, propofol is a drug of choice, widely used to sedate patients for their comfort or render them fully unconscious for invasive procedures.
Propofol works quickly and is tolerated well by most patients when administered by an anesthesiologist. But what is happening inside the brain when patients are put under and what does this reveal about consciousness itself?
Investigators at U-M who are studying the nature of consciousness have successfully used the drug to identify the intricate brain geometry behind the unconscious state, offering an unprecedented ...
New research suggests that a family member’s cancer diagnosis may increase first-degree relatives’ and spouses’ risks of developing psychological and cardiovascular illnesses. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Having a family member diagnosed with cancer can be a stressful and traumatic experience for the entire family. Because stress influences not only mental health but also cardiovascular health, investigators explored whether a cancer diagnosis contributes ...
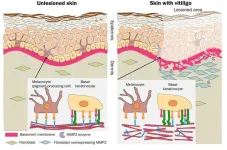
Skin pigmentation disorders affect people across the world. One of them, vitiligo, is said to have a worldwide incidence of 1-2%. What causes the loss of pigmentation in vitiligo has long been unclear, but an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has uncovered clues to the mechanism behind the disorder.
In findings published in The Journal of Pathology, Graduate School of Medicine Specially Appointed Associate Professor Lingli Yang, the corresponding author, and researchers including Specially Appointed Professor Ichiro ...
Solving the problem of error is essential for the practical application of quantum computing technologies that surpass the performance of digital computers. Information input into a qubit, the smallest unit of quantum computation, is quickly lost and error-prone. No matter how much we mitigate errors and improve the accuracy of qubit control, as the system size and computation scale increase, errors accumulate and algorithms become impossible to perform. Quantum error correction is a way to solve this problem. As the race for global supremacy in quantum technology intensifies, most major companies and research groups leading the development of quantum ...
Humans will build Artificial Intelligence (AI) which surpasses our own capabilities once we crack the ‘neural code’, says an AI technology analyst.
Eitan Michael Azoff, a specialist in AI analysis, argues that humans are set to engineer superior intelligence with greater capacity and speed than our own brains.
What will unlock this leap in capability is understanding the ‘neural code’, he explains. That’s how the human brain encodes sensory information, and how it ...
Targeting vaccination programs for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) to older adults with underlying health conditions is a cost-effective way to reduce disease, according to a new modelling study https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240452 in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
RSV infections cause major illness, especially in infants and older adults, and rates of infection increase with age. There are now vaccines available to prevent disease caused by RSV in adults, and vaccination campaigns may reduce the incidence in older adults and associated ...