(Press-News.org) Molybdenum (Mo) carbides, known for their unique electronic and structural properties, are considered promising alternatives to noble metal catalysts in heterogeneous catalysis. However, traditional methods for preparing Mo carbides suffer from complex processes, stringent synthesis conditions, challenging crystal regulation, and high energy consumption. Additionally, Mo carbides are susceptible to oxidation and deactivation, which poses a significant barrier to their widespread application.
In a study published in Nature Chemistry, a research group led by Prof. SUN Jian from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed a facile strategy to establish Mo carbide catalysts for efficient CO2 conversion, bypassing the complicated carburization process of traditional methods.
The researchers fabricated an Ir-modified MoO3 catalyst using a one-step flame spray pyrolysis (FSP) method, resulting in metastable Mo oxide species due to the rapid quenching from high temperatures. This unique structure facilitated reaction-induced carburization during the RWGS reaction, thus creating oxidation-resistant Mo oxycarbide (MoOxCy) active sites.
The catalyst exhibited excellent activity and stability, highlighting the superiority of reaction-induced Mo carbide catalysts. At 600°C, it achieved a CO production rate of 17.5 molgcat-1 h-1 with 100% CO selectivity. No significant deactivation was observed over a 2,000-hour stability test, showing its great potential for industrial applications.
Further investigation revealed that the crucial active sites in the RWGS reaction were the unsaturated MoOxCy species on the surface of Mo carbides. These species could maintain a dynamic equilibrium in the combined reduction, carburization, and oxidation atmosphere, preventing severe deactivation.
Additionally, the researchers proposed a new carbon cycle pathway in the RWGS reaction that was more thermodynamically favorable than the traditional redox pathway by promoting the H2 dissociation through *COH species. This pathway could act as a supplement to the redox mechanism, enhancing CO2 conversion on Mo carbides and leading to superior catalytic performance.
"Our study provides a low energy-consuming strategy for developing Mo carbides as efficient catalysts and paves the way for the application of a low-cost Mo-based catalyst system for CO2 utilization," said Prof. SUN.
END
Researchers develop reaction-induced molybdenum carbides for efficient carbon dioxide conversion
2024-09-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify factor that drives prostate cancer-causing genes
2024-09-09
For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
EMBARGOED for release at 5 a.m. ET Sept. 9, 2024
Researchers identify factor that drives prostate cancer-causing genes
Factor previously known to play a role in advanced cancer is fundamental in early stages of cancer development
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — Researchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center have uncovered a key reason why a typically normal protein goes awry and fuels ...
New molecular engineering technique allows for complex organoids
2024-09-09
A new molecular engineering technique can precisely influence the development of organoids. Microbeads made of specifically folded DNA are used to release growth factors or other signal molecules inside the tissue structures. This gives rise to considerably more complex organoids that imitate the respective tissues much better and have a more realistic cell mix than before. An interdisciplinary research team from the Cluster of Excellence “3D Matter Made to Order” with researchers based at the Centre for Organismal Studies and the Center ...
How the brain's inner chamber governs our state of consciousness
2024-09-09
In hospital operating rooms and intensive care units, propofol is a drug of choice, widely used to sedate patients for their comfort or render them fully unconscious for invasive procedures.
Propofol works quickly and is tolerated well by most patients when administered by an anesthesiologist. But what is happening inside the brain when patients are put under and what does this reveal about consciousness itself?
Investigators at U-M who are studying the nature of consciousness have successfully used the drug to identify the intricate brain geometry behind the unconscious state, offering an unprecedented ...
Can coping with a cancer diagnosis contribute to psychological and cardiovascular problems in family members?
2024-09-09
New research suggests that a family member’s cancer diagnosis may increase first-degree relatives’ and spouses’ risks of developing psychological and cardiovascular illnesses. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Having a family member diagnosed with cancer can be a stressful and traumatic experience for the entire family. Because stress influences not only mental health but also cardiovascular health, investigators explored whether a cancer diagnosis contributes ...
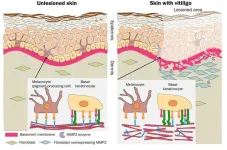
Loss of skin’s pigment-producing cells could be related to basement membrane disruption
2024-09-09
Skin pigmentation disorders affect people across the world. One of them, vitiligo, is said to have a worldwide incidence of 1-2%. What causes the loss of pigmentation in vitiligo has long been unclear, but an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has uncovered clues to the mechanism behind the disorder.
In findings published in The Journal of Pathology, Graduate School of Medicine Specially Appointed Associate Professor Lingli Yang, the corresponding author, and researchers including Specially Appointed Professor Ichiro ...
Developed proprietary quantum error correction technology beyond the world's leading quantum computing companies
2024-09-09
Solving the problem of error is essential for the practical application of quantum computing technologies that surpass the performance of digital computers. Information input into a qubit, the smallest unit of quantum computation, is quickly lost and error-prone. No matter how much we mitigate errors and improve the accuracy of qubit control, as the system size and computation scale increase, errors accumulate and algorithms become impossible to perform. Quantum error correction is a way to solve this problem. As the race for global supremacy in quantum technology intensifies, most major companies and research groups leading the development of quantum ...
AI will surpass human brains once we crack the ‘neural code’
2024-09-09
Humans will build Artificial Intelligence (AI) which surpasses our own capabilities once we crack the ‘neural code’, says an AI technology analyst.
Eitan Michael Azoff, a specialist in AI analysis, argues that humans are set to engineer superior intelligence with greater capacity and speed than our own brains.
What will unlock this leap in capability is understanding the ‘neural code’, he explains. That’s how the human brain encodes sensory information, and how it ...
RSV vaccination in older adults with health conditions is cost-effective
2024-09-09
Targeting vaccination programs for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) to older adults with underlying health conditions is a cost-effective way to reduce disease, according to a new modelling study https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240452 in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
RSV infections cause major illness, especially in infants and older adults, and rates of infection increase with age. There are now vaccines available to prevent disease caused by RSV in adults, and vaccination campaigns may reduce the incidence in older adults and associated ...
Melanoma incidence and mortality trends in Sweden
2024-09-09
About The Study: The findings of this cohort study showed a significant recent downward trend in both melanoma incidence and melanoma mortality in the age group 30 to 49 years in Sweden. The reasons for these declines are unclear but may include UV protection, public health campaigns, changing population demographics, and the introduction of effective melanoma treatment. None of these possibilities were evaluated; further study is needed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hildur Helgadottir, MD, PhD, email hildur.helgadottir@sll.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Breaking the trend: Skin cancer incidence in young adults declines
2024-09-09
The risk of skin cancer, malignant melanoma, now appears to be decreasing in Sweden - at least in those under 50, according to a new study.
“We can see a trend break in young adults around 2015 where the incidence curves are falling,” says first author Hildur Helgadottir, senior consultant and associate professor of oncology at the Department of Oncology-Pathology, Karolinska Institutet.
She and her research colleagues have analyzed data from the Swedish Melanoma Registry and followed melanoma incidence and mortality for different age segments over time. This means that they have compared individuals in a certain age range at one ...