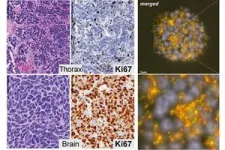
(Press-News.org) A team of doctors and researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) have identified a new, rare type of small cell lung cancer that primarily affects younger people who have never smoked.
Their findings, which include a detailed analysis of the clinical and genetic features of the disease, also highlight vulnerabilities that could help doctors make better treatment decisions for people diagnosed with it.
“It’s not every day you identify a new subtype of cancer,” says Natasha Rekhtman, MD, PhD, an MSK pathologist specializing in lung cancer and the first author of a paper published August 26 in Cancer Discovery presenting the team’s analysis. “This new disease type has distinct clinical and pathological features, and a distinct molecular mechanism.”
The study brought together the expertise of 42 physicians and researchers across MSK — from the doctors who treat lung cancer and the pathologists who evaluate cells and tissues to make a diagnosis, to specialists in tumor genetics and computational analysis.
“Understanding this new type of lung cancer required a broad spectrum of expertise from the laboratory to the clinic,” says Charles Rudin, MD, PhD, a lung cancer specialist and the study’s senior author.
Defining a New Lung Cancer Subtype: Atypical Small Cell Carcinoma
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is relatively rare to begin with, accounting for 10% to 15% of all lung cancers, according to the American Cancer Society. And the newly discovered subtype accounts for just a fraction of those. Out of 600 patients with SCLC whose cancers were analyzed for the study, only 20 people (or 3%) were found to have the rare subtype.
SCLC is normally characterized by the deactivation of two genes that protect against the development of cancer — RB1 and TP53 — but patients with the new subtype have intact copies of those genes. Instead, most carried a signature “shattering” of one or more of the chromosomes in their cancer cells, an event known as chromothripsis.
The new subtype appears to arise through a transformation of lower-grade neuroendocrine tumors (pulmonary carcinoids) into more aggressive carcinomas. The research team has dubbed the new type “atypical small cell lung carcinoma.”
“Patients who develop small cell lung cancer tend to be older and have a significant history of smoking,” says Dr. Rudin, the Deputy Director of MSK’s Cancer Center. “The first patient we identified with atypical SCLC, and whose case led us to look for more, was just 19 years old and not a smoker.”
This held true for the others with the subtype as well. The mean age at diagnosis was 53 — which is considered young; the average age for a lung cancer diagnosis is 70. Sixty-five percent of these patients were never smokers, while 35% reported a history of light smoking (less than 10 pack-years).
Treating Atypical Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
The analysis also found that the unique genomic changes that give rise to atypical SCLC mean that standard, first-line, platinum-based chemotherapies don’t work as well. And their findings point toward some treatment strategies that may work better.
“We often talk about cancer as an ongoing buildup of mutations,” Dr. Rekhtman says. “But this cancer has a very different origin story. With chromothripsis, there’s one major catastrophic event that creates a Frankenstein out of the chromosome, rearranging things in a way that creates multiple gene aberrations, including amplification of certain cancer genes.”
That’s why patients with atypical SCLC may benefit, for example, from investigational drugs that target the unusual DNA structures that result from chromothripsis, known as extrachromosomal circular DNA, the researchers note.
One Patient Spurs a Detective Story
Khaliq Sanda was 19 and a college sophomore at Duke University when he was diagnosed with small cell lung cancer. By the time it was discovered, the cancer had already spread to other parts of his body.
“That is very unusual,” says Dr. Rudin, who was one of Khaliq’s doctors along with Lisa DeAngelis, MD, and others. “This is a type of cancer that’s almost always associated with heavy smoking. So that prompted us to begin looking for other similar examples of never-smokers with small cell lung cancer. And between the medical oncologists in the clinic and the pathologists examining these specimens, we identified a group of patients who fit this pattern.”
“And then we started to dig in to understand what’s really happening with these unusual cancers,” Dr. Rekhtman adds.
Family and Friends Show Their Love
Khaliq’s family lived in Georgia, but his academic excellence led to his acceptance into a program in Connecticut called A Better Chance of Westport, which provides young scholars of color an opportunity to attend one of the nation’s top-performing high schools. In Westport, he lived with Lori and Dave Sochol, who became a second family to him. When things got tough, the Sochols were right there with him.
“I never missed an appointment with him,” Lori Sochol says. “I loved him like a son.”
This photo of Khaliq Sanda with his mom Angela (right) and “second mom” Lori Sochol (center) graces the MSK Giving page set up in his memory. His friends and family raised more than $150,000 to help other young adults with cancer..
After his diagnosis, Khaliq’s mother, Angela Sanda, also relocated to Connecticut to help care for Khaliq until the doctors gave him the OK to return to college.
Despite interruptions for his treatments, Khaliq was determined to continue his college coursework. He graduated from Duke in 2018 with a bachelor’s degree in global health and biology. He hoped to one day go to medical school and become a psychiatrist. After graduation, Khaliq worked as a community outreach coordinator at MSK, where he helped to enroll taxi drivers in a program focused on reducing hypertension.
“People fell in love with him the first time they met him,” his mother says. That’s why he was affectionately known as the “Mayor of Westport” and the “King of Duke,” she added.
As Khaliq’s disease progressed, his family and friends never left his side. His parents, Angela and Oumarou Sanda, and his brother, Kimbo Sanda, temporarily relocated to spend Khaliq’s final months with him.
As Khaliq moved from crutches to a walker to a wheelchair, his mind remained sharp and his spirits high, Kimbo says.
“A point came where I had to physically pick him up and carry him,” says Kimbo, a physician who lives in Oklahoma. “But he never lost his spirit and his positivity. I can’t explain how much admiration and pride I have for the way he held himself through it all. It helped all of us — his family, his friends.”
When he could no longer negotiate stairs, his college friends and their families rented him an apartment with an elevator. Lori brought her Goldendoodle, Stella, by for visits.
Then, as the end came, dozens of his friends filled the waiting room at the hospital — some canceling vacations to come pay their respects.
“I’ve never seen anything like it,” Lori says. “And they all got to say goodbye.”
‘An Amazing Gift to Society and Science’
Khaliq lived for five years after his diagnosis, which is itself unusual — the five-year survival rate for patients with advanced SCLC is miniscule. The atypical form of the disease, however, tends to be somewhat less aggressive, the researchers say, noting that these patients also tend to be considerably younger and healthier than most people diagnosed with SCLC.
After Khaliq died in March 2021, local officials named a bridge in Westport in his memory. Loved ones raised more than $150,000 for MSK to help other young adults with cancer.
“The way you lived after your diagnosis inspired me,” one Sigma Nu fraternity brother wrote in one of the many online tributes to Khaliq. “I had no idea what to say to you, other than to say that I loved you, but you seemed fearless in the face of this new challenge.”
“The infectious laugh, the warmth, the intellect, the desire to be a part of a conversation. Khaliq was mine and everyone’s friend,” another tribute reads.
Dr. Rekhtman and Dr. Rudin praised Khaliq’s decision to donate tissue after he died so that his cancer could be further analyzed to help future patients.
“It was an amazing gift to society and science,” Dr. Rekhtman says.
Angela Sanda agrees, saying, “The doctors did everything they could for him. He received the best care. And I’m glad that they are learning things from his cancer that could help others.”
Research That Can Only Be Done in a Place Like MSK
The fact that Khaliq and his family turned to MSK for his care paved the way for the discovery of the new subtype, the doctors note.
That’s because MSK patients routinely have the DNA in their tumors sequenced with a test called MSK-IMPACT®. It analyzes changes to more than 500 key genes known to drive cancer and helps doctors identify drugs that will work best against the specific mutations that a patient’s cancer harbors.
“So not only were we looking at patients with specific demographic characteristics — young never-smokers — we were able to take advantage of this unique MSK resource to look for patients whose tumors shared the same genomic features as Khaliq’s,” Dr. Rekhtman says.
Moreover, the wealth of sequencing and treatment data available at MSK allowed researchers to compare treatment programs and outcomes from the patients they identified with the new subtype, which helped them zero in on strategies that may help other patients diagnosed with atypical SCLC.
“There were some major lessons we learned from these patients,” Dr. Rudin says. “In general, they don’t respond as well to standard treatments as typical SCLC patients, but our study suggests several potential emerging or established therapeutic opportunities.”
“This effort exemplifies the deep interconnection one finds between patient care and research at MSK,” Dr. Rudin says.
Additional Authors, Funding, and Disclosures
For a full list of authors, please refer to the journal article.
This work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute (R35 CA263816, U24 CA213274, P30 CA0087448), the Druckenmiller Center for Lung Cancer Research, and the Sharon and Jon Corzine Foundation.
Dr. Rekhtman reports serving on the scientific advisory board of Merck. Dr. Rudin reports serving as consultant for Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Chugai, D2G, Daiichi Sankyo, Hoffman-La Roche, Jazz, and Legend; and he serves on the scientific advisory boards of Auron, Bridge Medicines, DISCO, Earli, and Harpoon Therapeutics. For a full list of disclosures, please refer to the journal article.
Read the article: “Chromothripsis-mediated small cell lung carcinoma,” Cancer Discovery. DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0286
END
New, rare type of small cell lung cancer identified by MSK research team
2024-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Light pollution a new Alzheimer’s risk factor
2024-09-11
Outdoor light at night could be a significant risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, according to new research from Rush.
While light pollution is associated with increased risk of some disorders and diseases, this is the first time it had been associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
The study was conducted at Rush University System for Health and published in Frontiers in Neuroscience.
“Our research shows that there is an association in the U.S. between Alzheimer’s disease prevalence and exposure to light at night, particularly in those under the age of 65,” said lead investigator, Robin Voigt-Zuwala, PhD, an associate professor at Rush. “Nightly ...
Clovis people used Great Lakes camp annually 13,000 years ago
2024-09-11
Graphics // Photos
The earliest humans to settle the Great Lakes region likely returned to a campsite in southwest Michigan for several years in a row, according to a University of Michigan study.
Until recently, there was no evidence that people from the Clovis period had settled the Great Lakes region. Clovis people appeared in North America about 13,000 years ago, during the geologic epoch called the Pleistocene. During the Pleistocene, sheets of glaciers covered much of the world, including Michigan, making the land inhospitable for human settlers. But a 2021 U-M study confirmed that Clovis people built ...
Can having a stroke change your sleep?
2024-09-11
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 11, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have had a stroke may be more likely to sleep too much or too little compared to those without prior stroke, according to a study published in the September 11, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that stroke causes abnormal sleep; it only shows an association.
“Sleeping the right amount is considered essential for ideal brain and heart health,” said study author Sara Hassani, ...
Microscale robot folds into 3D shapes and crawls
2024-09-11
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have created microscale robots less than 1 millimeter in size that are printed as a 2D hexagonal “metasheet” but, with a jolt of electricity, morph into preprogrammed 3D shapes and crawl.
The robot’s versatility is due to a novel design based on kirigami, a cousin of origami, in which slices in the material enable it to fold, expand and locomote.
The team’s paper, “Electronically Configurable Microscopic Metasheet Robots,” published Sept. 11 in Nature Materials. The paper’s co-lead authors are postdoctoral ...
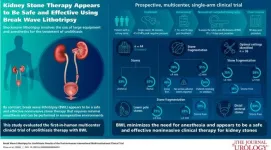
New noninvasive technique provides effective treatment for urinary stones
2024-09-11
September 11, 2024 — A noninvasive ultrasound technology called Break Wave™ lithotripsy (BWL) offers a safe and effective new option for treatment of urinary stones, reports a clinical trial in the October issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"In this initial experience, BWL provided a high treatment success rate, using a portable technology that can be used in a range of settings, without the need for anesthesia" comments lead ...
Researchers uncover new infection-fighting molecules through “molecular de-extinction”
2024-09-11
A new study led by Cesar de la Fuente, PhD, Presidential Assistant Professor of Psychiatry, Microbiology, Chemistry, Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania, has uncovered sequences for infection-fighting molecules in the genomic data of extinct species. This most recent study in the emerging field of “molecular de-extinction”, pioneered by Prof. de la Fuente, offers the potential to develop new antimicrobial treatments in the fight against rising antibiotic resistance.
The study, published in Cell Reports Physical Science, analyzed genomic data from the extinct moa, a flightless bird from New Zealand, ...
Keeping mold out of future space stations
2024-09-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Mold can survive the harshest of environments, so to stop harmful spores from growing on future space stations, a new study suggests a novel way to prevent its spread.
Researchers created a predictive approach for modeling unintended microbial growth in critical spaces and applied it to life on the International Space Station.
An analysis of dust samples obtained from the space station found that repeated elevated humidity exposures for even a short time can lead to rapid microbial growth and composition changes in dust that make it easier for microbes, ...
"It feels like I'm moving my own hand". A research team from the Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa has developed the prosthesis of the future, the first in the world with magnetic control
2024-09-11
Pisa, 11 september. It is the first magnetically controlled prosthetic hand, that allows amputees to reproduce all movements simply by thinking and to control the force applied when grasping fragile objects. No wires, no electrical connection, only magnets and muscles to control the movements of the fingers and enable everyday activities such as opening a jar, using a screwdriver, picking up a coin.
A research team from the BioRobotics Institute of the Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna in Pisa, coordinated by Prof. Christian Cipriani, has ...
Self-medicating gorillas and traditional healers provide clues for new drug discovery
2024-09-11
Four plants consumed by wild gorillas in Gabon and used by local communities in traditional medicine show antibacterial and antioxidant properties, find Leresche Even Doneilly Oyaba Yinda from the Interdisciplinary Medical Research Center of Franceville in Gabon and colleagues in a new study publishing September 11 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Wild great apes often consume medicinal plants that can treat their ailments. The same plants are often used by local people in traditional medicine.
To investigate, researchers observed the behavior of western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla ...
Trust in police declined among Black Chicago residents after Jacob Blake shooting
2024-09-11
Survey data collected from Chicago, Illinois at the time of the 2020 police shooting of Jacob Blake in nearby Wisconsin shows that trust in police plummeted among Black residents after the shooting. Jonathan Ben-Menachem and Gerard Torrats-Espinosa of Columbia University in New York, U.S., present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on September 11, 2024.
For young minority men in the U.S., police violence has become a leading cause of death. Prior research has explored how police violence and misconduct might reduce trust in police, but most studies have been limited in ...