(Press-News.org) A new convergent manufacturing platform, developed in only five months at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, is debuting at the International Manufacturing Technology Show, or IMTS, in Chicago, Sept. 9–12, 2024.
The technology, called Future Foundries, opens the door for hundreds of thousands of small- and medium-sized companies to join the convergent manufacturing revolution, according to ORNL researchers. It is a cutting-edge platform that integrates multiple advanced manufacturing systems into a single, agile platform.
“The democratization of manufacturing will be a key component to keep U.S. manufacturers internationally competitive,” said ORNL’s Chief Manufacturing Officer Craig Blue. “The convergent manufacturing approach we are demonstrating at IMTS is a significant step toward realizing this vision. It has the potential to enable the expansion of domestic supply chains by enabling small companies to have significant impacts in a broader range of products.”
Around 400,000 U.S. manufacturing companies employing more than 15 million people compete globally, with more than 80% of those companies small- or medium-sized. Scalable, flexible and cost-effective, Future Foundries levels the playing field for those companies.
“This is a game-changer,” said Thomas Feldhausen, R&D staff member in ORNL’s Disruptive Manufacturing Systems Development group and principal investigator for the initiative. “Convergent manufacturing platforms significantly reduce production times, enhance material properties and streamline the transition from prototype to deployment.”
In the past 20 years, the U.S. has lost 40% of domestic casting abilities to overseas facilities. Future Foundries offers a way to supplement existing U.S. casting facilities and, in doing so, help increase domestic production of critical energy components to help the country achieve its clean energy goals. This technology will also help strengthen the U.S. manufacturing base and support national security.
Multiple systems for many products
In Booth 236700 (North Building, Level 3, Emerging Technology Center) at IMTS, Future Foundries demonstrates wire-arc additive manufacturing, heat treatment, inspection and machining systems that are physically connected by a pallet changer that moves components between each of the systems. A smart manufacturing thread interconnects the entire platform, enabling communication between each robotic system and providing data to operators that can speed up production and inform future process improvements.
Core industry partners include Okuma and Fastems, which have provided both equipment and staff to help bring the platform together with ORNL’s team.
“This collaborative effort will provide attendees a glimpse at what can be done when talented engineers from several companies come together to demonstrate the future of manufacturing,” said Bob Baldizzi, Fastems sales manager. “Additive manufacturing technology has grown leaps and bounds in the last few years, but combining it with subtractive manufacturing and automation is quite a unique approach. Our automation solutions and dynamic scheduling software are a perfect fit for this application.”
ORNL will demonstrate the platform’s agility by running three demonstrations simultaneously — the repair of a wind turbine gear; the production of a component using readily available materials that typically would be cast; and the creation of six unique challenge coins, each made daily from the same injection mold. The platform makes variability of each mold possible.
“Now manufacturers can be adaptable,” Feldhausen said. “If you have a machine shop and you have to change something in your process, you no longer have to start from the ground up. This is modular, so you can easily change out different aspects. We’re presenting a solution with unprecedented modularity, flexibility, connectivity, reconfigurability, portability and customization capabilities.”
A history of “MDF Moonshots” at IMTS
ORNL’s manufacturing program has a reputation for cutting-edge, high-impact results with a long line of emerging technologies, or “moonshots,” that have been displayed at IMTS. A decade ago, the lab collaborated with Local Motors and Cincinnati Incorporated to print, machine and assemble a fully operational car, called Strati, in real time at the trade show.
“Moonshots like the Strati and, now, Future Foundries underscore the innovative nature of the MDF for bringing together multidisciplinary research teams to solve complex challenges in collaboration with industry,” said Ryan Dehoff, Manufacturing Demonstration Facility, or MDF, director. “The MDF takes strategic risks so industry doesn’t have to, and we demonstrate what’s possible through the development of advanced manufacturing technology platforms of the future like Future Foundries.”
Printing the Strati demonstrated what could be possible through big area additive manufacturing, or BAAM, another ORNL-developed technology. The event 10 years ago, along with subsequent technology advancements, helped launch today’s thriving global large-scale polymer printing industry.
To celebrate the 10th anniversary of Strati’s printing, the car will be on display at the outside entrance to IMTS at McCormick Place in Chicago all week.
Future Foundries was developed by a 40-plus-member, cross-disciplinary team at MDF that started work on the platform in April 2024. Following the IMTS show, the platform will return to MDF at ORNL where it will continue to serve as a foundation for ongoing research and development of convergent manufacturing technologies in support of U.S. industry. A 3D animation of the technology is available here.
The MDF, supported by DOE’s Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Office, or AMMTO, is a nationwide consortium of collaborators working with ORNL to innovate, inspire and catalyze the transformation of U.S. manufacturing. Funding for the platform is provided by AMMTO, as well as the Department of Defense Industrial Base and Analysis and Sustainment program.
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for DOE’s Office of Science, the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States. DOE’s Office of Science is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit energy.gov/science
A new convergent manufacturing platform, developed in only five months at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, is debuting at the International Manufacturing Technology Show, or IMTS, in Chicago, Sept. 9–12, 2024.
The technology, called Future Foundries, opens the door for hundreds of thousands of small- and medium-sized companies to join the convergent manufacturing revolution, according to ORNL researchers. It is a cutting-edge platform that integrates multiple advanced manufacturing systems into a single, agile platform.
“The democratization of manufacturing will be a key component to keep U.S. manufacturers internationally competitive,” said ORNL’s Chief Manufacturing Officer Craig Blue. “The convergent manufacturing approach we are demonstrating at IMTS is a significant step toward realizing this vision. It has the potential to enable the expansion of domestic supply chains by enabling small companies to have significant impacts in a broader range of products.”
Around 400,000 U.S. manufacturing companies employing more than 15 million people compete globally, with more than 80% of those companies small- or medium-sized. Scalable, flexible and cost-effective, Future Foundries levels the playing field for those companies.
“This is a game-changer,” said Thomas Feldhausen, R&D staff member in ORNL’s Disruptive Manufacturing Systems Development group and principal investigator for the initiative. “Convergent manufacturing platforms significantly reduce production times, enhance material properties and streamline the transition from prototype to deployment.”
In the past 20 years, the U.S. has lost 40% of domestic casting abilities to overseas facilities. Future Foundries offers a way to supplement existing U.S. casting facilities and, in doing so, help increase domestic production of critical energy components to help the country achieve its clean energy goals. This technology will also help strengthen the U.S. manufacturing base and support national security.
Multiple systems for many products
In Booth 236700 (North Building, Level 3, Emerging Technology Center) at IMTS, Future Foundries demonstrates wire-arc additive manufacturing, heat treatment, inspection and machining systems that are physically connected by a pallet changer that moves components between each of the systems. A smart manufacturing thread interconnects the entire platform, enabling communication between each robotic system and providing data to operators that can speed up production and inform future process improvements.
Core industry partners include Okuma and Fastems, which have provided both equipment and staff to help bring the platform together with ORNL’s team.
“This collaborative effort will provide attendees a glimpse at what can be done when talented engineers from several companies come together to demonstrate the future of manufacturing,” said Bob Baldizzi, Fastems sales manager. “Additive manufacturing technology has grown leaps and bounds in the last few years, but combining it with subtractive manufacturing and automation is quite a unique approach. Our automation solutions and dynamic scheduling software are a perfect fit for this application.”
ORNL will demonstrate the platform’s agility by running three demonstrations simultaneously — the repair of a wind turbine gear; the production of a component using readily available materials that typically would be cast; and the creation of six unique challenge coins, each made daily from the same injection mold. The platform makes variability of each mold possible.
“Now manufacturers can be adaptable,” Feldhausen said. “If you have a machine shop and you have to change something in your process, you no longer have to start from the ground up. This is modular, so you can easily change out different aspects. We’re presenting a solution with unprecedented modularity, flexibility, connectivity, reconfigurability, portability and customization capabilities.”
A history of “MDF Moonshots” at IMTS
ORNL’s manufacturing program has a reputation for cutting-edge, high-impact results with a long line of emerging technologies, or “moonshots,” that have been displayed at IMTS. A decade ago, the lab collaborated with Local Motors and Cincinnati Incorporated to print, machine and assemble a fully operational car, called Strati, in real time at the trade show.
“Moonshots like the Strati and, now, Future Foundries underscore the innovative nature of the MDF for bringing together multidisciplinary research teams to solve complex challenges in collaboration with industry,” said Ryan Dehoff, Manufacturing Demonstration Facility, or MDF, director. “The MDF takes strategic risks so industry doesn’t have to, and we demonstrate what’s possible through the development of advanced manufacturing technology platforms of the future like Future Foundries.”
Printing the Strati demonstrated what could be possible through big area additive manufacturing, or BAAM, another ORNL-developed technology. The event 10 years ago, along with subsequent technology advancements, helped launch today’s thriving global large-scale polymer printing industry.
To celebrate the 10th anniversary of Strati’s printing, the car will be on display at the outside entrance to IMTS at McCormick Place in Chicago all week.
Future Foundries was developed by a 40-plus-member, cross-disciplinary team at MDF that started work on the platform in April 2024. Following the IMTS show, the platform will return to MDF at ORNL where it will continue to serve as a foundation for ongoing research and development of convergent manufacturing technologies in support of U.S. industry. A 3D animation of the technology is available here.
The MDF, supported by DOE’s Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Office, or AMMTO, is a nationwide consortium of collaborators working with ORNL to innovate, inspire and catalyze the transformation of U.S. manufacturing. Funding for the platform is provided by AMMTO, as well as the Department of Defense Industrial Base and Analysis and Sustainment program.
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for DOE’s Office of Science, the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States. DOE’s Office of Science is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit energy.gov/science
END
ORNL debuts convergent manufacturing platform at IMTS 2024
2024-09-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insights could help prevent psychosis relapses in youth and young adults
2024-09-11
New findings from McGill University researchers could help clinicians understand the course of delusions in youth and young adults that signal the need for a timely intervention to prevent a full relapse of psychosis.
Delusions — strong beliefs that don't align with commonly accepted reality— are a defining symptom of psychosis but are not sufficiently understood.
For the first time, researchers studied whether delusion themes, such as paranoia or grandiosity, stay the same or shift between psychotic episodes in youth and young adults undergoing early intervention treatment.
The importance of timely ...
Biogeochemistry scientists from around the world, led by the ASC's Margenot, publish position paper on tackling “hidden” phosphorus
2024-09-11
As the world tries to mitigate agriculture’s effect on the environment, much of the story can be found in the soils, which stores and cycles nutrient elements of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Biogeochemistssuch as Andrew Margenot, Associate Director of the Agroecosystem Sustainability Center, are set to find answers, but for Margenot and other biogeochemistry experts who specialize in studying phosphorus cycling, the challenge is first being able to accurately measure where phosphorus has accumulated in the <100 years since humans began to increase ...
New, rare type of small cell lung cancer identified by MSK research team
2024-09-11
A team of doctors and researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) have identified a new, rare type of small cell lung cancer that primarily affects younger people who have never smoked.
Their findings, which include a detailed analysis of the clinical and genetic features of the disease, also highlight vulnerabilities that could help doctors make better treatment decisions for people diagnosed with it.
“It’s not every day you identify a new subtype of cancer,” says Natasha Rekhtman, MD, PhD, an MSK pathologist specializing in lung cancer and the first author of a paper published August 26 in Cancer Discovery presenting ...
Light pollution a new Alzheimer’s risk factor
2024-09-11
Outdoor light at night could be a significant risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, according to new research from Rush.
While light pollution is associated with increased risk of some disorders and diseases, this is the first time it had been associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
The study was conducted at Rush University System for Health and published in Frontiers in Neuroscience.
“Our research shows that there is an association in the U.S. between Alzheimer’s disease prevalence and exposure to light at night, particularly in those under the age of 65,” said lead investigator, Robin Voigt-Zuwala, PhD, an associate professor at Rush. “Nightly ...
Clovis people used Great Lakes camp annually 13,000 years ago
2024-09-11
Graphics // Photos
The earliest humans to settle the Great Lakes region likely returned to a campsite in southwest Michigan for several years in a row, according to a University of Michigan study.
Until recently, there was no evidence that people from the Clovis period had settled the Great Lakes region. Clovis people appeared in North America about 13,000 years ago, during the geologic epoch called the Pleistocene. During the Pleistocene, sheets of glaciers covered much of the world, including Michigan, making the land inhospitable for human settlers. But a 2021 U-M study confirmed that Clovis people built ...
Can having a stroke change your sleep?
2024-09-11
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 11, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have had a stroke may be more likely to sleep too much or too little compared to those without prior stroke, according to a study published in the September 11, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that stroke causes abnormal sleep; it only shows an association.
“Sleeping the right amount is considered essential for ideal brain and heart health,” said study author Sara Hassani, ...
Microscale robot folds into 3D shapes and crawls
2024-09-11
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have created microscale robots less than 1 millimeter in size that are printed as a 2D hexagonal “metasheet” but, with a jolt of electricity, morph into preprogrammed 3D shapes and crawl.
The robot’s versatility is due to a novel design based on kirigami, a cousin of origami, in which slices in the material enable it to fold, expand and locomote.
The team’s paper, “Electronically Configurable Microscopic Metasheet Robots,” published Sept. 11 in Nature Materials. The paper’s co-lead authors are postdoctoral ...
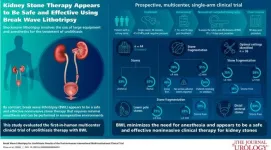
New noninvasive technique provides effective treatment for urinary stones
2024-09-11
September 11, 2024 — A noninvasive ultrasound technology called Break Wave™ lithotripsy (BWL) offers a safe and effective new option for treatment of urinary stones, reports a clinical trial in the October issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"In this initial experience, BWL provided a high treatment success rate, using a portable technology that can be used in a range of settings, without the need for anesthesia" comments lead ...
Researchers uncover new infection-fighting molecules through “molecular de-extinction”
2024-09-11
A new study led by Cesar de la Fuente, PhD, Presidential Assistant Professor of Psychiatry, Microbiology, Chemistry, Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania, has uncovered sequences for infection-fighting molecules in the genomic data of extinct species. This most recent study in the emerging field of “molecular de-extinction”, pioneered by Prof. de la Fuente, offers the potential to develop new antimicrobial treatments in the fight against rising antibiotic resistance.
The study, published in Cell Reports Physical Science, analyzed genomic data from the extinct moa, a flightless bird from New Zealand, ...
Keeping mold out of future space stations
2024-09-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Mold can survive the harshest of environments, so to stop harmful spores from growing on future space stations, a new study suggests a novel way to prevent its spread.
Researchers created a predictive approach for modeling unintended microbial growth in critical spaces and applied it to life on the International Space Station.
An analysis of dust samples obtained from the space station found that repeated elevated humidity exposures for even a short time can lead to rapid microbial growth and composition changes in dust that make it easier for microbes, ...