(Press-News.org)
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), encompassing Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract that significantly impacts the quality of life of patients. With an incidence of approximately one in 200 individuals in developed countries and a rising trend in developing and newly industrialized nations, IBD poses a substantial burden on healthcare systems. Due to the nonspecific nature of its clinical manifestations and the lack of a gold-standard diagnostic test, managing IBD effectively remains a challenge. Therefore, reliable and widely available biomarkers for monitoring disease activity and predicting treatment response are essential.
This review comprehensively examines the current landscape of biomarkers used in IBD management. The authors focus on both established and novel biomarkers, emphasizing their uses, threshold values, and clinical considerations.
Established Biomarkers
C-reactive protein (CRP): CRP is one of the most widely used biomarkers for monitoring IBD activity due to its low cost, ease of testing, and well-established protocols. It is an acute-phase reactant produced by hepatocytes in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines. However, its diagnostic value is limited by a lack of specificity, as elevations can also be caused by other inflammatory conditions. CRP is particularly useful in CD, where it correlates with moderate to severe clinical activity and evidence of active disease on ileocolonoscopy. In UC, the correlation is less clear, and normal CRP levels do not necessarily rule out active disease. Recent guidelines recommend monitoring CRP alongside fecal calprotectin in asymptomatic patients to avoid more invasive and costly testing.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): ESR is another commonly tested marker of inflammation, though it lacks specificity similar to CRP. It differs from CRP in its slower response to inflammation and longer normalization time. ESR can be affected by physiological factors such as pregnancy, age, and gender, as well as medication use, highlighting the importance of interpreting results in context.
Vitamin D: Vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in IBD patients and is associated with increased risk of disease recurrence, hospitalizations, and surgeries. Its role as an immune modulator suggests therapeutic potential, though further research is needed to determine optimal supplementation levels and therapeutic benefits.
Platelets: Platelets, often overlooked in IBD evaluations, play an active role in inflammatory processes. Reactive thrombocytosis, a well-established phenomenon in inflammation, has been observed in IBD patients, with platelets exhibiting increased sensitivity to activation even in clinically silent disease. Platelet changes may correlate with disease relapse in UC.
Novel Biomarkers
Recent studies have focused on developing novel biomarkers with improved specificity and predictive value for IBD management. Examples include:
Mucosal addressin cell-adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1): Elevated levels of MAdCAM-1 have been associated with inflammation and may predict response to vedolizumab, a monoclonal antibody used in IBD treatment.
Oncostatin M: Elevated oncostatin M levels could predict the risk of IBD development and potentially nonresponse to vedolizumab or corticosteroids.
NOD2 mutations: Genetic analysis for NOD2 mutations may be predictive of fibrostenotic disease in CD, though it is not specific for treatment response.
Anti-Integrin αvβ6: Blood levels of anti-Integrin αvβ6 are useful for diagnosing and predicting disease severity in UC, though they do not specifically predict treatment response.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the review highlights the crucial role of biomarkers in the management of IBD. While established biomarkers such as CRP, ESR, vitamin D, and platelets continue to play a vital role, novel biomarkers offer promise for improving diagnostic accuracy and predicting treatment response. Future research should focus on developing more sensitive and specific biomarkers that can guide personalized treatment plans, ultimately leading to better outcomes for IBD patients. The combination of established and novel biomarkers in biomarker panels and ratios may hold the key to more efficient and effective IBD management in the years to come.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2994-8754/JTG-2023-00086
The study was recently published in the Journal of Translational Gastroenterology.
Journal of Translational Gastroenterology (JTG) dedicates to improving clinical diagnosis and treatment, advancing understanding of the molecular mechanisms, and promoting translation from bench to bedside of gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary, and pancreatic diseases. The aim of JTG is to provide a forum for the exchange of ideas and concepts on basic, translational, and clinical aspects of gastroenterology, and promote cross-disciplinary research and collaboration.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
Researchers in Germany can harvest protein and vitamin B9 from microbes by feeding them nothing much more than hydrogen, oxygen, and CO2. The technology, published September 12 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Biotechnology, runs on renewable energy to produce a sustainable, micronutrient-enriched protein alternative that may one day make it to our plates.
“This is a fermentation process similar to how you make beer, but instead of giving the microbes sugar, we gave them gas and acetate,” says corresponding author Largus Angenent of the University of Tübingen, Germany. “We knew that yeast could produce vitamin B9 on their own with sugar, however, we didn’t ...
Neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders (NPD) including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, autism, and depression are detrimental to individuals, their families and society as a whole, and in many cases still lack effective treatments. It’s becoming more and more clear that genetic mutations in certain genes can increase the likelihood of developing NPD, and several hundreds of those “risk genes” have been identified to date, but their role related to NPD remains a mystery. “Very little is known about the basic function of most of these genes, and what we do know ...
About The Study: This case report describes a woman who presented with bilateral blurry vision a few days after dyeing her hair with hair dye containing aromatic amines.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicolas Chirpaz, MD, email nicolas.chirpaz@chu-lyon.fr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.3453)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
About The Study: This study found that certain social determinants of health affected monitoring for diabetic retinopathy similarly for Black and white patients with diabetes while others affected them differently. Patients living in rural communities, Black patients with preexisting diabetic retinopathy, and Hispanic white patients were not receiving eye care in accordance with clinical practice guidelines, which may contribute to worse outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dustin D. French, PhD, email dustin.french@northwestern.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
About The Study: This single-center cohort study identified substantial overall survival disparity and differing frequencies of driver gene variations by race and ethnicity. Socioeconomic status had the largest contribution but accounted for less than one-third of the disparity, with substantial contribution from tumor molecular features. Further study of the associations of genetic ancestry and the molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer with chemotherapy response is needed.
Corresponding ...
City of Hope and Biopharmaceutical Research Company announce first patient has received BRC-001, a first-in-class cannabinoid therapeutic, in a clinical trial investigating supportive care in breast cancer
Researchers will evaluate whether the cannabinoid therapeutic candidate can address joint pain resulting from cancer treatment using aromatase inhibitors
This side effect has caused many breast cancer patients to discontinue treatment
LOS ANGELES and MONTEREY, Calif. — City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, and Biopharmaceutical Research ...
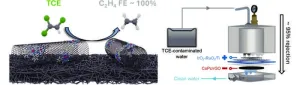
Connecticut, U.S.A -- Some chemicals create environmental problems; others, fortunately, can help clean them up.
Chemists from Yale University and their colleagues have developed an electrochemical catalyst and membrane that offers an efficient and sustainable way to treat water contaminated with trichloroethylene (TCE), a common and persistent environmental pollutant. Their findings highlight the potential for advanced electrochemical treatments in environmental remediation and open the door for further innovations in the field.
Their results were published in Carbon Future ...
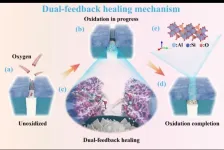
Fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) have been the primary choice for radome materials in hypersonic vehicles due to their high toughness, strength, and other advantageous properties. However, oxidation by oxygen in the atmospheric environment at elevated temperatures remains a significant obstacle to their further development. Thermal protection coatings offer a crucial avenue to mitigate this issue. Nonetheless, inherent material differences or fiber orientations within CMCs can lead to disparate thermal expansion rates between the matrix and fibers during temperature variations, inevitably ...
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [September 12, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—and the NCCN Foundation® proudly announce plans to make every book in the library of NCCN Guidelines for Patients® available in Spanish; with select editions available in additional languages as well.
NCCN publishes the NCCN Guidelines for Patients library through funding from the NCCN Foundation. It now features more than 70 books with easy-to-understand information about prevention, ...
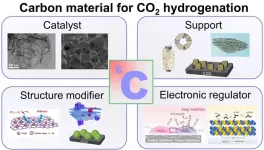
One of the primary drivers of climate change, CO2 emissions, have reached over 35 million tons worldwide. With global annual temperatures still rising, reducing CO2 emissions has become a necessity. To turn this necessity into an opportunity, researchers have been working to find ways to capture the CO2, thereby reducing emissions and then converting that CO2 into valuable chemicals and fuels.
One of the difficulties in working with CO2 is that it is very thermodynamically stable. To overcome this, additional ...