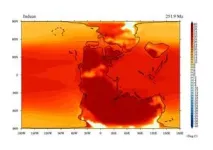
(Press-News.org) Mega ocean warming El Niño events were key in driving the largest extinction of life on planet Earth some 252 million years ago, according to new research.
The study, published today in Science and co-led by the University of Bristol and China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), has shed new light on why the effects of rapid climate change in the Permian-Triassic warming were so devastating for all forms of life in the sea and on land.
Scientists have long linked this mass extinction to vast volcanic eruptions in what is now Siberia. The resulting carbon dioxide emissions rapidly accelerated climate warming, resulting in widespread stagnation and the collapse of marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
But what caused life on land, including plants and usually resilient insects, to suffer just as badly has remained a source of mystery.
Co-lead author Dr Alexander Farnsworth, Senior Research Associate at the University of Bristol, said: “Climate warming alone cannot drive such devastating extinctions because, as we are seeing today, when the tropics become too hot, species migrate to the cooler, higher latitudes. Our research has revealed that increased greenhouse gases don’t just make the majority of the planet warmer, they also increase weather and climate variability making it even more ‘wild’ and difficult for life to survive.”
The Permian-Triassic catastrophe shows the problem of global warming is not just a matter of it becoming unbearably hot, but also a case of conditions swinging wildly over decades.
“Most life failed to adapt to these conditions, but thankfully a few things survived, without which we wouldn’t be here today. It was nearly, but not quite, the end of the life on Earth,” said co-lead author Professor Yadong Sun at China University of Geosciences, Wuhan.
The scale of Permian-Triassic warming was revealed by studying oxygen isotopes in the fossilised tooth material of tiny extinct swimming organisms called conodonts. By studying the temperature record of conodonts from around the world, the researchers were able to show a remarkable collapse of temperature gradients in the low and mid latitudes.
Dr Farnsworth, who used pioneering climate modelling to evaluate the findings, said: “Essentially, it got too hot everywhere. The changes responsible for the climate patterns identified were profound because there were much more intense and prolonged El Niño events than witnessed today. Species were simply not equipped to adapt or evolve quickly enough.”
In recent years El Niño events have caused major changes in rainfall patterns and temperature. For example, the weather extremes that caused the June 2024 North American heatwave when temperatures were around 15°C hotter than normal. 2023-2024 was also one of the hottest years on record globally due to a strong El Niño in the Pacific, which was further exacerbated by increased human-induced CO2 driving catastrophic drought and fires around the world.
“Fortunately such events so far have only lasted one to two years at a time. During the Permian-Triassic crisis, El Niño persisted for much longer resulting in a decade of widespread drought, followed by years of flooding. Basically, the climate was all over the place and that makes it very hard for any species to adapt,” co-author Paul Wignall, Professor of Palaeoenvironments at the University of Leeds.
The results of the climate modelling also help explain the abundant charcoal found in rock layers of that age.
“Wildfires become very common if you have a drought-prone climate. Earth got stuck in a crisis state where the land was burning and the oceans stagnating. There was nowhere to hide,” added co-author Professor David Bond, a palaeontologist at the University of Hull.
The researchers observed that throughout Earth’s history there have been many volcanic events similar to those in Siberia, and many caused extinctions, but none led to a crisis of the scale of the Permian-Triassic event.
They found Permian-Triassic extinction was so different because these Mega-El Niños created positive feedback on the climate which led to incredibly warm conditions starting in the tropics and then beyond, resulting in the dieback of vegetation. Plants are essential for removing CO2 from the atmosphere, as well as the foundation of the food web, and if they die so does one of the Earth's mechanisms to stop CO2 building up in the atmosphere as a result of continued volcanism.
This also helps explain the conundrum regarding the Permian-Triassic mass extinction whereby the extinction on land occurred tens of thousands of years before extinction in the oceans.
“Whilst the oceans were initially shielded from the temperature rises, the mega-El Nino’s caused temperatures on land to exceed most species thermal tolerances at rates so rapid that they could not adapt in time,” explained Dr Sun.
“Only species that could migrate quickly could survive, and there weren’t many plants or animals that could do that.”
Mass extinctions, although rare, are the heartbeat of the Earth’s natural system resetting life and evolution along different paths.
“The Permo-Triassic mass extinction, although devastating, would ultimately see the rise of Dinosaurs becoming the dominant species thereafter as would the Cretaceous mass extinction lead to the rise of mammals, and humans,” Dr Farnsworth concluded.
END
New research reveals how El Nino caused the greatest ever mass extinction
2024-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate-change-triggered landslide caused Earth to vibrate for nine days
2024-09-12
A landslide in a remote part of Greenland caused a mega-tsunami that sloshed back and forth across a fjord for nine days, generating vibrations throughout Earth, according to a new study involving UCL researchers.
The study, published in the journal Science, concluded that this movement of water was the cause of a mysterious, global seismic signal that lasted for nine days and puzzled seismologists in September 2023.
The initial event, not observed by human eye, was the collapse of a 1.2km-high mountain peak into the remote Dickson Fjord beneath, causing a backsplash of water 200 metres in the air, with a wave up to 110 metres high. This ...
Microbe dietary preferences influence the effectiveness of carbon sequestration in the deep ocean
2024-09-12
Woods Hole, Mass. (September 13, 2024) - The movement of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the surface of the ocean, where it is in active contact with the atmosphere, to the deep ocean, where it can be sequestered away for decades, centuries, or longer, depends on a number of seemingly small processes.
One of these key microscale processes is the dietary preferences of bacteria that feed on organic molecules called lipids, according to a journal article, "Microbial dietary preference and interactions affect the export of lipids to the deep ocean," published in Science.
"In ...
The insulator unraveled
2024-09-12
Aluminum oxide (Al2O3), also known as alumina, corundum, sapphire, or ruby, is one of the best insulators used in a wide range of applications: in electronic components, as a support material for catalysts, or as a chemically resistant ceramic, to name a few. Knowledge of the precise arrangement of the surface atoms is key to understanding how chemical reactions occur on this material, such as those in catalytic processes. Atoms inside the material follow a fixed arrangement, giving rise to the characteristic shapes ...
$3.5M grant to Georgia State will fuel space research across the globe
2024-09-12
ATLANTA — A new three-year, $3.5 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation will foster new research at Georgia State’s Center for High Angular Resolution Astronomy (CHARA) Array by astronomers from around the world.
The grant will fund open-access time at the CHARA Array through the NSF National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory (NSF NOIRLab). The program offers astronomers the opportunity to apply for observing time at the CHARA Array to investigate all kinds of objects ...
Polar molecules dance to the tunes of microwaves
2024-09-12
The interactions between quantum spins underlie some of the universe’s most interesting phenomena, such as superconductors and magnets. However, physicists have difficulty engineering controllable systems in the lab that replicate these interactions.
Now, in a recently published Nature paper, JILA and NIST Fellow and University of Colorado Boulder Physics Professor Jun Ye and his team, along with collaborators in Mikhail Lukin’s group at Harvard University, used periodic microwave pulses in a process known as Floquet engineering, to tune interactions between ultracold potassium-rubidium molecules in a system appropriate for studying fundamental magnetic ...
Quantum researchers cause controlled ‘wobble’ in the nucleus of a single atom
2024-09-12
Researchers from Delft University of Technology in The Netherlands have been able to initiate a controlled movement in the very heart of an atom. They caused the atomic nucleus to interact with one of the electrons in the outermost shells of the atom. This electron could be manipulated and read out through the needle of a scanning tunneling microscope. The research, published in Nature Communications today, offers prospects for storing quantum information inside the nucleus, where it is safe from external disturbances.
For weeks on end, the researchers studied a single titanium atom. “A Ti-47 atom, to be precise,” ...
Foods with low Nutri-Scores associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases
2024-09-12
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality in Western Europe, accounting for 1/3 of deaths in 2019. Diet is thought to be responsible for around 30% of such deaths. Nutrition-related prevention policies therefore constitute a major public health challenge for these diseases.
In an article to be published on 11 September 2024 in Lancet Regional Health - Europe, researchers from the Nutritional Epidemiology Research Team (CRESS-EREN), with members from Inserm, Inrae, Cnam, Université Sorbonne Paris Nord and Université Paris ...
Research reveals reality of Ice Age teen puberty
2024-09-12
Landmark new research shows Ice Age teens from 25,000 years ago went through similar puberty stages as modern-day adolescents. In a study published today in the Journal of Human Evolution of the timing of puberty in Pleistocene teens, researchers are addressing a knowledge gap about how early humans grew up.
Found in the bones of 13 ancient humans between 10 and 20 years old is evidence of puberty stages. Co-led by University of Victoria (UVic) paleoanthropologist April Nowell, researchers found specific markers in the bones that allowed them to assess the progress of adolescence.
“By analyzing specific areas of the skeleton, we inferred things like menstruation ...
Use of biomarkers in the management of inflammatory bowel disease
2024-09-12
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), encompassing Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract that significantly impacts the quality of life of patients. With an incidence of approximately one in 200 individuals in developed countries and a rising trend in developing and newly industrialized nations, IBD poses a substantial burden on healthcare systems. Due to the nonspecific nature of its clinical manifestations and the lack of a gold-standard diagnostic test, managing IBD effectively remains a challenge. Therefore, reliable and widely available biomarkers ...
Powered by renewable energy, microbes turn CO2 into protein and vitamins
2024-09-12
Researchers in Germany can harvest protein and vitamin B9 from microbes by feeding them nothing much more than hydrogen, oxygen, and CO2. The technology, published September 12 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Biotechnology, runs on renewable energy to produce a sustainable, micronutrient-enriched protein alternative that may one day make it to our plates.
“This is a fermentation process similar to how you make beer, but instead of giving the microbes sugar, we gave them gas and acetate,” says corresponding author Largus Angenent of the University of Tübingen, Germany. “We knew that yeast could produce vitamin B9 on their own with sugar, however, we didn’t ...