(Press-News.org)
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality in Western Europe, accounting for 1/3 of deaths in 2019. Diet is thought to be responsible for around 30% of such deaths. Nutrition-related prevention policies therefore constitute a major public health challenge for these diseases.
In an article to be published on 11 September 2024 in Lancet Regional Health - Europe, researchers from the Nutritional Epidemiology Research Team (CRESS-EREN), with members from Inserm, Inrae, Cnam, Université Sorbonne Paris Nord and Université Paris Cité, in collaboration with researchers from the International Agency for Research on Cancer (WHO-IARC), report an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases associated with the consumption of foods that rank less favourably on the Nutri-Score scale (new 2024 version) within the European cohort EPIC. A total of 345,533 participants from the cohort, spread across 7 European countries and followed for 12 years, were included in the analyses.
Officially adopted in France in 2017 (and in 6 other European countries since), the Nutri-Score aims to provide rapid information on the nutritional quality of foods and drinks to help and encourage consumers to compare them and choose those that offer a better nutritional quality. In parallel, it encourages manufacturers to improve the nutritional quality of their products.
The Nutri-Score has 5 categories, ranging from A (dark green – higher nutritional quality) to E (dark orange – lower nutritional quality). An algorithm ranks each product according to its levels – per 100 g – of energy, sugars, saturated fatty acids and salt (to limit) and proteins, fruits, vegetables and pulses (to favour).
A number of studies published in international scientific journals have shown the validity of Nutri-Score in characterising the nutritional quality of foods and its efficacy in guiding consumers towards more nutritious choices (over 140 publications). In particular, links between the consumption of foods with a less favourable Nutri-Score (lower nutritional quality) and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases have so far been observed in French studies (SU.VI.MAX and NutriNet-Santé cohorts). Studies in France, UK, Spain and Italy have also seen similar associations with an increased risk of various chronic diseases as well as higher mortality.
In this new study, the researchers focused on the latest version of the Nutri-Score algorithm (updated in 2024, see box), linked to the risk of cardiovascular diseases, in a large population spread across 7 European countries, with the aim of providing new scientific evidence for validating the Nutri-Score on a European scale. It follows two studies published in 2018 and 2020 in the same population on cancer risk and mortality.
A total of 345 533 participants from the EPIC (European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition) cohort were included in the analyses. During the follow-up (12 years, between 1992 and 2010), 16 214 participants developed a cardiovascular disease (6 565 of whom had myocardial infarction and 6 245 stroke). The findings show that the participants consuming on average more foods with less favourable Nutri-Score, reflecting lower nutritional quality, were at increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, particularly myocardial infarction and stroke. These associations were significant after a large number of sociodemographic and lifestyle factors were taken into account.
'These findings confirm the relevance of Nutri-Score as a public health tool to guide consumers in their food choices with the goal of preventing chronic diseases', emphasises Inserm researcher Mélanie Deschasaux-Tanguy.
‘They also provide key elements to support the adoption of Nutri-Score as a mandatory nutritional logo in Europe', explains Mathilde Touvier, Inserm research director.
A new version of the Nutri-Score in 2024
Changes to the calculation of the Nutri-Score[2] were recently proposed by the international scientific committee responsible for its monitoring in order to improve its consistency with nutritional recommendations. This new version of the Nutri-Score is expected to come into force in 2024 with a gradual roll-out in the months to come. However, due to European labelling regulations, manufacturers are under no obligation to use Nutri-Score on their packaging.
While many companies and brands (over 1,400 in France) have so far committed to using Nutri-Score on their products, harmonisation at European level is needed to ensure the mandatory implementation of a single logo that is effective and useful for citizens. This harmonisation is envisaged as part of the European Commission's Farm to Fork strategy.
[1] https://sante.gouv.fr/prevention-en-sante/preserver-sa-sante/nutrition/nutri-score/etudes-et-rapports-scientifiques/
[2] https://theconversation.com/en-2024-le-nutri-score-evolue-pourquoi-et-que-faut-il-en-retenir-221697
END
Landmark new research shows Ice Age teens from 25,000 years ago went through similar puberty stages as modern-day adolescents. In a study published today in the Journal of Human Evolution of the timing of puberty in Pleistocene teens, researchers are addressing a knowledge gap about how early humans grew up.
Found in the bones of 13 ancient humans between 10 and 20 years old is evidence of puberty stages. Co-led by University of Victoria (UVic) paleoanthropologist April Nowell, researchers found specific markers in the bones that allowed them to assess the progress of adolescence.
“By analyzing specific areas of the skeleton, we inferred things like menstruation ...
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), encompassing Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract that significantly impacts the quality of life of patients. With an incidence of approximately one in 200 individuals in developed countries and a rising trend in developing and newly industrialized nations, IBD poses a substantial burden on healthcare systems. Due to the nonspecific nature of its clinical manifestations and the lack of a gold-standard diagnostic test, managing IBD effectively remains a challenge. Therefore, reliable and widely available biomarkers ...
Researchers in Germany can harvest protein and vitamin B9 from microbes by feeding them nothing much more than hydrogen, oxygen, and CO2. The technology, published September 12 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Biotechnology, runs on renewable energy to produce a sustainable, micronutrient-enriched protein alternative that may one day make it to our plates.
“This is a fermentation process similar to how you make beer, but instead of giving the microbes sugar, we gave them gas and acetate,” says corresponding author Largus Angenent of the University of Tübingen, Germany. “We knew that yeast could produce vitamin B9 on their own with sugar, however, we didn’t ...
Neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders (NPD) including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, autism, and depression are detrimental to individuals, their families and society as a whole, and in many cases still lack effective treatments. It’s becoming more and more clear that genetic mutations in certain genes can increase the likelihood of developing NPD, and several hundreds of those “risk genes” have been identified to date, but their role related to NPD remains a mystery. “Very little is known about the basic function of most of these genes, and what we do know ...
About The Study: This case report describes a woman who presented with bilateral blurry vision a few days after dyeing her hair with hair dye containing aromatic amines.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicolas Chirpaz, MD, email nicolas.chirpaz@chu-lyon.fr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.3453)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
About The Study: This study found that certain social determinants of health affected monitoring for diabetic retinopathy similarly for Black and white patients with diabetes while others affected them differently. Patients living in rural communities, Black patients with preexisting diabetic retinopathy, and Hispanic white patients were not receiving eye care in accordance with clinical practice guidelines, which may contribute to worse outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dustin D. French, PhD, email dustin.french@northwestern.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
About The Study: This single-center cohort study identified substantial overall survival disparity and differing frequencies of driver gene variations by race and ethnicity. Socioeconomic status had the largest contribution but accounted for less than one-third of the disparity, with substantial contribution from tumor molecular features. Further study of the associations of genetic ancestry and the molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer with chemotherapy response is needed.
Corresponding ...
City of Hope and Biopharmaceutical Research Company announce first patient has received BRC-001, a first-in-class cannabinoid therapeutic, in a clinical trial investigating supportive care in breast cancer
Researchers will evaluate whether the cannabinoid therapeutic candidate can address joint pain resulting from cancer treatment using aromatase inhibitors
This side effect has caused many breast cancer patients to discontinue treatment
LOS ANGELES and MONTEREY, Calif. — City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, and Biopharmaceutical Research ...
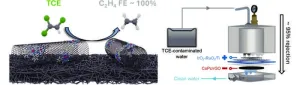
Connecticut, U.S.A -- Some chemicals create environmental problems; others, fortunately, can help clean them up.
Chemists from Yale University and their colleagues have developed an electrochemical catalyst and membrane that offers an efficient and sustainable way to treat water contaminated with trichloroethylene (TCE), a common and persistent environmental pollutant. Their findings highlight the potential for advanced electrochemical treatments in environmental remediation and open the door for further innovations in the field.
Their results were published in Carbon Future ...
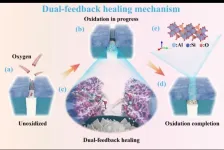
Fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) have been the primary choice for radome materials in hypersonic vehicles due to their high toughness, strength, and other advantageous properties. However, oxidation by oxygen in the atmospheric environment at elevated temperatures remains a significant obstacle to their further development. Thermal protection coatings offer a crucial avenue to mitigate this issue. Nonetheless, inherent material differences or fiber orientations within CMCs can lead to disparate thermal expansion rates between the matrix and fibers during temperature variations, inevitably ...