(Press-News.org)
Paprika oleoresin (PO), extracted from chili peppers, is renowned for its vibrant color and beneficial health properties, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. However, its lipophilic nature and sensitivity to factors like oxygen, heat, and light restrict its use in water-based foods. While previous approaches, including emulsions and liposomes, have aimed to improve PO’s stability, the results have been limited. These persistent challenges underscore the need for new stabilization methods for PO.
The study (DOI: 10.26599/FSAP.2024.9240064), led by scientists from Chengdu University and Huazhong Agricultural University, was published in the journal Food Science of Animal Products on August 23. The research utilized high-pressure homogenization (HPH) to restructure low-density lipoprotein (LDL) from egg yolk, producing a stable aqueous PO solution. By examining microstructure, particle size, encapsulation efficiency, and stability under various conditions, the study confirmed that HPH significantly enhances PO's solubility and stability, offering a greener, safer method of utilizing LDL as a bioactive carrier.
The researchers found that HPH at 100 MPa for 10 cycles decreased the average particle size of the LDL-PO complex by 37.2% and improved encapsulation efficiency by 9.2%. Stability assessments showed notable enhancements in storage, thermal, and UV irradiation resistance, with stability rates increasing from 30.83% to 62.90%, 64.42% to 76.97%, and 77.56% to 92.98%, respectively. Structural analysis revealed that HPH promotes better interaction between LDL and PO, optimizing the dispersion and stability of PO in water without compromising the lipoprotein’s structure.
“The innovative use of HPH to remodel LDL represents a significant advance in the stabilization of natural pigments like PO,” stated Dr. Jinqiu Wang, the study’s lead researcher. “This technique not only boosts LDL’s role as an effective carrier but also broadens the potential uses of natural colorants in various food products, marking a greener and safer approach to food processing.”
The study’s findings suggest that HPH could be extended to stabilize other fat-soluble bioactive compounds, enhancing their application in the food industry. This method offers a promising pathway toward more sustainable and efficient food production, leveraging LDL’s versatility as a carrier for diverse nutrients and active ingredients in aqueous solutions.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32072236), and Sichuan Innovation Team Project of National Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System (SCCXTD-2024-24).
About Food Science of Animal Products
Food Science of Animal Products, sponsored by Beijing Academy of Food Sciences, published by Tsinghua University Press and exclusively available via SciOpen, is a peer-reviewed, open access international journal that publishes the latest research findings in the field of animal-origin foods, involving food materials such as meat, aquatic products, milk, eggs, animal offals and edible insects. The research scope includes the quality and processing characteristics of food raw materials, the relationships of nutritional components and bioactive substances with human health, product flavor and sensory characteristics, the control of harmful substances during processing or cooking, product preservation, storage and packaging; microorganisms and fermentation, illegal drug residues and food safety detection; authenticity identification; cell-cultured meat, regulations and standards.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is an open access resource of scientific and technical content published by Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, identity management, and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
Atlanta, Georgia - In the wake of mounting evidence for the efficacy of psychedelic-assisted therapies, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is considering approving psilocybin, the active ingredient in “magic mushrooms,” for treating depression in the near future. As this watershed moment approaches, a critical question arises: Just how many people might stand to benefit from this promising but still unproven therapy?
Shedding light on this high-stakes inquiry, a first-of-its-kind peer-reviewed study led by researchers at Emory University, the University of Wisconsin-Madison and ...
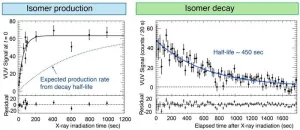
Scientists use atomic clocks to measure ‘second,’ the smallest standard unit of time, with great precision. These clocks use natural oscillations of electrons in atoms, similar to how pendulums work in old grandfather clocks. The quest for an even more precise timekeeper led to the discovery of nuclear clocks, which use the transitions of atomic nuclei instead of electrons to keep time.
A rising contender for the development of ultra-precise nuclear optical clocks is the nuclear first-excited state of 229Th isotope. Its long half-life of 103 seconds and low excitation energy of a few electron ...
In a new study by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), researchers analysed how erratic weather events, increasingly intensified by global warming, affect global production and consumption across different income groups. The results confirm previous studies that the poorest people worldwide bear the greatest economic risks from climate change. Surprisingly, the risk for the wealthy is growing the fastest. Economies in transition like Brazil or China are also highly vulnerable to severe impacts and negative trade ...
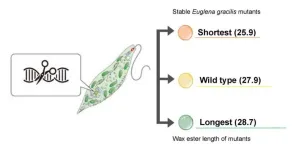
News about biofuels sometimes mentions used cooking oil as a feedstock, but if these substances contain animal fat, they can solidify in colder temperatures. This happens because, chemically, the fatty acids of these and many other saturated fats have long carbon chains with single bonds. Enter the euglena. An Osaka Metropolitan University team has found a way to have one species of this microalgae produce wax esters with shorter carbon chains than usual.
Using CRISPR/Cas9 to edit the genome of Euglena gracilis, Dr. Masami Nakazawa and her team at the Graduate School of Agriculture’s ...
A team led by Dr. Hyeon-Gyun Im and Dr. Dong Jun Kang from the Insulation Materials Research Center of Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI), in collaboration with Dr. Jung-keun Yoo from KIST and Professor Jong-soon Kim from Sungkyunkwan University, have developed a technology that enhances the performance of binders—often the 'unsung heroes' in the field of secondary batteries—while using environmentally friendly materials. This technology has been published in a prestigious international ...
CHICAGO (Sept 13, 2024)—Menopause is a natural life transition occurring when many women are at the “top of their game.” Unsupported menopause symptoms drive up employer healthcare costs and cause roughly $1.8 billion in missed workdays. To help employers retain these valued workers and build cultures of well-being, The Menopause Society launched Making Menopause Work™ based on new science-based Consensus Recommendations. The Recommendations are published online in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause ...
One of the most promising avenues for actively reducing CO2 levels in the atmosphere is recycling it into valuable chemicals via electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reactions. With a suitable electrocatalyst, this can be achieved under mild conditions and at a low energy cost. Many types of electrocatalysts are being actively investigated, but most suffer from either low electrocatalytic activity, poor selectivity, or low stability.
Metal sulfides might hold the huge potential solution to this puzzle. By combining ionic and covalent characteristics, this unique family of materials offers good catalytic activity and energy efficiency. The ternary metal system is expected to be a better ...
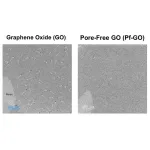
Kumamoto University’s research team, led by Assistant Professor Kazuto Hatakeyama and Professor Shintaro Ida of Institute of Industrial Nanomaterials, has announced a groundbreaking development in hydrogen ion barrier films using graphene oxide (GO) that lacks internal pores. This innovative approach promises significant advancements in protective coatings for various applications.
In their study, the research team successfully synthesized and developed a thin film from a new form of graphene oxide that does not contain pores. Traditionally, ...
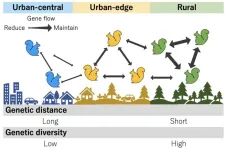
Since many kinds of wildlife have started living in urban environments, urban environments have been recognized as places of biodiversity conservation. What kind of factors facilitate or prohibit wildlife from living in urban environments? Understanding the population genetic structure of urban wildlife living would suggest the hint. In this study, we investigated the population genetic structure of Eurasian red squirrels living in urban to rural areas in Obihiro City, Hokkaido, Japan. As a result, we found that ...
Interim data from the Phase I dose escalation part of the mRNA cancer immunotherapy (mRNA-4359), show promise in patients with advanced solid cancers.
The investigational mRNA cancer immunotherapy is targeted for patients with lung cancer, melanoma and other solid tumours. Nineteen patients with advanced stage cancers received between one and nine doses of the immunotherapy treatment. Scientists have found the immunotherapy created an immune response against cancer and was well tolerated, with adverse events ...