(Press-News.org)
As the global demand for energy storage solutions grows, the limitations of current lithium-ion batteries, such as safety concerns and high costs, have driven the exploration of alternative technologies. Aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) have emerged as a promising candidate due to their inherent safety, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. However, challenges like zinc dendrite growth continue to hinder their widespread adoption. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing need to delve deeper into innovative solutions to improve AZIB performance.
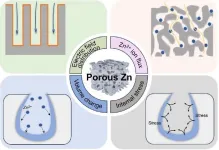
The study (DOI: 10.26599/EMD.2024.9370040), conducted by researchers from Tsinghua University and the University of Technology Sydney, was published in Energy Materials and Devices on August 16, 2024. It provides a comprehensive review of recent advancements in the engineering of porous zinc metal anodes for AZIBs. The focus of the research is on the structural orderliness of these porous anodes and their critical role in enhancing battery performance. The review underscores the potential of porous zinc anodes in overcoming the limitations of traditional planar zinc anodes.
The research highlights the significant advantages of porous zinc anodes over traditional planar zinc anodes. The porous structures provide numerous nucleation sites, which reduce the nuclear energy barriers and mitigate localized charge accumulation. This, in turn, suppresses dendrite growth, ensuring a longer battery lifespan. The study also emphasizes the role of three-dimensional porous structures in facilitating uniform electric field distribution and homogeneous ion flux, which are crucial for stable zinc deposition and stripping. Additionally, the substantial internal volume in these anodes accommodates volume changes and deposition stress, further enhancing battery performance. The review presents various fabrication techniques for porous zinc anodes, including etching, self-assembly, laser lithography, electrochemical methods, and 3D printing. The researchers also provide strategic insights into the design of porous zinc anodes to facilitate the practical implementation of AZIBs for grid-scale energy storage applications.
Prof. Dong Zhou, one of the lead researchers, remarked, "The development of porous zinc anodes represents a significant step forward in the advancement of zinc-ion batteries. By addressing the dendrite growth issue, we are moving closer to making AZIBs a commercially viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries. Our work not only provides a comprehensive understanding of the current advancements but also offers strategic insights into future research directions."
The innovative design of porous zinc anodes has the potential to revolutionize the field of energy storage. By improving the performance and safety of AZIBs, these anodes could enable the development of large-scale, sustainable energy storage systems, crucial for integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. Moreover, the advancements in porous zinc anodes could also lead to the development of safer and more cost-effective batteries for a wide range of applications, from electric vehicles to portable electronics, thus contributing to the global transition towards cleaner energy solutions.
This work is granted by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22309102), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2222M711788), National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No.2022YFB2404500), Fundamental Research Project of Shenzhen (Grant No. JCYJ20230807111702005), the Australian Research Council through the ARC Discovery Project (Grant No. DP230101579) and ACR Linkage Project (Grant No. LP200200926).
About Energy Materials and Devices
Energy Materials and Devices is launched by Tsinghua University, published quarterly by Tsinghua University Press, exclusively available via SciOpen, aiming at being an international, single-blind peer-reviewed, open-access and interdisciplinary journal in the cutting-edge field of energy materials and devices. It focuses on the innovation research of the whole chain of basic research, technological innovation, achievement transformation and industrialization in the field of energy materials and devices, and publishes original, leading and forward-looking research results, including but not limited to the materials design, synthesis, integration, assembly and characterization of devices for energy storage and conversion etc.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is an open access resource of scientific and technical content published by Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, identity management, and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
Trastuzumab deruxtecan shows substantial anti-cancer activity in brain metastases in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer in major international clinical trial
Results confirm findings of previous, smaller studies
BARCELONA, Spain - A drug that delivers chemotherapy directly to tumors has shown impressive activity against some of the hardest-to-reach cancer cells: those that have spread to the brain in patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer. The findings, from an international clinical trial led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers, reinforce earlier findings of the benefits ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Though a founding concept of ecology suggests that the physical environment determines where organisms can survive, modern scientists have suspected there is more to the story of how microbial communities form in the soil.
In a new study, researchers have determined through both statistical analysis and in experiments that soil pH is a driver of microbial community composition – but that the need to address toxicity released during nitrogen cycling ultimately shapes the final microbial community.
“The physical environment is affecting the nature of microbial interactions, and that affects the assembly of the community,” ...
Media Contact:
John Dudley
(814) 490-3290 (cell)
jjdudley@usf.edu
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
A species of single-celled organisms called foraminifera (forams) is increasing in warm, alkaline waters of the eastern Mediterranean, building beaches with their calcium carbonate skeletons.
In regions like Turke, forams are creating sandy shorelines where there used to be rocky terrain, benefiting tourism.
Forams thrive in warm waters with high CO2, suggesting they might continue growing as climate change accelerates.
This species of foram, once native to the Mediterranean, is returning as human activities make ...
In a world where organizing a simple meeting can feel like herding cats, new research from Case Western Reserve University reveals just how challenging finding a suitable meeting time becomes as the number of participants grows.
The study, published in the European Physical Journal B, dives into the mathematical complexities of this common task, offering new insights into why scheduling often feels so impossible.
“If you like to think the worst about people, then this study might be for you,” quipped researcher Harsh Mathur, ...
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 9 A.M. ET ON SEPT. 13, 2024
TAMPA, Fla. (Sept. 10, 2024) – Employees often feel pressure to work while sick, leading to lost productivity, deviant behaviors such as theft and mistreatment of coworkers and intent to leave the organization, according to new research led by University of South Florida Assistant Professor of Psychology Claire Smith. The cost of such behavior, known as “presenteeism,” can be staggering – as much as $150 billion annually, according to Harvard Business Review.
The findings will be ...
Paprika oleoresin (PO), extracted from chili peppers, is renowned for its vibrant color and beneficial health properties, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. However, its lipophilic nature and sensitivity to factors like oxygen, heat, and light restrict its use in water-based foods. While previous approaches, including emulsions and liposomes, have aimed to improve PO’s stability, the results have been limited. These persistent challenges underscore the need for new stabilization methods for PO.
The study (DOI: 10.26599/FSAP.2024.9240064), led by scientists from Chengdu University and Huazhong Agricultural ...
Atlanta, Georgia - In the wake of mounting evidence for the efficacy of psychedelic-assisted therapies, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is considering approving psilocybin, the active ingredient in “magic mushrooms,” for treating depression in the near future. As this watershed moment approaches, a critical question arises: Just how many people might stand to benefit from this promising but still unproven therapy?
Shedding light on this high-stakes inquiry, a first-of-its-kind peer-reviewed study led by researchers at Emory University, the University of Wisconsin-Madison and ...
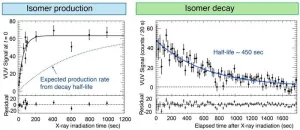
Scientists use atomic clocks to measure ‘second,’ the smallest standard unit of time, with great precision. These clocks use natural oscillations of electrons in atoms, similar to how pendulums work in old grandfather clocks. The quest for an even more precise timekeeper led to the discovery of nuclear clocks, which use the transitions of atomic nuclei instead of electrons to keep time.
A rising contender for the development of ultra-precise nuclear optical clocks is the nuclear first-excited state of 229Th isotope. Its long half-life of 103 seconds and low excitation energy of a few electron ...
In a new study by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), researchers analysed how erratic weather events, increasingly intensified by global warming, affect global production and consumption across different income groups. The results confirm previous studies that the poorest people worldwide bear the greatest economic risks from climate change. Surprisingly, the risk for the wealthy is growing the fastest. Economies in transition like Brazil or China are also highly vulnerable to severe impacts and negative trade ...
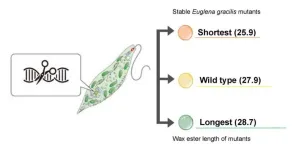
News about biofuels sometimes mentions used cooking oil as a feedstock, but if these substances contain animal fat, they can solidify in colder temperatures. This happens because, chemically, the fatty acids of these and many other saturated fats have long carbon chains with single bonds. Enter the euglena. An Osaka Metropolitan University team has found a way to have one species of this microalgae produce wax esters with shorter carbon chains than usual.
Using CRISPR/Cas9 to edit the genome of Euglena gracilis, Dr. Masami Nakazawa and her team at the Graduate School of Agriculture’s ...