(Press-News.org)
As the global population grows and traditional livestock production increasingly strains environmental resources, there is a rising interest in alternative protein sources. Edible insects, particularly grasshoppers, are abundant in regions like Cameroon and provide essential nutrients, including proteins, amino acids, and minerals vital for health and growth. Addressing these challenges calls for in-depth studies on the nutritional benefits of insects such as Ruspolia nitidula.
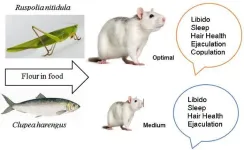
Conducted by the University of Dschang, Cameroon, and published (DOI: 10.26599/FSAP.2024.9240068) in the journal Food Science of Animal Products on August 30, this study examined the effects of substituting traditional Clupea harengus fish meal with Ruspolia nitidula grasshopper meal in rat diets. Over 12 weeks, researchers evaluated how this dietary change impacted libido, sleep, hair growth, and overall health, assessing the insect meal's potential as a viable alternative protein source.
The study demonstrated that replacing fish meal with Ruspolia nitidula grasshopper meal resulted in significant health improvements in rats. Those on the grasshopper diet exhibited enhanced libido, with increased intromissions and ejaculations compared to rats on fish meal or protein-deficient diets. Sleep quality also improved, with rats experiencing longer, more restful sleep. Hair quality was notably superior, with 94.58% of hairs in optimal condition in the grasshopper-fed group, compared to just 5.55% and 0.27% in the fish meal and protein-deficient groups. Additionally, the grasshopper-fed rats showed greater body weight gain, indicating overall better health and nutrition. These findings underscore the grasshopper meal's potential as a sustainable and nutritionally superior alternative protein source.
Dr. Ngnaniyyi Abdoul, the study's lead researcher, remarked, "Our findings highlight the significant potential of edible insects like Ruspolia nitidula as alternative protein sources. The grasshopper meal not only meets nutritional needs but also offers substantial health benefits, including improved libido, better sleep, and enhanced hair quality, with far-reaching implications for both animal and human diets."
This research emphasizes the potential of Ruspolia nitidula as a sustainable, nutrient-rich protein alternative. Beyond animal feed, the findings suggest that grasshopper meal could play a role in addressing human malnutrition, particularly in low-resource settings. With ecological advantages and health benefits, edible insects present a compelling solution for future food security and dietary enhancement.
The North Cameroon Association for Ecological and Food Transition (ABC-ECOLO) for funding this study.
About Food Science of Animal Products
Food Science of Animal Products, sponsored by Beijing Academy of Food Sciences, published by Tsinghua University Press and exclusively available via SciOpen, is a peer-reviewed, open access international journal that publishes the latest research findings in the field of animal-origin foods, involving food materials such as meat, aquatic products, milk, eggs, animal offals and edible insects. The research scope includes the quality and processing characteristics of food raw materials, the relationships of nutritional components and bioactive substances with human health, product flavor and sensory characteristics, the control of harmful substances during processing or cooking, product preservation, storage and packaging; microorganisms and fermentation, illegal drug residues and food safety detection; authenticity identification; cell-cultured meat, regulations and standards.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is an open access resource of scientific and technical content published by Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, identity management, and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
A new study sheds light on a promising approach using machine learning to more effectively allocate medical treatments during a pandemic or any time there’s a shortage of therapeutics.
The findings, published today in JAMA Health Forum, found a significant reduction in expected hospitalizations when using machine learning to help distribute medication using the COVID-19 pandemic to test the model. The model proves to reduce hospitalizations relatively by about 27 percent compared to actual and observed care.
“During the pandemic, the healthcare system was at a breaking point and many health care facilities relied on a first-come, first-serve or a patient’s ...
Island breeze, blue lagoon, dew drop—these aren’t the names of scented candles on display at your local home goods store. They’re flavors of synthetic nicotine used in e-cigarettes, often advertised with neon-electric colors and bright lettering to make them look like boxes of candy or fruit juice. But underneath all the flair, a specific label written clearly in black text on a white background is required by law to be there: a warning that says the product contains nicotine and that nicotine is an addictive substance.
Even though health warnings need to be written on physical products sold in stores ...
Mount Sinai researchers have identified a key driver of a blood vessel disorder known as fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) which affects up to five percent of the adult population and can lead to high blood pressure, heart attack, or stroke.
In a study published September 13 in Nature Cardiovascular Research, the team said changes in the gene UBR4 played an important role as a key driver of FMD. They suggested the discovery could be an important step toward developing a therapeutic approach for the disorder.
“Although fibromuscular dysplasia was first recognized more than 80 years ago, until now ...
About The Study: From 2019 to 2022, overall prescription volumes for stimulant and antidepressant medications increased, while prescription volume for opioids decreased. Concurrently, the proportion of telehealth prescriptions climbed across medications, increasing by a factor of 188 in opioids and more than 20 for antidepressants. These findings align with existing research highlighting the shift toward telehealth and the rise in stimulant and opioid telehealth prescribing during the pandemic. While in-person prescribing remains the most common, increasing telehealth ...
About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study of 3,389 patients with obesity, weight reduction at 1 year was associated with the medication’s active agent, its dosage, treatment indication, persistent medication coverage, and patient sex. Future research should focus on identifying the reasons for discontinuation of medication use and interventions aimed at improving long-term persistent coverage.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hamlet Gasoyan, PhD, email gasoyah@ccf.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
About The Study: This study’s results suggest discrepancies between preferred and actual sources of contraceptive information for assigned female at birth adolescents and young adults in the U.S. Findings underscore the role of clinicians in supporting informed contraceptive decision-making among adolescents and young adults. Clinicians were the most commonly preferred source, and receiving information from them was associated with having sufficient information to choose a contraceptive method; however, clinicians were the source with the largest discrepancy between preferred and actual use.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of synthetic nicotine brand Instagram accounts, 87% of sampled posts did not adhere to FDA health warning requirements in tobacco promotions. Enforcement of FDA compliant health warnings on social media may reduce youth engagement with tobacco marketing.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Traci Hong, PhD, email tjhong@bu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34434)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
UNDER EMBARGO Friday, September 13, 2024, 11 a.m. ET, CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study identified key factors that can impact the long-term weight loss of patients with obesity who were prescribed injectable semaglutide or liraglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes or obesity. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
“In patients with obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or liraglutide, we found that long-term weight reduction varied significantly based on the medication’s active agent, treatment indication, dosage and persistence with the medication,” said Hamlet Gasoyan, Ph.D., lead author of the study ...
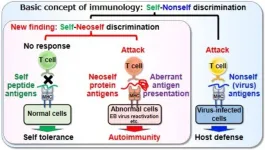
Osaka, Japan – Autoimmune diseases are widespread and notoriously difficult to treat. In part, this is because why the immune system attacks its own tissues in patients with these conditions remains poorly understood.
In a study recently published in Cell, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that the body’s own proteins with unusual structure trigger immune cells to unleash a wave of inflammation that leads to autoimmunity.
Autoimmune diseases develop when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues instead of fighting off foreign invaders like bacteria or viruses. However, it has long been a mystery why this happens, as ...
Scientists have developed new potential therapies that selectively remove aggregated tau proteins, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease, and improve symptoms of neurodegeneration in mice.
The team of scientists, from the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology (MRC LMB) in Cambridge, UK, and the UK Dementia Research Institute (UK DRI) at the University of Cambridge, say this promising approach could also be applied in future to other brain disorders driven by protein aggregation inside cells, ...