(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this retrospective cohort study of 3,389 patients with obesity, weight reduction at 1 year was associated with the medication’s active agent, its dosage, treatment indication, persistent medication coverage, and patient sex. Future research should focus on identifying the reasons for discontinuation of medication use and interventions aimed at improving long-term persistent coverage.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hamlet Gasoyan, PhD, email gasoyah@ccf.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.33326)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.33326?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=091324
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
One-year weight reduction with semaglutide or liraglutide in clinical practice
JAMA Network Open
2024-09-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adolescents and young adults’ sources of contraceptive information
2024-09-13
About The Study: This study’s results suggest discrepancies between preferred and actual sources of contraceptive information for assigned female at birth adolescents and young adults in the U.S. Findings underscore the role of clinicians in supporting informed contraceptive decision-making among adolescents and young adults. Clinicians were the most commonly preferred source, and receiving information from them was associated with having sufficient information to choose a contraceptive method; however, clinicians were the source with the largest discrepancy between preferred and actual use.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
Health warnings on Instagram advertisements for synthetic nicotine e-cigarettes and engagement
2024-09-13
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of synthetic nicotine brand Instagram accounts, 87% of sampled posts did not adhere to FDA health warning requirements in tobacco promotions. Enforcement of FDA compliant health warnings on social media may reduce youth engagement with tobacco marketing.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Traci Hong, PhD, email tjhong@bu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34434)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Cleveland Clinic study identifies key factors that can impact long-term weight loss in patients with obesity who were prescribed GLP-1 RA medications
2024-09-13
UNDER EMBARGO Friday, September 13, 2024, 11 a.m. ET, CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study identified key factors that can impact the long-term weight loss of patients with obesity who were prescribed injectable semaglutide or liraglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes or obesity. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
“In patients with obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or liraglutide, we found that long-term weight reduction varied significantly based on the medication’s active agent, treatment indication, dosage and persistence with the medication,” said Hamlet Gasoyan, Ph.D., lead author of the study ...
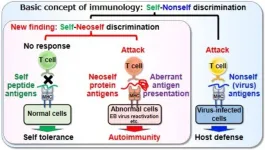
Neoself-antigens induce autoimmunity in lupus
2024-09-13
Osaka, Japan – Autoimmune diseases are widespread and notoriously difficult to treat. In part, this is because why the immune system attacks its own tissues in patients with these conditions remains poorly understood.
In a study recently published in Cell, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that the body’s own proteins with unusual structure trigger immune cells to unleash a wave of inflammation that leads to autoimmunity.
Autoimmune diseases develop when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues instead of fighting off foreign invaders like bacteria or viruses. However, it has long been a mystery why this happens, as ...
New therapy that targets and destroys tau tangles is a promising future Alzheimer’s disease treatment
2024-09-13
Scientists have developed new potential therapies that selectively remove aggregated tau proteins, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease, and improve symptoms of neurodegeneration in mice.
The team of scientists, from the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology (MRC LMB) in Cambridge, UK, and the UK Dementia Research Institute (UK DRI) at the University of Cambridge, say this promising approach could also be applied in future to other brain disorders driven by protein aggregation inside cells, ...
Study finds ‘supercharging’ T cells with mitochondria enhances their antitumor activity
2024-09-13
Fighting cancer is exhausting for T cells. Hostile tumor microenvironments can drain their mitochondrial activity, leading to a condition known as T cell exhaustion. This phenomenon also hinders adoptive cell therapies, in which healthy, tumor-targeting T cells are infused into patients with cancer. A novel method to boost mitochondrial activity and charge up T cells is needed.
Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, in collaboration with colleagues at Leibniz Institute for Immunotherapy in Germany, have developed a way to “supercharge” T cells by supplying them with extra mitochondria ...
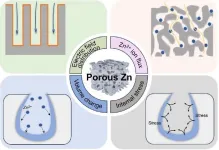
Harnessing the power of porosity: A new era for aqueous zinc-ion batteries and large-scale energy storage
2024-09-13
As the global demand for energy storage solutions grows, the limitations of current lithium-ion batteries, such as safety concerns and high costs, have driven the exploration of alternative technologies. Aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) have emerged as a promising candidate due to their inherent safety, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. However, challenges like zinc dendrite growth continue to hinder their widespread adoption. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing need to delve deeper ...
Antibody-drug conjugate found effective against brain metastases in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer
2024-09-13
Trastuzumab deruxtecan shows substantial anti-cancer activity in brain metastases in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer in major international clinical trial
Results confirm findings of previous, smaller studies
BARCELONA, Spain - A drug that delivers chemotherapy directly to tumors has shown impressive activity against some of the hardest-to-reach cancer cells: those that have spread to the brain in patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer. The findings, from an international clinical trial led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers, reinforce earlier findings of the benefits ...
Bacteria work together to thrive in difficult conditions
2024-09-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Though a founding concept of ecology suggests that the physical environment determines where organisms can survive, modern scientists have suspected there is more to the story of how microbial communities form in the soil.
In a new study, researchers have determined through both statistical analysis and in experiments that soil pH is a driver of microbial community composition – but that the need to address toxicity released during nitrogen cycling ultimately shapes the final microbial community.
“The physical environment is affecting the nature of microbial interactions, and that affects the assembly of the community,” ...
An ‘invasive’ marine organism has become an economic resource in the eastern Mediterranean
2024-09-13
Media Contact:
John Dudley
(814) 490-3290 (cell)
jjdudley@usf.edu
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
A species of single-celled organisms called foraminifera (forams) is increasing in warm, alkaline waters of the eastern Mediterranean, building beaches with their calcium carbonate skeletons.
In regions like Turke, forams are creating sandy shorelines where there used to be rocky terrain, benefiting tourism.
Forams thrive in warm waters with high CO2, suggesting they might continue growing as climate change accelerates.
This species of foram, once native to the Mediterranean, is returning as human activities make ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
[Press-News.org] One-year weight reduction with semaglutide or liraglutide in clinical practiceJAMA Network Open