(Press-News.org) UNDER EMBARGO Friday, September 13, 2024, 11 a.m. ET, CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study identified key factors that can impact the long-term weight loss of patients with obesity who were prescribed injectable semaglutide or liraglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes or obesity. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
“In patients with obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or liraglutide, we found that long-term weight reduction varied significantly based on the medication’s active agent, treatment indication, dosage and persistence with the medication,” said Hamlet Gasoyan, Ph.D., lead author of the study and a researcher with Cleveland Clinic’s Center for Value-Based Care Research.
Semaglutide (sold under the brand names Wegovy and Ozempic) and liraglutide (sold under the brand names Saxenda and Victoza) are glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, or GLP-1 RA medications. Those FDA-approved medications help lower blood sugar levels and promote weight loss.
Obesity is a complex chronic disease that affects more than 41% of the U.S. adult population. Clinical trials have shown that anti-obesity medications are effective; however, there is limited data in real-world settings regarding the factors associated with long-term weight change and clinically significant weight loss.
In this study, the researchers identified key factors that were associated with long-term weight loss of patients with obesity. They also indicated the elements that were linked to the probability of achieving 10% or more weight loss.
This retrospective cohort study included 3,389 adult patients with obesity who initiated treatment with injectable semaglutide or liraglutide between July 1, 2015, and June 30, 2022. Follow-up ended in July 2023.
At the start of the study, the median baseline body mass index among study participants was 38.5; 82.2% had type 2 diabetes as treatment indication. Among the patients, 68.5% were white, 20.3% were Black, and 7.0% were Hispanic. More than half of the participants were female (54.7%). Most of the patients received treatment for type 2 diabetes. Overall, 39.6% were prescribed semaglutide for type 2 diabetes, 42.6% liraglutide for type 2 diabetes, 11.1% semaglutide for obesity, and 6.7% liraglutide for obesity.
Results show that one year after the initial prescription’s fill, weight change was associated with the following factors:
The medication’s active agent. On average, weight change was -5.1% with semaglutide versus -2.2% with liraglutide.
The dosage. Patients experienced -3.5% mean weight change with low maintenance dose versus -6.6% with high dose.
Treatment indication. Patients who received the medications for type 2 diabetes experienced -3.2% in mean weight change compared to -5.9% for obesity treatment.
Persistence with medication. On average, patients who were persistent with the medication at one year experienced -5.5% weight change versus -2.8% among patients who had 90-275 medication coverage days within the first year and -1.8% among those with less than 90 covered days.
Researchers found that four in 10 patients (40.7%) were persistent with their medication one year after their initial prescription’s fill. The proportion of patients who were persistent with semaglutide was 45.8% versus 35.6% in patients receiving liraglutide.
Among patients who persisted with their medication at 12 months, the average reduction in body weight was -12.9% with semaglutide for obesity, compared to -5.9% with semaglutide for type 2 diabetes. The reduction in body weight was -5.6% with liraglutide for obesity, compared to -3.1% with liraglutide for type 2 diabetes.
Studies have shown that achieving sustained weight loss of 10% or more provides clinically significant health benefits. With that in mind, Dr. Gasoyan and colleagues looked at the proportion of patients who achieved 10% or more weight reduction.
Overall, 37.4% of patients receiving semaglutide for obesity achieved 10% or more body weight reduction compared to 16.6% of patients receiving semaglutide for type 2 diabetes. In comparison, 14.5% of those receiving liraglutide for obesity achieved 10% or more body weight reduction versus 9.3% of those receiving liraglutide for type 2 diabetes.
Among patients who persisted with their medication one year after their initial prescriptions, the proportion who achieved 10% or more weight reduction was 61% with semaglutide for obesity, 23.1% with semaglutide for type 2 diabetes, 28.6% with liraglutide for obesity, and 12.3% with liraglutide for type 2 diabetes.
Based on the study’s multivariable analysis that accounted for relevant socio-demographic and clinical variables, the following factors were associated with higher odds of achieving 10% or more weight reduction one year after the initial prescriptions:
Patients who received semaglutide versus liraglutide
A high maintenance dose of the medication versus low
Obesity as a treatment indication versus type 2 diabetes
Patients who persisted with the medication within the first year or had between 90-275 days of medication coverage versus less than 90 days of medication coverage
Patients who had higher initial BMI
Patients who were female versus male
“Our findings could help inform patients and providers regarding some of the key factors that are associated with the probability of achieving sustained weight loss of a magnitude large enough to provide clinically significant health benefits,” said Dr. Gasoyan. “Having real-world data could help manage expectations regarding weight reduction with GLP-1 RA medications and reinforce that persistence is key to achieve meaningful results.”
In a previous study, Dr. Gasoyan and colleagues looked at the factors influencing the long-term use of anti-obesity medications. Future research will continue to explore patients’ persistence and health outcomes with GLP-1 RA medications.
Dr. Gasoyan is supported by a grant from the National Cancer Institute.
About Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic is a nonprofit multispecialty academic medical center that integrates clinical and hospital care with research and education. Located in Cleveland, Ohio, it was founded in 1921 by four renowned physicians with a vision of providing outstanding patient care based upon the principles of cooperation, compassion and innovation. Cleveland Clinic has pioneered many medical breakthroughs, including coronary artery bypass surgery and the first face transplant in the United States. Cleveland Clinic is consistently recognized in the U.S. and throughout the world for its expertise and care. Among Cleveland Clinic’s 81,000 employees worldwide are more than 5,743 salaried physicians and researchers, and 20,160 registered nurses and advanced practice providers, representing 140 medical specialties and subspecialties. Cleveland Clinic is a 6,690-bed health system that includes a 173-acre main campus near downtown Cleveland, 23 hospitals, 276 outpatient facilities, including locations in northeast Ohio; Florida; Las Vegas, Nevada; Toronto, Canada; Abu Dhabi, UAE; and London, England. In 2023, there were 13.7 million outpatient encounters, 323,000 hospital admissions and observations, and 301,000 surgeries and procedures throughout Cleveland Clinic’s health system. Patients came for treatment from every state and 132 countries. Visit us at clevelandclinic.org. Follow us at twitter.com/CleClinicNews. News and resources available at newsroom.clevelandclinic.org.
Editor’s Note: Cleveland Clinic News Service is available to provide broadcast-quality interviews and B-roll upon request.
END
Cleveland Clinic study identifies key factors that can impact long-term weight loss in patients with obesity who were prescribed GLP-1 RA medications
Study focuses on FDA-approved injectable semaglutide and liraglutide
2024-09-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
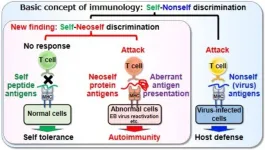
Neoself-antigens induce autoimmunity in lupus
2024-09-13
Osaka, Japan – Autoimmune diseases are widespread and notoriously difficult to treat. In part, this is because why the immune system attacks its own tissues in patients with these conditions remains poorly understood.
In a study recently published in Cell, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that the body’s own proteins with unusual structure trigger immune cells to unleash a wave of inflammation that leads to autoimmunity.
Autoimmune diseases develop when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues instead of fighting off foreign invaders like bacteria or viruses. However, it has long been a mystery why this happens, as ...
New therapy that targets and destroys tau tangles is a promising future Alzheimer’s disease treatment
2024-09-13
Scientists have developed new potential therapies that selectively remove aggregated tau proteins, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease, and improve symptoms of neurodegeneration in mice.
The team of scientists, from the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology (MRC LMB) in Cambridge, UK, and the UK Dementia Research Institute (UK DRI) at the University of Cambridge, say this promising approach could also be applied in future to other brain disorders driven by protein aggregation inside cells, ...
Study finds ‘supercharging’ T cells with mitochondria enhances their antitumor activity
2024-09-13
Fighting cancer is exhausting for T cells. Hostile tumor microenvironments can drain their mitochondrial activity, leading to a condition known as T cell exhaustion. This phenomenon also hinders adoptive cell therapies, in which healthy, tumor-targeting T cells are infused into patients with cancer. A novel method to boost mitochondrial activity and charge up T cells is needed.
Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, in collaboration with colleagues at Leibniz Institute for Immunotherapy in Germany, have developed a way to “supercharge” T cells by supplying them with extra mitochondria ...
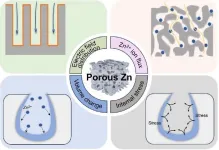
Harnessing the power of porosity: A new era for aqueous zinc-ion batteries and large-scale energy storage
2024-09-13
As the global demand for energy storage solutions grows, the limitations of current lithium-ion batteries, such as safety concerns and high costs, have driven the exploration of alternative technologies. Aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) have emerged as a promising candidate due to their inherent safety, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. However, challenges like zinc dendrite growth continue to hinder their widespread adoption. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing need to delve deeper ...
Antibody-drug conjugate found effective against brain metastases in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer
2024-09-13
Trastuzumab deruxtecan shows substantial anti-cancer activity in brain metastases in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer in major international clinical trial
Results confirm findings of previous, smaller studies
BARCELONA, Spain - A drug that delivers chemotherapy directly to tumors has shown impressive activity against some of the hardest-to-reach cancer cells: those that have spread to the brain in patients with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer. The findings, from an international clinical trial led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers, reinforce earlier findings of the benefits ...
Bacteria work together to thrive in difficult conditions
2024-09-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Though a founding concept of ecology suggests that the physical environment determines where organisms can survive, modern scientists have suspected there is more to the story of how microbial communities form in the soil.
In a new study, researchers have determined through both statistical analysis and in experiments that soil pH is a driver of microbial community composition – but that the need to address toxicity released during nitrogen cycling ultimately shapes the final microbial community.
“The physical environment is affecting the nature of microbial interactions, and that affects the assembly of the community,” ...
An ‘invasive’ marine organism has become an economic resource in the eastern Mediterranean
2024-09-13
Media Contact:
John Dudley
(814) 490-3290 (cell)
jjdudley@usf.edu
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
A species of single-celled organisms called foraminifera (forams) is increasing in warm, alkaline waters of the eastern Mediterranean, building beaches with their calcium carbonate skeletons.
In regions like Turke, forams are creating sandy shorelines where there used to be rocky terrain, benefiting tourism.
Forams thrive in warm waters with high CO2, suggesting they might continue growing as climate change accelerates.
This species of foram, once native to the Mediterranean, is returning as human activities make ...
Unveiling the math behind your calendar
2024-09-13
In a world where organizing a simple meeting can feel like herding cats, new research from Case Western Reserve University reveals just how challenging finding a suitable meeting time becomes as the number of participants grows.
The study, published in the European Physical Journal B, dives into the mathematical complexities of this common task, offering new insights into why scheduling often feels so impossible.
“If you like to think the worst about people, then this study might be for you,” quipped researcher Harsh Mathur, ...
New research finds employees feel pressure to work while sick, which has been shown to cost companies billions
2024-09-13
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 9 A.M. ET ON SEPT. 13, 2024
TAMPA, Fla. (Sept. 10, 2024) – Employees often feel pressure to work while sick, leading to lost productivity, deviant behaviors such as theft and mistreatment of coworkers and intent to leave the organization, according to new research led by University of South Florida Assistant Professor of Psychology Claire Smith. The cost of such behavior, known as “presenteeism,” can be staggering – as much as $150 billion annually, according to Harvard Business Review.
The findings will be ...
Harnessing egg yolk power: A new approach to paprika oleoresin stability
2024-09-13
Paprika oleoresin (PO), extracted from chili peppers, is renowned for its vibrant color and beneficial health properties, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. However, its lipophilic nature and sensitivity to factors like oxygen, heat, and light restrict its use in water-based foods. While previous approaches, including emulsions and liposomes, have aimed to improve PO’s stability, the results have been limited. These persistent challenges underscore the need for new stabilization methods for PO.
The study (DOI: 10.26599/FSAP.2024.9240064), led by scientists from Chengdu University and Huazhong Agricultural ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Cleveland Clinic study identifies key factors that can impact long-term weight loss in patients with obesity who were prescribed GLP-1 RA medicationsStudy focuses on FDA-approved injectable semaglutide and liraglutide