(Press-News.org) Each passing year, climate change drives summer temperatures to new extremes, with heat records being shattered one after another. In a new study, scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research (MPIDR) have examined how extreme temperatures in the US affect the mortality of people from different racial groups. Risto Conte Keivabu, Ugofilippo Basellini, and Emilio Zagheni (director of MPIDR) analyzed data from 1993 to 2005 and examined racial differences in temperature-related deaths. The study found that both extreme cold (temperatures in the coldest 5%) and extreme heat (temperatures in the hottest 5%) increase mortality rates, with heat disproportionate impacting racial minorities.
For their study, the researchers analyzed data from death registries in more than 3,000 U.S. counties and found clear evidence that hot days, in particular, have a disproportionate effect on minority communities. Using these results, the researchers extended their analysis to predict trends from 2006 to 2023, since they do not have data for that period. Their calculations suggest that the recent rise in temperatures has only worsened the racial disparities in heat-related deaths.
Minorities bear the brunt
These disparities are particularly pronounced when looking at the year 2022, one of the hottest summers on record. During this period, researchers calculated that the excess death rate for Non-Hispanic Blacks was about 26 per 100,000, while for whites it was about 15 per 100,000. The study also revealed large geographical differences in such estimates, further highlighting the uneven burden of extreme heat.
"While our study reveals critical insights, it also has some limitations. The data only goes back to 2005, so the effects of recent temperature increases may not have been fully reflected in our calculations. In addition, we also lacked Individual level socioeconomic data, which may be important for understanding the effects of temperature on mortality. Finally, our counterfactual analysis assumes that the association between heat and mortality persisted after the study period," explains Risto Conte Keivabu.
Despite these limitations the study makes a compelling case for immediate action. "Our findings highlight the critical needs of adaptation measures to shield vulnerable populations to the growing dangers of extreme temperatures," the researcher concludes.
END
Hardest hit by heat
Study exposes racial disparities in U.S. mortality rates
2024-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pigs may be transmission route of rat hepatitis E to humans
2024-09-25
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research suggests that pigs may function as a transmission vehicle for a strain of the hepatitis E virus (HEV) common in rats that has recently been found to infect humans.
The Rocahepevirus ratti strain is called “rat HEV” because rats are the primary reservoir of the virus. Since the first human case was reported in a person with a suppressed immune system in Hong Kong in 2018, at least 20 total human cases have been reported – including in people with normal immune function.
People infected with rat HEV did not report exposure to rats, leaving the cause of infection undefined. ...
The Foundation of Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (FCMSC) receives $100,000 gift for the June Halper MS Nursing Scholarship Fund
2024-09-25
(Hackensack, NJ, September 2024) The Foundation of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (FCMSC) recently received a generous donation of $100,000 from EMD Serono Inc., in honor of June Halper, MSN, APN-C, FAAN, MSCN. Ms. Halper a longtime pioneer in the comprehensive care movement for multiple sclerosis (MS), and leading nurse practitioner and MS advocate, passed away on July 24, 2024, at the age of 86, working until her final days as CEO of the CMSC, FCMSC and IOMSN (International Organization of MS Nurses).
Since 1978, Ms. ...
Effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on renal and pulmonary function in hepatic decompensation with and without hepatorenal and hepatopulmonary syndromes
2024-09-25
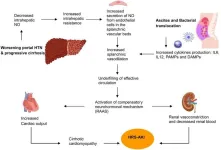
Cirrhosis is one of the leading causes of mortality from non-communicable diseases, with complications arising as liver function deteriorates. HRS and HPS represent the most severe outcomes of cirrhosis, associated with systemic vasodilation driven by elevated levels of vasodilators like nitric oxide (NO). These complications significantly impair renal and pulmonary functions, leading to high mortality rates. TIPS, by shunting blood from the portal to systemic circulation, can potentially improve renal function by increasing systemic blood volume. However, the diversion of NO through TIPS could exacerbate systemic hypotension, posing a risk to renal ...
Encoding human experience: Study reveals how brain cells compute the flow of time
2024-09-25
A landmark study led by UCLA Health has begun to unravel one of the fundamental mysteries in neuroscience – how the human brain encodes and makes sense of the flow of time and experiences.
The study, published in the journal Nature, directly recorded the activity of individual neurons in humans and found specific types of brain cells fired in a way that mostly mirrored the order and structure of a person’s experience. They found the brain retains these unique firing patterns after the experience is concluded and can rapidly replay them while at rest. Furthermore, the brain is also able to utilize these learned patterns to ready itself for future stimuli following that experience. ...
New study: Deep-sea discovery shines light on life in the twilight zone
2024-09-25
TAMPA, Fla. (Sept. 23, 2024) – The ocean’s twilight zone is deep, dark, and — according to new research — iron deficient.
No sunlight reaches this region 200 to 1,000 meters below the sea surface, where levels of iron, a key micronutrient, are so low that the growth of bacteria is restricted. To compensate, these bacteria produce molecules called siderophores, which help the bacteria scavenge trace amounts of iron from the surrounding seawater.
The paper detailing these unexpected findings from the Pacific Ocean will publish on Wednesday, Sept. 25, at 11 a.m. ET (4 p.m. London Time) in Nature, and will be viewable at that time at this link. The ...
Brazilian fossils reveal jaw-dropping discovery in mammal evolution
2024-09-25
These fossils, belonging to the mammal-precursor species Brasilodon quadrangularis and Riograndia guaibensis, offer critical insights into the development of the mammalian jaw and middle ear, revealing evolutionary experiments that occurred millions of years earlier than previously thought.
Mammals stand out among vertebrates for their distinct jaw structure and the presence of three middle ear bones. This transition from earlier vertebrates, which had a single middle ear bone, has long fascinated scientists. The new study explores how mammal ancestors, known as cynodonts, evolved these features ...
Now we know why children with Down’s syndrome have higher risk of Leukemia
2024-09-25
People with Down’s syndrome face a higher risk of developing Leukemia. Now researchers from the University of Copenhagen and Stanford University explain why, by identifying specific changes in blood cells of people with Down’s syndrome.
In the world, one out of 700 children are born with Down’s syndrome. A syndrome, where the child has an extra copy of chromosome 21, resulting in 47 chromosomes instead of 46. This typically results in characteristic physical features and some level of learning disability.
But newborns with Downs syndrome also tend to have an elevated number of red blood ...
Emerging SARS-CoV-2 resistance after antiviral treatment
2024-09-25
About The Study: Treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations were commonly detected, especially in individuals who were immunosuppressed in this cohort study of 156 participants. However, these mutations were generally present at low frequencies and were transient in nature, suggesting a low risk for the spread of nirmatrelvir resistance in the community with the current variants and drug usage patterns.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jonathan Z. Li, MD, MMsc, email jli@bwh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Semaglutide and opioid overdose risk in patients with type 2 diabetes and opioid use disorder
2024-09-25
About The Study: In this study, semaglutide was associated with reduced opioid overdose risk in patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes and opioid use disorder, suggesting its potential therapeutic value for preventing overdoses. The results need validation from other data resources and study populations. Further research is warranted to investigate the underlying mechanisms and randomized clinical trials are necessary to corroborate the clinical effects on opioid use disorder.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Rong Xu, PhD, (rxx@case.edu) ...
Bronze age lactobacillus genomes clarify kefir history
2024-09-25
Food fermentation is the oldest production practice using microorganisms in human history. Milk fermentation, for example, can be traced back to 6000–4000 BC in India, and Mediterranean populations produced and consumed cheese as early as 7000 before present (BP).
Despite the long history of human consumption of fermented products, though, little has been known about the history of the use of fermentative microorganisms and the history of related cultural transmission. In particular, the evolutionary trajectories, especially functional adaptation, of these ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Hardest hit by heatStudy exposes racial disparities in U.S. mortality rates