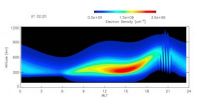
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON -- The first global simulation study of equatorial spread F (ESF) bubble evolution using a comprehensive 3D ionosphere model, SAMI3, has been demonstrated. The model self-consistently solves for the neutral wind driven dynamo electric field and the gravity driven electric field associated with plasma bubbles.
Developed by Dr. Joseph Huba and Dr. Glenn Joyce at the NRL Plasma Physics Division, SAMI3 is a fully three-dimensional model of the low- to mid-latitude ionosphere. SAMI3 has been modified recently to use a sun-fixed coordinate system to eliminate rotation of the dawn-dusk line and a high-resolution longitudinal grid to capture the evolution of equatorial plasma bubbles in the pre- to post-sunset sector.
The new modeling capability with SAMI3 has found that ESF can be triggered by pre-sunset ionospheric density perturbations and that an existing ESF plasma bubble can trigger a new bubble.
"Understanding and modeling ESF is important because of its impact on space weather," said Dr. Joseph Huba, head of the Space Plasma Physics Section of the Beam Physics Branch. "ESF anomalies can cause radio wave scintillation that degrades communication and navigation systems and serves as the primary focus of the Air Force Communications/ Navigation Outage Forecast System.
Post-sunset ionospheric irregularities in the equatorial F-region were first observed in 1938 by terrestrial magnetism researchers, H.G. Booker and H.W. Wells at the Carnegie Institution of Washington. During that time, analysis of the scattering of radio waves by the F-region of the ionosphere at an equatorial location (Huancayo, Peru) revealed ESF is fundamentally a nighttime event, with greatest frequency of occurrence in the period from four hours before midnight to four hours after midnight.
"The ionosphere builds up after sunrise and reaches a maximum electron density in mid-afternoon, said Huba. "Subsequently, the ionosphere can be lifted to higher altitudes just after sunset because of the pre-reversal enhancement of the eastward electric field. During this time the ionosphere can become unstable."
The F-region of the ionosphere is home to the F-layer, or Appleton layer, and is the densest part of the ionosphere as it extends from about 200 km to more than 500 km above the surface of Earth. Beyond this layer is the topside ionosphere. Here extreme ultraviolet solar radiation ionizes atomic oxygen. The F-layer consists of one layer at night, but during the day, a deformation often forms creating layers labeled F1 and F2 . The F-region is the region of the ionosphere that is very important for high-frequency (HF) radio wave propagation facilitating HF radio communications over long distances.
The upgraded version of SAMI3 represents a unique resource to investigate the physics of equatorial spread F, particularly the processes that control the day-to-day variability of ESFs. Future improvements to the current model include: modification to the geomagnetic field to have a tilt allowing the inclusion of longitudinal effects; coupling SAMI3 with a physics-based model of the thermosphere; and replacement of the full donor cell algorithm, currently being used for crossfield transport, with a high-order flux transport algorithm allowing for the capture of complex bubble evolution involving bifurcation.
INFORMATION:
NRL scientists develop 3-D model of the ionosphere F-region
2011-01-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The right food supplements during pregnancy?
2011-01-19
Nutrients, vitamins, minerals – during pregnancy a woman's body needs more of them. For most nutrients this increase in demand can be covered with a balanced diet. However, mothers-to-be should ingest some nutrients in the form of tablets. Research conducted by the Chair of Nutritional Medicine at the Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM) indicates there are knowledge gaps: According to this study, pregnant women often start taking sensible dietary supplements too late or not at all. At the same time, other micronutrients are unwittingly overdosed whose effects during ...
Surgeons, CCTV and TV football gain from new video technology that banishes shadows and flare
2011-01-19
Researchers at the University of Warwick have developed the world's first complete High Dynamic Range (HDR) video system, from video capture to image display, that will help a range of users including: surveillance camera operators, surgeons using video to conduct or record surgery, and camera crews following a football being kicked from sunshine into shadow.
The researchers will be premiering footage of the world's first ever showing of a short film shot using this new HDR technology in the WMG Digital Laboratory at the University of Warwick on Wednesday January 19 ...
Storytelling may help control blood pressure in African-Americans
2011-01-19
Controlling blood pressure is not only a medical challenge, but a social one as well. Because patients are required to strictly adhere to a treatment plan that may include medication, dietary restrictions and regular doctor visits, the ideas of wellness and health are also powerful parts of the social reinforcement needed for behavioral change.
This is especially true in the African American population, which is particularly susceptible to hypertension. Social and cultural barriers have been found to contribute to African American patients being far more likely than white ...
Research discovers why first impressions are so persistent
2011-01-19
New research by a team of psychologists from Canada, Belgium, and the United States shows there is more than a literal truth to the saying that 'you never get a second chance to make a first impression'. The findings suggest that new experiences that contradict a first impression become 'bound' to the context in which they were made. As a result, the new experiences influence people's reactions only in that particular context, whereas first impressions still dominate in other contexts.
"Imagine you have a new colleague at work and your impression of that person is not ...
First liver transplant patients receive experimental drug to prevent hepatitis C infection
2011-01-19
Boston, Mass. — Following a successful Phase 1 study for safety, researchers at MassBiologics of the University of Massachusetts Medical School (UMMS) today announced the beginning of a Phase 2 clinical trial testing the ability of a human monoclonal antibody they developed to prevent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection of a donor liver in transplant patients.
The first patients were enrolled in the study in December. The primary goal of this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study is to test if the monoclonal antibody, designated MBL-HCV1, prevents re-infection ...
Youth adapt faster than seniors to unexpected events
2011-01-19
Montreal, January 18, 2011 – Does experience give seniors an edge in reacting to sudden change or are younger people quicker to respond? A new study from Concordia University shows that when a routine task is interrupted by an unexpected event, younger adults are faster at responding. Published in the Journal of Gerontology, the findings have implications for educators and for older adults in situations where performance is crucial.
"When we frequently perform a task, our reactions become automatic," says Kevin Trewartha, first author and a PhD student in Concordia's ...
ESA's Mercury mapper feels the heat
2011-01-19
Key components of the ESA-led Mercury mapper BepiColombo have been tested in a specially upgraded European space simulator. ESA's Large Space Simulator is now the most powerful in the world and the only facility capable of reproducing Mercury's hellish environment for a full-scale spacecraft.
The Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter (MMO) has survived a simulated voyage to the innermost planet. The octagonal spacecraft, which is Japan's contribution to BepiColombo, and its ESA sunshield withstood temperatures higher than 350°C.
This is a taste of things to come for the ...
Discovery of a gene associated with a leukemia mostly affecting children
2011-01-19
Montreal, January 18, 2011 – Cyndia Charfi, a Ph. D student in biology at Université du Québec à Montréal (UQAM), supported by her thesis supervisors, Professor Éric Rassart, and Adjunct Professor Elsy Edouard, UQAM, Department of Biological Sciences and BIOMED Research Centre, made a major breakthrough in research on B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia, a disease that occurs most commonly in children. She has successfully identified a gene that may facilitate the diagnosis of this cancer, which is characterized by an abnormal proliferation of B-cells, antibody-producing ...
Keeping your digital secrets safe
2011-01-19
Privacy in the digital age is a sensitive issue for both governments and individuals, as recent news about WikiLeaks and Facebook proved. A new research project at Tel Aviv University may better educate citizens of the virtual world about their privacy -- and even help Facebook users avoid truly embarrassing moments.
It's all about fine-tuning privacy settings based on user information and behavior, says Dr. Eran Toch of Tel Aviv University's Iby and Aladar Fleischman Faculty of Engineering. His software solution, Locacino, is based on better security design, and provides ...
Adolescents with severe mental disorders have never received treatment
2011-01-19
18 January 2011 - A recent study by Merikangas and colleagues published in the January 2011 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP) shows that only half of adolescents that are affected with severely impairing mental disorders ever receive treatment for their disorders.
The researchers found that approximately one third of adolescents with any mental disorder received services for their illness (36.2%). Disorder severity was significantly associated with an increased likelihood of receiving treatment, yet only half of ...