(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA (September 26, 2024) – A groundbreaking article published in the latest issue of Nursing Outlook proposes a significant shift in how nursing care is measured within acute and critical care settings. This "Blueprint for Action" seeks to revolutionize current methods by recognizing the full scope of a nurse's work and its profound impact on patient outcomes.
"The current measurement systems fail to capture the essence of what nurses truly do," explains lead-author Martha A.Q. Curley, PhD, RN, FAAN, Professor of Nursing in Penn Nursing’s Department of Family and Community Health, and the Ruth M. Colket Endowed Chair in Pediatric Nursing at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. "This blueprint outlines a new framework that acknowledges the diverse skillsets and contributions of nurses, ultimately leading to improved patient care delivery and outcomes."
Key Components of the Proposed Blueprint
Nine Domains of Practice: The framework outlines nine core areas where nurses provide essential care, encompassing not just clinical expertise but also patient education, advocacy, and emotional support.
Supportive Hospital Environment: The blueprint highlights the importance of fostering a supportive hospital environment that empowers nurses to provide optimal patient care.
Precision-Based Outcomes: Moving beyond a simple focus on preventing negative events, the proposal advocates for measuring positive outcomes directly linked to nursing interventions.
Collaborative Partnerships: The article emphasizes the need for collaboration between stakeholders – nurses, researchers, policymakers, and healthcare systems – to develop and implement new outcome measures.
Benefits for Patients and the Profession
By highlighting the work of bedside nurses, this blueprint has the potential to:
Enhance Patient Outcomes: Making nurses' contributions visible can lead to better recognition of their impact on patient well-being.
Empower Nursing Practice: Highlighting the full scope of nursing practice can lead to a more rewarding and fulfilling career path for nurses.
A Call to Action for Stakeholders
The article outlines specific actions for individuals within the healthcare system:
Nurses: Engage in discussions about impactful nursing practices and participate in data collection efforts.
Nurse Leaders: Utilize data and analytics to focus on patient outcomes derived from the full spectrum of nursing care.
Nurse Researchers: Partner with data scientists to develop new outcome metrics.
Hospital Systems: Implement information systems that capture data encompassing all nine domains of nursing practice.
Policymakers and Accreditors: Hold the profession accountable for developing metrics that reflect nursing excellence.
Moving Forward
"This blueprint marks a pivotal step towards a future where the value of acute and critical care nurses is fully recognized," said Curley. "By working together, we can ensure that the impact of nurses’ work is clearly visible, leading to better patient outcomes and a more rewarding profession for nurses."
# # #
About the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing
The University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing is one of the world’s leading schools of nursing. For the ninth year in a row, it is ranked the #1 nursing school in the world by QS University. Our Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program is consistently ranked among the top nursing programs in the country by U.S. News & World Report’s Best Colleges rankings. Our School is also consistently ranked highly in the U.S. News & World Report annual list of best graduate schools and is ranked as one of the top schools of nursing in funding from the National Institutes of Health. Penn Nursing prepares nurse scientists and nurse leaders to meet the health needs of a global society through innovation in research, education, and practice. Follow Penn Nursing on: Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, & Instagram.
END
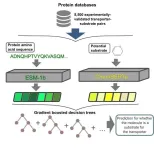
Transport proteins are responsible for the ongoing movement of substrates into and out of a biological cell. However, it is difficult to determine which substrates a specific protein can transport. Bioinformaticians at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) have developed a model – called SPOT – which can predict this with a high degree of accuracy using artificial intelligence (AI). They now present their approach, which can be used with arbitrary transport proteins, in the scientific journal PLOS Biology.
Substrates in biological cells need to be continuously transported inwards and outwards across the cell membrane to ensure the survival of the cells and ...
Spontaneous mutations tend to reduce fitness in populations of living organisms, but this erosion of fitness is countered by natural selection. This study uses the first mutation accumulation experiment in a mammal to show that even in the absence of natural selection, the rate of fitness loss should not be of concern, which is reassuring for humans.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002795
Article Title: An estimate of fitness ...
For uncovering how a cell population helps ensure food, liquid and acid reflux are kept out of our airway – and instead sent to our GI tract – Laura Seeholzer is the winner of the 2024 Eppendorf & Science Prize for Neurobiology. Her findings, detailed in April in Science, have motivated her to study what’s happening with these cells in diseases where this critical protective reflex is compromised.
“These findings are crucial for understanding potentially life-saving reflexes that are activated in the airway, ...
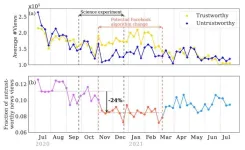
AMHERST, Mass. – An interdisciplinary team of researchers led by the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently published work in the prestigious journal Science calling into question the conclusions of a widely reported study — published in Science in 2023 and funded by Meta — finding the social platform’s algorithms successfully filtered out untrustworthy news surrounding the 2020 election and were not major drivers of misinformation.
The UMass Amherst-led team’s work shows that the Meta-funded research was conducted during a short ...
In 2023, Science published the study, “How do social media feed algorithms affect attitudes and behavior in an election campaign?” by Andrew Guess et al. Now, Chhandak Bagchi and colleagues – in an eLetter that will appear on the 2023 study – state that the study’s “reporting and conclusions did not account for a series of temporary emergency changes to Facebook’s news feed algorithm in the wake of the 2020 U.S. presidential election that were designed to diminish the spread of voter-fraud misinformation. This issue may have led readers to misinterpret ...
New interpretations following the recent Sackett v. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) United States Supreme Court ruling could strip federal protections from up to 90 million acres of U.S. nontidal wetlands – nearly all that exist in the coterminous US – according to a new study. The findings reveal the potential scope and impacts of the regulatory changes and highlight the uncertainty introduced by the ruling. Enacted in 1972, the Clean Water Act (CWA) aims to restore and protect the quality of U.S. waters ...
Inspired by an ancient buried log, researchers present a novel method to remove and store atmospheric carbon for hundreds of years or more. It involves locking woody biomass away in “wood vaults.” The approach could provide a cost-effective solution to mitigate climate change. Achieving net-zero carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions is crucial for combating climate change, yet reducing fossil fuel emissions alone is insufficient to meet the Paris Agreement's targets. To achieve these goals, carbon dioxide removal (CDR) methods must be implemented, including engineering solutions, like direct air capture, ...
Large-scale removal of discarded fishing gear and other plastic debris from the waters of Northwestern Hawaii meaningfully reduced entanglement rates of endangered Hawaiian monk seals, according to a new study. The findings, which are drawn from more than four decades of data, offer promising evidence that marine debris cleanup programs are successful and that reducing plastic inputs and scaling up removal efforts could maximize conservation outcomes across marine ecosystems worldwide. Plastic pollution severely threatens marine ecosystems, ...
By 2100, hospitalizations from diarrheal diseases are predicted to increase in the city of Dhaka in Bangladesh as a result of climate change, even if global warming stays under 2 degrees Celsius. Farhana Haque and colleagues from University College London, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and icddr,b report these findings in a new study published September 26 in the open access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
As one of the world’s most densely population cities, Dhaka deals with a high burden of diarrheal diseases. While some studies have looked at how weather affects diarrhea in Bangladesh, few have examined the future impact of climate ...
September 26, 2024, Cleveland: Cleveland Clinic researchers have discovered a new bacterium that weakens the immune system in the gut, potentially contributing to certain inflammatory and infectious gut diseases.
The team identified the bacterium, Tomasiella immunophila (T. immunophila), which plays a key role in breaking down a crucial immune component of the gut’s multi-faceted protective immune barrier.
Identifying this bacterium is the first step to developing new treatments for a variety of inflammatory and infectious gut diseases. These conditions, including inflammatory ...