(Press-News.org) September 26, 2024, Cleveland: Cleveland Clinic researchers have discovered a new bacterium that weakens the immune system in the gut, potentially contributing to certain inflammatory and infectious gut diseases.
The team identified the bacterium, Tomasiella immunophila (T. immunophila), which plays a key role in breaking down a crucial immune component of the gut’s multi-faceted protective immune barrier.
Identifying this bacterium is the first step to developing new treatments for a variety of inflammatory and infectious gut diseases. These conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis, are associated with decreased levels of secretory immunoglobulin A (SIgA), an antibody that protects mucosal surfaces.
The study, published in Science, was led by Thaddeus Stappenbeck, M.D., Ph.D., chair of Cleveland Clinic’s Department of Inflammation and Immunity, and Qiuhe Lu, Ph.D., research associate and the paper’s first author.
“Our research represents a critical role of a specific component of the gut microbiome in human health and disease,” said Dr. Stappenbeck. “By identifying this specific bacterium, we have not only enhanced our understanding of gut diseases but also opened a promising new avenue for treatment. Pinpointing the culprit behind the breakdown of the gut’s protective adaptive immune barrier is a significant step toward developing much-needed therapies for conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis.”
In the gut, SIgA binds continuously to microbes, preventing them from reaching and damaging the body’s tissue. In previous research, the team discovered that intestinal bacteria could reduce SIgA levels, which can lead to increased risk of infection and excess inflammation.
In this new study, researchers found that T. immunophila’s presence in the gut increases susceptibility to pathogens and delays repair of the gut’s protective barrier. T. immunophila’s name is an homage to a pioneer in immunology. SIgA was discovered by Dr. Thomas Tomasi, who published his findings in a foundational paper in Science in 1963.
“Drs. Stappenbeck and Lu's rigorous and elegant study provides a key insight and an exciting potential mechanism for why some people have low or absent levels of SIgA in their gut, yet retain normal levels of SIgA in their bloodstream,” says Michael Silverman, M.D., Ph.D., a physician with the Division of Infectious Diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Dr. Silverman, whose expertise includes immune system development, provided input on the research findings. “This discovery is quite important, as SIgA in the intestine functions as a critical component of the barrier for the trillions of microbes that live in our intestines,” Dr. Silverman said. “This study provides a new avenue to develop therapeutics to manipulate SIgA in the gut and improve health.”
“We know that there are a substantial number of patients that have this defect in are at risk for infection and inflammation in the intestine,” said Dr. Lu. “We surmised that a gut microbe that can degrade SIgA was the culprit. We believe that important therapeutic targets for a variety of inflammatory and infectious diseases in humans can be found through our work.”
END
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 19:00hrs Thursday 26 September 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have shown that the balance of bacteria in the gut can influence symptoms of hypopituitarism in mice.
They also showed that aspirin was able to improve hormone deficiency symptoms in mice with this condition.
People with mutations in a gene called Sox3 develop hypopituitarism, where the pituitary gland doesn’t ...
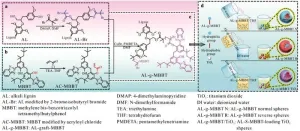
In a significant breakthrough for the cosmetics industry, researchers have developed a new type of sunscreen using lignin, a naturally abundant polymer, and titanium dioxide (TiO2). The study, led by Yarong Li and Zhiguang Tang, was published in the Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts and details the innovative use of a dual-modified lignin sub-microsphere to enhance the SPF and improve the color of sunscreens.
Lignin, a byproduct of the pulp industry, is known for its UV-absorbing properties and antioxidant capabilities. However, its application in commercial sunscreens has been limited due ...
How did the bodies of animals, including ours, become such fine-tuned movement machines? How vertebrates coordinate the eternal tug-o-war between involuntary reflexes and seamless voluntary movements is a mystery that Francisco Valero-Cuevas’ Lab in USC Alfred E. Mann Department of Biomedical Engineering, set out to understand. The Lab’s newest computational paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) adds to the thought leadership about the processing of sensory information and control of reflexes during voluntary movements—with implications as to how its disruption could ...
Crohn’s disease — an autoimmune disorder — is characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, resulting in a slew of debilitating gastrointestinal symptoms that vary from patient to patient. Complications of the disease can destroy the gut lining, requiring repeated surgeries. The poorly understood condition, which currently has no cure and few treatment options, often strikes young people, causing significant ill-health throughout their lifetime. One barrier to making progress in developing treatments has been the lack of preclinical animal models that accurately ...
HERSHEY, Pa. — The risk of sudden unexpected infant death (SUID) and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) increased during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to the pre-pandemic period, especially in 2021, according to a new study led by researchers at the Penn State College of Medicine. Monthly increases in SUID in 2021 coincided with a resurgence of seasonal respiratory viruses, particularly respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), suggesting that the shift in SUID rates may be associated with altered infectious disease transmission.
They ...
A rescue effort can take many forms – a life raft, a firehose, an airlift. For animals whose populations are in decline from inbreeding, genetics itself can be a lifesaver.
Genomic research led by the University of California, Davis, reveals clues about montane red foxes’ distant past that may prove critical to their future survival. The study, published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, examines the potential for genetic rescue to help restore populations of these mountain-dwelling red foxes. The research is especially relevant for the estimated ...
A groundbreaking new study conducted by a team of researchers from Arizona State University, University of Washington and the University of Texas at Austin reveals that extreme heat significantly alters how people go about their daily lives, influencing everything from time spent at home to transportation choices. The study, titled "Understanding How Extreme Heat Impacts Human Activity-Mobility and Time Use Patterns," was recently published in Transportation Research Part D and underscores the urgent need for policy action ...
Digital Science announces ReadCube Pro, an AI-powered expansion of ReadCube, offering researchers new tools to simplify and accelerate literature management and literature monitoring workflows.
The new AI Assistant and Literature Monitoring in ReadCube – an award-winning leader in literature management and full-text document delivery – transform the way research teams access, organize, review and monitor scholarly literature by providing them with enhanced search capabilities while helping to significantly reduce time spent ...
Leuven, 26 September 2024 – A team of scientists led by Prof. Patrik Verstreken (VIB-KU Leuven) has identified a new genetic mutation that may cause a form of early-onset Parkinsonism. The mutation, located in a gene called SGIP1, was discovered in an Arab family with a history of Parkinson's symptoms that began at a young age. The study reveals that this mutation affects how brain cells communicate, providing new insights into the disease's development and potential treatment strategies.
A genetic clue to Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism is a group of neurological disorders that share similar symptoms, including motor dysfunction ...
More than a dozen bacterial species among the hundreds that live in people’s mouths have been linked to a collective 50% increased chance of developing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), a new study shows. Some of these microbes had previously been shown to contribute to periodontal disease, serious gum infections that can eat away at the jawbone and the soft tissues that surround teeth.
Experts have long observed that those with poor oral health are statistically more vulnerable than those with healthier ...