(Press-News.org) More than a dozen bacterial species among the hundreds that live in people’s mouths have been linked to a collective 50% increased chance of developing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), a new study shows. Some of these microbes had previously been shown to contribute to periodontal disease, serious gum infections that can eat away at the jawbone and the soft tissues that surround teeth.
Experts have long observed that those with poor oral health are statistically more vulnerable than those with healthier mouths to HNSCC, a group that includes the most common cancers of the mouth and throat. While small studies have tied some bacteria in these regions (the oral microbiome) to the cancers, the exact bacterial types most involved had until now remained unclear.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, the new analyses looked at the genetic makeup of oral microbes collected from healthy men and women. Of the hundreds of different bacteria that are routinely found in the mouth, 13 species were shown to either raise or lower risk of HNSCC. Overall, this group was linked to a 30% greater likelihood of developing the cancers. In combination with five other species that are often seen in gum disease, the overall risk was increased by 50%.
“Our findings offer new insight into the relationship between the oral microbiome and head and neck cancers,” said study lead author Soyoung Kwak, PhD. “These bacteria may serve as biomarkers for experts to flag those at high risk,” added Kwak, a postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Population Health at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
Previous investigations had uncovered certain bacteria in tumor samples of people already diagnosed with these cancers, says Kwak. Then, in a small 2018 assessment, the current research team explored how microbes in healthy participants may over time contribute to future risk of HNSCC.
Their latest report, publishing online Sept. 26 in the journal JAMA Oncology, is the largest and most detailed analysis of its kind to date, says Kwak. It is also among the first to examine whether common fungi, organisms like yeast and mold that, along with bacteria, make up the oral microbiome, might play a role in HNSCC. The new experiments found no such role for fungal organisms.
For the research, the team analyzed data from three ongoing investigations tracking 159,840 Americans from across the country to better understand how diet, lifestyle, medical history, and many other factors are involved in cancer. The data were gathered for the American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study II; the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial; and the Southern Community Cohort Study.
Shortly after enrolling, participants rinsed with mouthwash, providing saliva samples that preserved the numbers and species of microbes for testing. Researchers then followed up for roughly 10 to 15 years to record any presence of tumors.
In the current study, the investigators analyzed bacterial and fungal DNA from the spit samples. Then, they identified 236 patients who were diagnosed with HNSCC and compared the DNA of their oral microbes with that of 458 randomly selected study subjects who had remained cancer-free. In their research, the team accounted for factors known to play a role, such as age, race, and how often they smoked cigarettes or drank alcohol.
“Our results offer yet another reason to keep up good oral-hygiene habits,” said study co-senior author Richard Hayes, DDS, MPH, PhD. “Brushing your teeth and flossing may not only help prevent periodontal disease, but also may protect against head and neck cancer,” added Hayes, a professor in the Department of Population Health at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and a member of its Perlmutter Cancer Center.
The researchers emphasized that their study was designed to identify correlations between risk of cancer and certain bacteria in the mouth, but not to establish a direct cause-and-effect link. That will require further research.
“Now that we have identified key bacteria that may contribute to this disease, we next plan to explore the mechanisms that allow them to do so and in what ways we can best intervene,” said study co-senior author Jiyoung Ahn, PhD. Ahn is a professor in the Departments of Population Health and Medicine at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and is the associate director for population research at its Perlmutter Cancer Center.
Ahn cautions that while the added risks from bacteria are concerning, overall cases of head and neck cancer remain fairly uncommon.
Funding for the study was provided by National Institutes of Health grants P20CA252728, R01CA159036, U01CA250186, and R01LM014085.
In addition to Kwak, Ahn, and Hayes, other NYU Langone Health and NYU researchers involved in the study are Chan Wang, PhD; Mykhaylo Usyk, PhD; Feng Wu, PhD; and Huilin Li, PhD. Other study co-investigators included Neal Freedman, PhD, and Wen-Yi Huang, PhD, at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.; Marjorie McCullough, ScD, and Caroline Um, PhD, at the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, Ga.; and Martha Shrubsole, PhD, and Qiuyin Cai, PhD, at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn.
Media Inquiries
Shira Polan
Phone: 212-404-4279
Shira.Polan@nyulangone.org
END
Bacteria involved in gum disease linked to increased risk of head and neck cancer
2024-09-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
These fish use legs to taste the seafloor
2024-09-26
Sea robins are unusual animals with the body of a fish, wings of a bird, and walking legs of a crab. Now, researchers show that the legs of the sea robin aren’t just used for walking. In fact, they are bona fide sensory organs used to find buried prey while digging. This work appears in two studies published in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 26.
“This is a fish that grew legs using the same genes that contribute to the development of our limbs and then repurposed these legs to find ...
This fish has legs
2024-09-26
Sea robins are ocean fish particularly suited to their bottom-dwelling lifestyle: Six leg-like appendages make them so adept at scurrying, digging, and finding prey that other fish tend to hang out with them and pilfer their spoils.
A chance encounter in 2019 with these strange, legged fish at Cape Cod’s Marine Biological Laboratory was enough to inspire Corey Allard to want to study them.
“We saw they had some sea robins in a tank, and they showed them to us, because they know we like weird animals,” said Allard, a ...
Climate change: Heat, drought, and fire risk increasing in South America
2024-09-26
The number of days per year that are simultaneously extremely hot, dry, and have a high fire risk have as much as tripled since 1970 in some parts of South America. The results are published in a study in Communications Earth & Environment.
South America is warming at a similar rate to the global average. However, some regions of the subcontinent are more at risk of the co-occurrence of multiple climate extremes. These compound extremes can have amplified impacts on ecosystems, economy, and human health.
Raúl Cordero and colleagues calculated the number of days per year that each approximately 30 by 30 km grid ...
Rates of sudden unexpected infant death before and during the pandemic
2024-09-26
About The Study: This cross-sectional study found increased rates of both sudden unexpected infant death (SUID) and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) during the COVID-19 pandemic, with a significant shift in epidemiology from the pre-pandemic period noted in June to December 2021. These findings support the hypothesis that off-season resurgences in endemic infectious pathogens may be associated with SUID rates, with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) rates in the U.S. closely approximating this shift. Further investigation into the role ...
Estimation of tax benefit of nonprofit hospitals
2024-09-26
About The Study: This study highlights the wide variation of nonprofit hospitals’ tax benefit across states, its high concentration among a small number of hospitals, and the primary role played by state and local taxes. Policy efforts to strengthen nonprofit hospitals’ taxpayer accountability are likely to be more effective when pursued at the local level.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ge Bai, PhD, CPA, email gbai@jhu.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
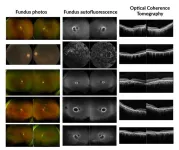
Scientists discover gene responsible for rare, inherited eye disease
2024-09-26
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their colleagues have identified a gene responsible for some inherited retinal diseases (IRDs), which are a group of disorders that damage the eye’s light-sensing retina and threatens vision. Though IRDs affect more than 2 million people worldwide, each individual disease is rare, complicating efforts to identify enough people to study and conduct clinical trials to develop treatment. The study’s findings published today in JAMA Ophthalmology.
In a small study of six unrelated participants, researchers linked the gene UBAP1L to different forms of ...
Scientists discover "pause button" in human development
2024-09-26
In some mammals, the timing of the normally continuous embryonic development can be altered to improve the chances of survival for both the embryo and the mother. This mechanism to temporarily slow development, called embryonic diapause, often happens at the blastocyst stage, just before the embryo implants in the uterus. During diapause, the embryo remains free-floating and pregnancy is extended. This dormant state can be maintained for weeks or months before development is resumed, when conditions are favorable. Although not all mammals use this reproductive ...
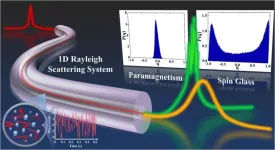
Replica symmetry breaking in 1D Rayleigh scattering system: Theory and validations
2024-09-26
In both the natural world and human society, there commonly exist complex systems such as climate systems, ecological systems, and network systems. Due to the involvement of numerous interacting elements, complex systems can stay in multiple different states, and their overall behavior generally exhibits randomness and high disorder. For example, due to the complex interactions between factors such as solar radiation, terrain, and ocean currents, the climate system can exhibit various states like sunny, cloudy, and rainy. The dynamic changes and mutual influences of these factors make the behavior of the climate highly uncertain and difficult to predict accurately. For instance, the formation ...
New research identifies strong link between childhood opportunities and educational attainment and earnings as a young adult
2024-09-26
Washington, September 26, 2024—The number of educational opportunities that children accrue at home, in early education and care, at school, in afterschool programs, and in their communities as they grow up are strongly linked to their educational attainment and earnings in early adulthood, according to new research. The results indicate that the large opportunity gaps between low- and high-income households from birth through the end of high school largely explain differences in educational and income achievement ...
Statement by NIH on research misconduct findings
2024-09-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE
Thursday, September 26, 2024 - 9 a.m. EDT
Contact:
NIH Office of Communications and Public Liaison
NIH News Media Branch
301-496-5787
Statement by NIH on Research Misconduct Findings
Following an investigation, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has made findings of research misconduct against Eliezer Masliah, M.D., due to falsification and/or fabrication involving re-use and relabel of figure panels representing different experimental results in two publications. NIH will notify the two journals of its findings so that appropriate action can be taken. NIH initiated its research misconduct review process ...